Israeli airstrikes in Gaza result in the deaths of at least 31 Palestinians, including children and police of…
Published on: 2026-01-31
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Israeli forces kill 12 Palestinians across Gaza attacks reported in Rafah
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The recent Israeli airstrikes in Gaza, resulting in the deaths of at least 31 Palestinians, including children and police officers, highlight a significant escalation in the conflict despite a nominal ceasefire. This development undermines regional stability efforts and raises questions about the durability of the truce. The most likely hypothesis is that these actions are retaliatory measures by Israel in response to perceived ceasefire violations by Palestinian factions, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Israeli airstrikes are a direct response to a breach of the ceasefire by Palestinian militants, specifically the tunnel incident in Rafah. Supporting evidence includes Israel’s official statements and the timing of the strikes. Contradicting evidence includes claims by Palestinian groups denying ceasefire violations.
- Hypothesis B: The airstrikes are part of a broader Israeli strategy to weaken Palestinian factions irrespective of ceasefire agreements. This is supported by the scale and targets of the strikes, including civilian areas, and the historical pattern of Israeli military actions. However, this hypothesis lacks direct evidence linking current actions to a broader strategy beyond immediate retaliation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct linkage between the tunnel incident and subsequent airstrikes, as well as Israel’s stated rationale. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new evidence of strategic planning beyond immediate retaliation or further unilateral actions by Israel.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The ceasefire terms are understood and agreed upon by all parties; Israeli military actions are primarily retaliatory; Palestinian factions are capable of adhering to ceasefire terms; regional mediators have influence over the conflict parties.
- Information Gaps: Details on the specific ceasefire terms and any recent amendments; comprehensive casualty figures and damage assessments; insights into internal decision-making processes within Israeli and Palestinian leadership.
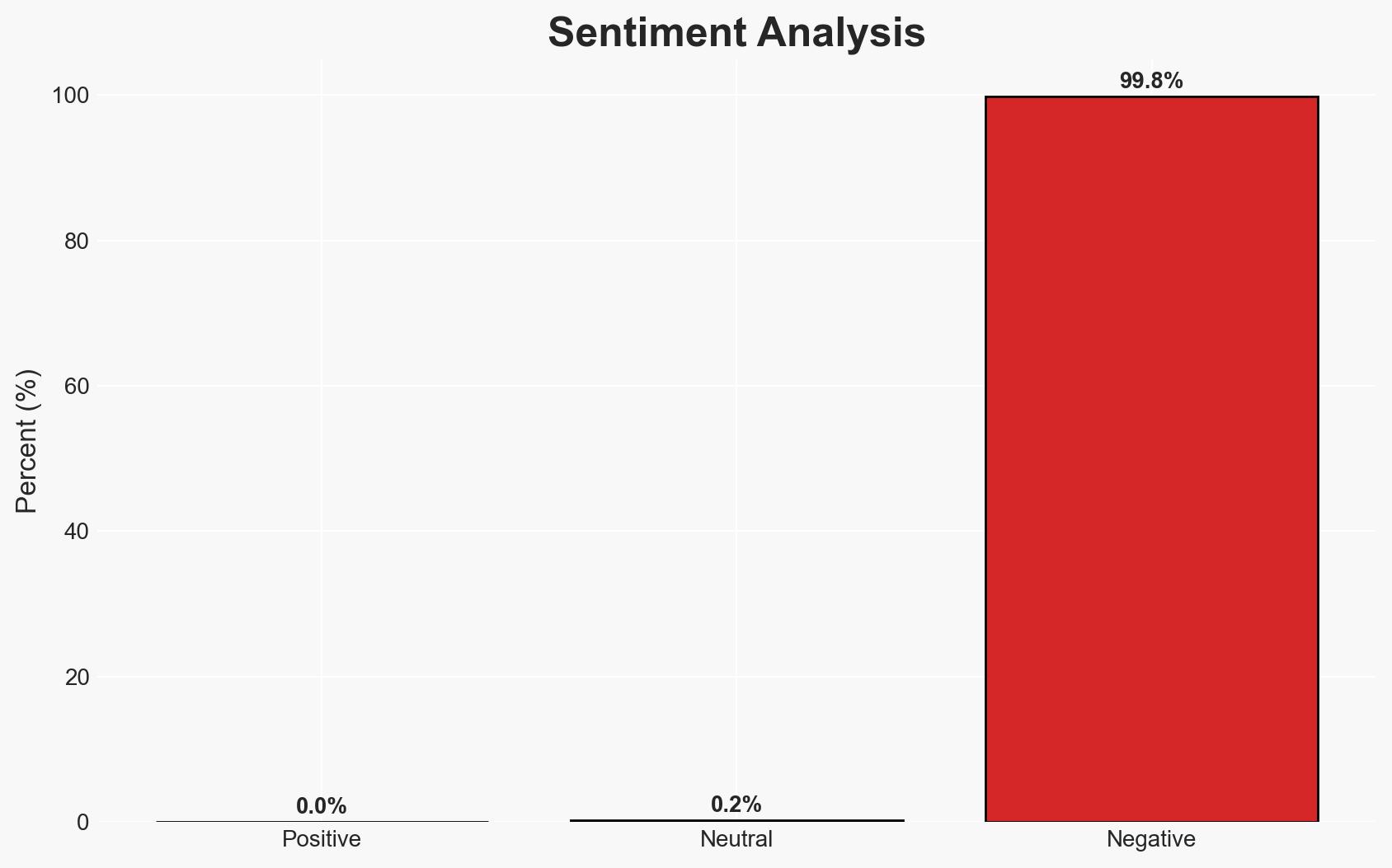
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in media reporting from both sides; Israeli and Palestinian official statements may contain elements of propaganda or strategic deception; risk of cognitive bias in interpreting retaliatory actions as part of a broader strategy.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continuation of hostilities despite a ceasefire agreement risks further destabilizing the region and undermining international mediation efforts. This could lead to increased violence and a broader regional conflict.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation could strain relations between Israel and neighboring countries, particularly Egypt and Qatar, who are mediating the ceasefire.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased hostilities may lead to heightened security measures and potential retaliatory attacks by Palestinian factions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations and propaganda campaigns by both sides to influence public perception and international opinion.
- Economic / Social: Prolonged conflict could exacerbate humanitarian conditions in Gaza, impacting social cohesion and economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of ceasefire violations; engage with regional mediators to reinforce truce terms; prepare for humanitarian assistance in Gaza.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen diplomatic channels with regional actors; develop contingency plans for potential escalation; support initiatives for long-term conflict resolution.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Ceasefire holds with renewed diplomatic efforts leading to de-escalation.
- Worst Case: Full-scale conflict resumes, destabilizing the region further.
- Most Likely: Intermittent skirmishes continue, with periodic breaches of the ceasefire.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Philippe Lazzarini, Head of UNRWA
- Suhail al-Hindi, Hamas Political Bureau Member
- Israeli Military Command
- Palestinian Factions (Hamas, Islamic Jihad)
- Egyptian and Qatari Mediators
7. Thematic Tags
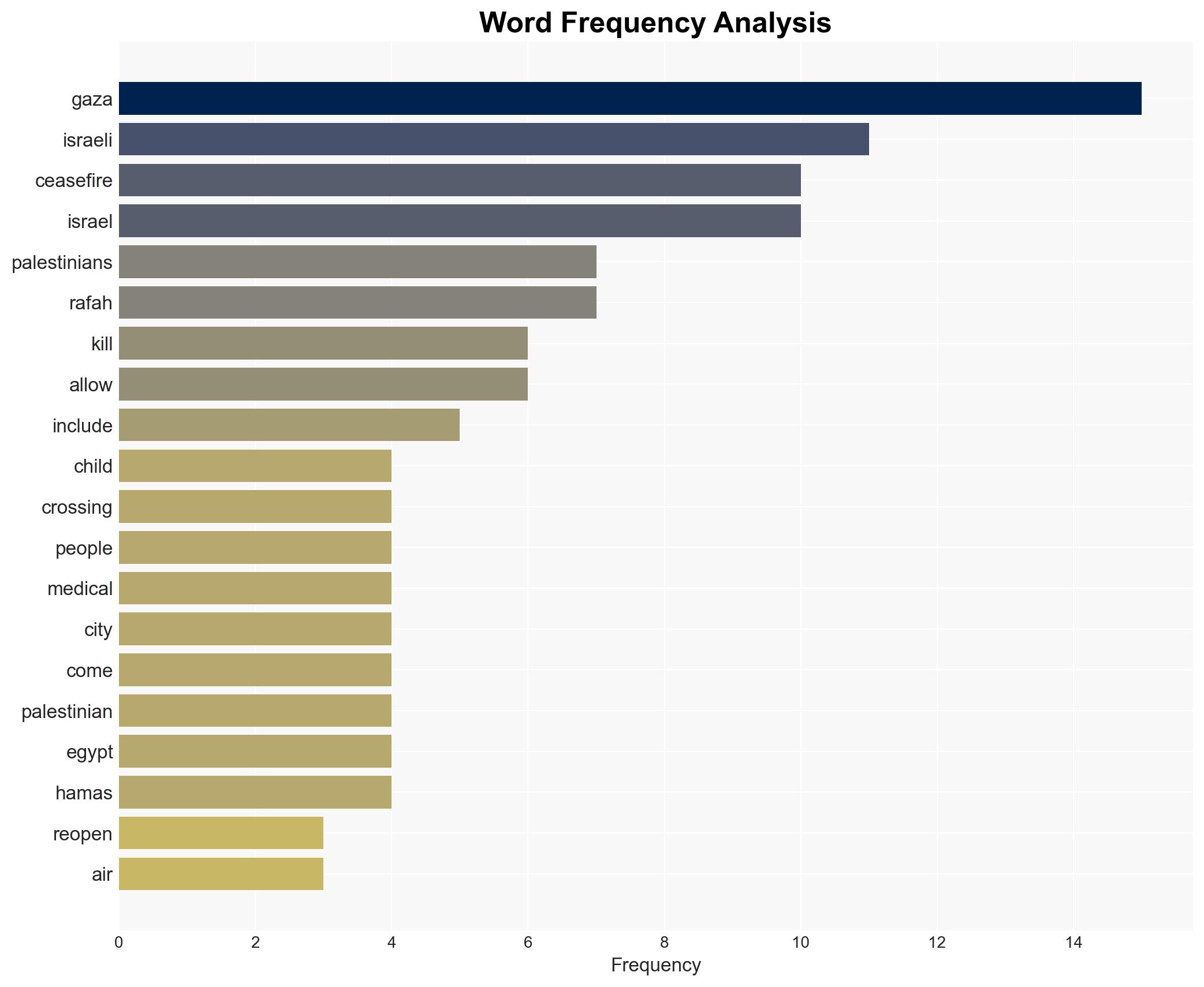
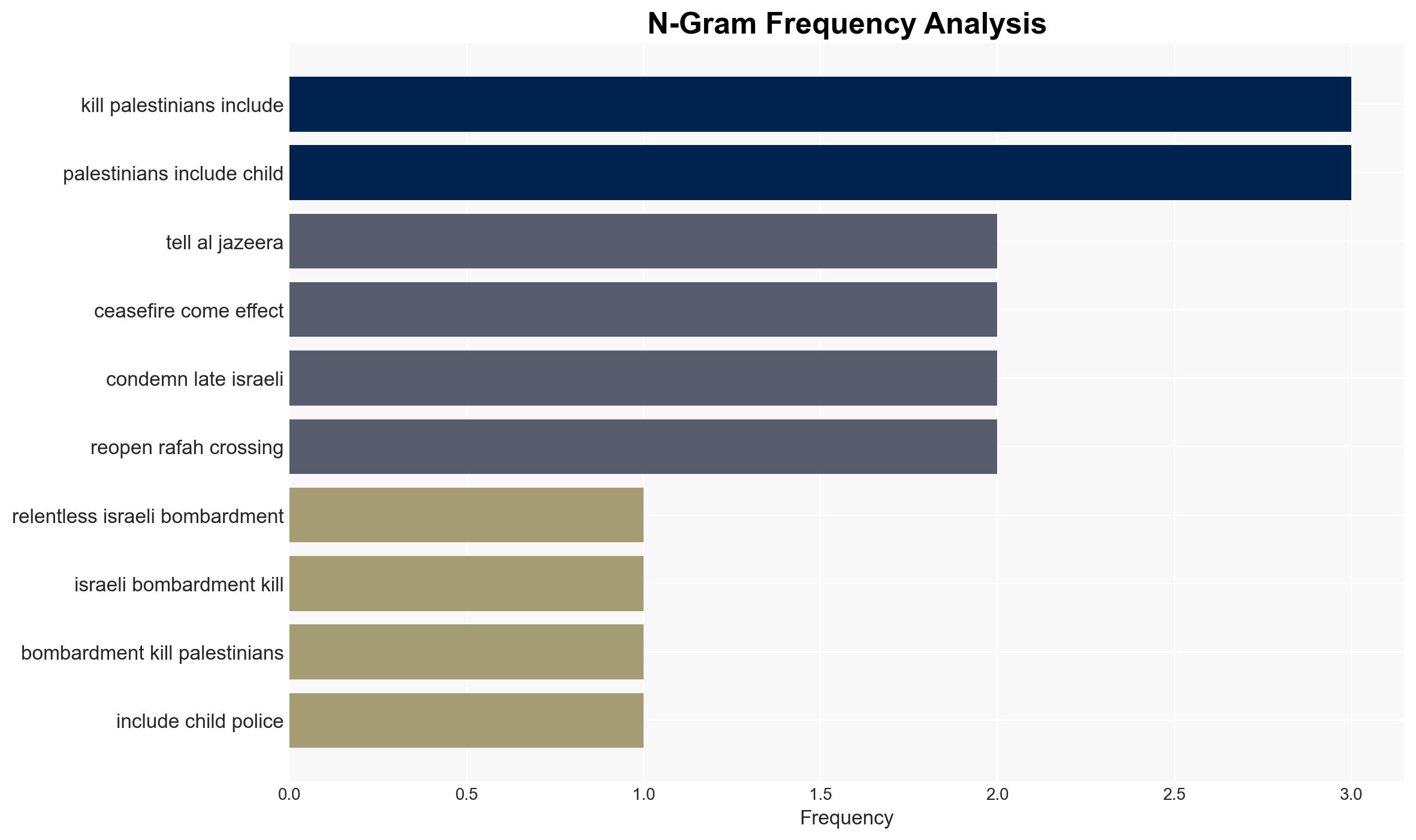
regional conflicts, Israeli-Palestinian conflict, ceasefire violations, regional stability, retaliatory strikes, humanitarian impact, diplomatic mediation, escalation risks
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us