Iran Labels EU Armed Forces as Terrorist Entities in Response to IRGC Designation
Published on: 2026-02-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Iran designates EU armies terrorist groups in retaliatory move
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Iran’s designation of EU armies as terrorist groups is a retaliatory measure against the EU’s similar designation of the IRGC. This development heightens geopolitical tensions and could impact diplomatic relations and regional security dynamics. The most likely hypothesis is that this is a strategic move by Iran to deter further international isolation. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to limited visibility into Iran’s internal decision-making processes.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Iran’s designation is primarily a symbolic gesture aimed at domestic audiences to bolster nationalistic sentiment and demonstrate defiance against Western pressure. Supporting evidence includes the timing of the announcement and the rhetoric used by Iranian officials. However, the lack of concrete actions following the designation raises uncertainties about its practical implications.
- Hypothesis B: The designation is a calculated move to escalate tensions and potentially leverage negotiations with the EU and the US. This is supported by Iran’s concurrent military exercises and public statements indicating readiness for conflict. Contradicting evidence includes ongoing diplomatic communications suggesting a preference for negotiation over escalation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the lack of immediate operational changes following the designation and the historical pattern of Iran using symbolic actions for domestic purposes. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include any military or economic measures directly targeting EU interests.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Iran seeks to avoid direct military conflict with the EU; the EU’s designation of the IRGC is primarily a political statement rather than a precursor to military action; Iran’s domestic stability is a priority for its leadership.
- Information Gaps: Details on Iran’s internal deliberations and strategic objectives; the EU’s contingency plans in response to Iran’s designation.
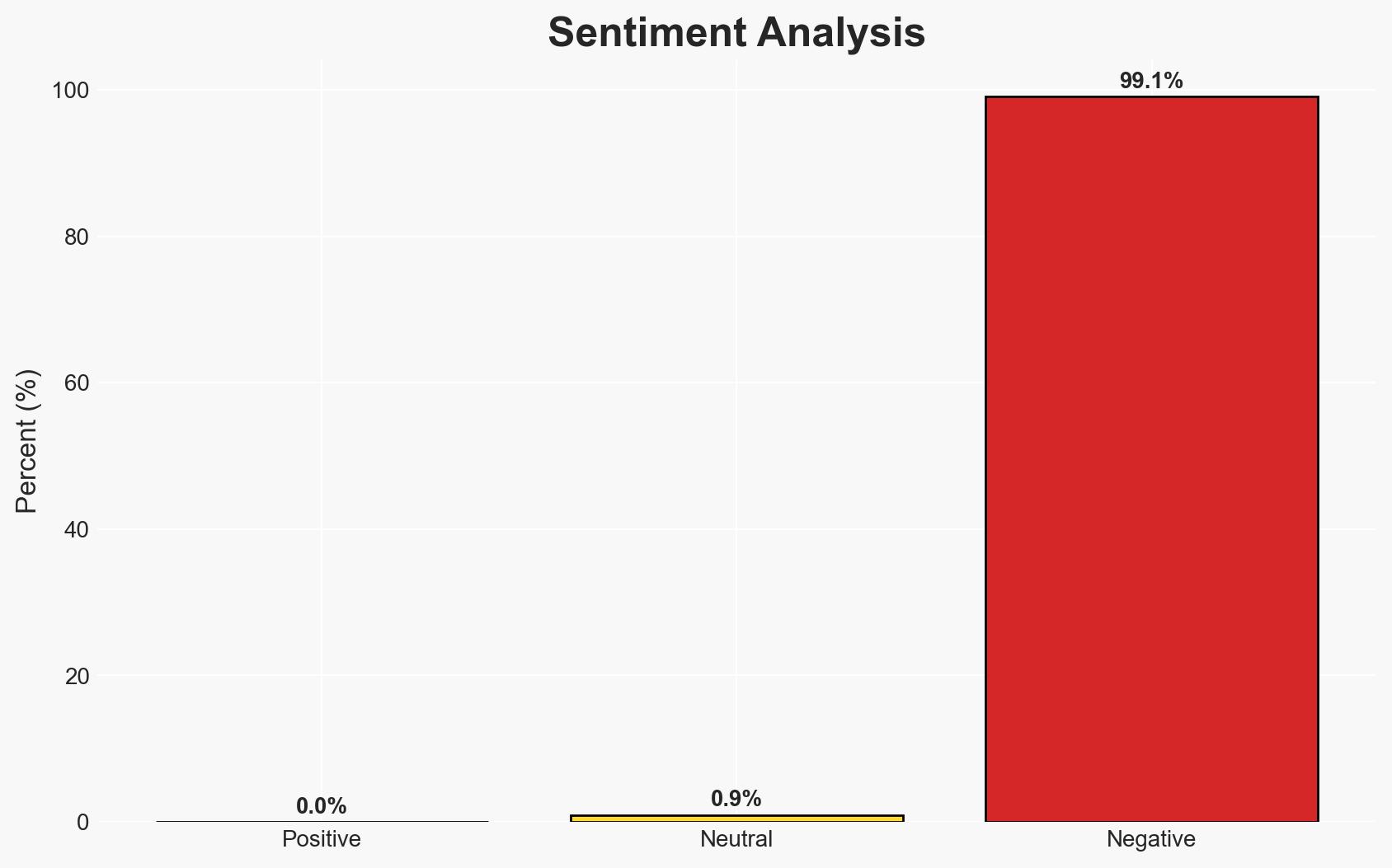
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential Iranian state media bias in reporting the EU’s actions; risk of Western media underestimating Iran’s strategic calculations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased diplomatic isolation for Iran and complicate EU-Iran relations, potentially affecting negotiations on nuclear and regional security issues. The situation may also influence regional alliances and security postures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic stalemate or escalation in EU-Iran relations; increased alignment between Iran and non-Western powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert levels for EU interests in the Middle East; potential for retaliatory actions by proxy groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber operations targeting EU entities; intensified propaganda efforts by Iranian state media.
- Economic / Social: Potential impact on EU-Iran trade relations; domestic economic pressures in Iran exacerbated by international isolation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Iranian military movements and communications; engage in diplomatic channels to de-escalate tensions; enhance security measures for EU assets in the region.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances with regional partners; develop contingency plans for potential economic disruptions; invest in cyber defense capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Diplomatic resolution and de-escalation; Worst: Military confrontation involving regional actors; Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic tensions without direct conflict, with periodic escalations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
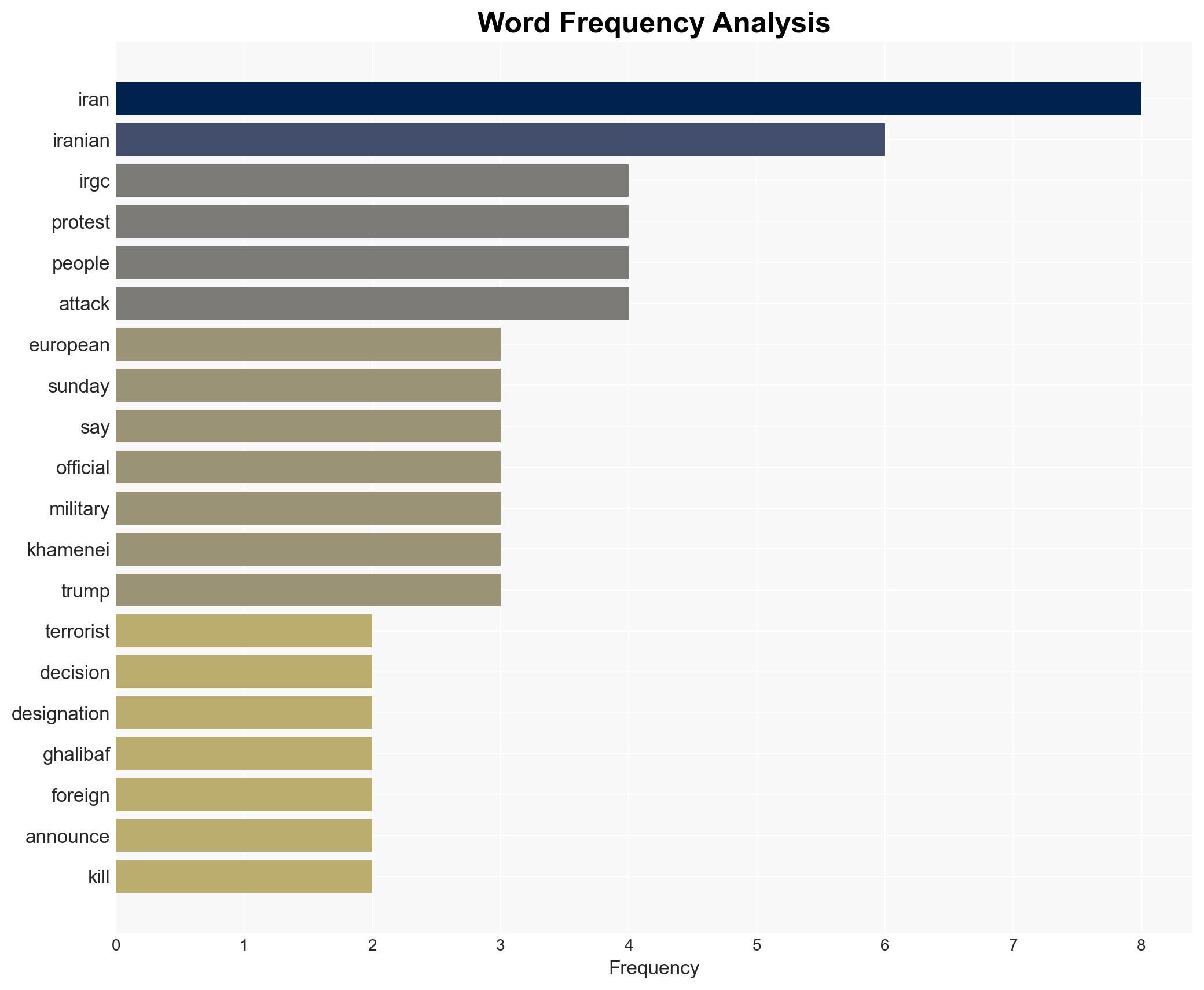
- Mohammad Bagher Ghalibaf, Parliament Speaker of Iran
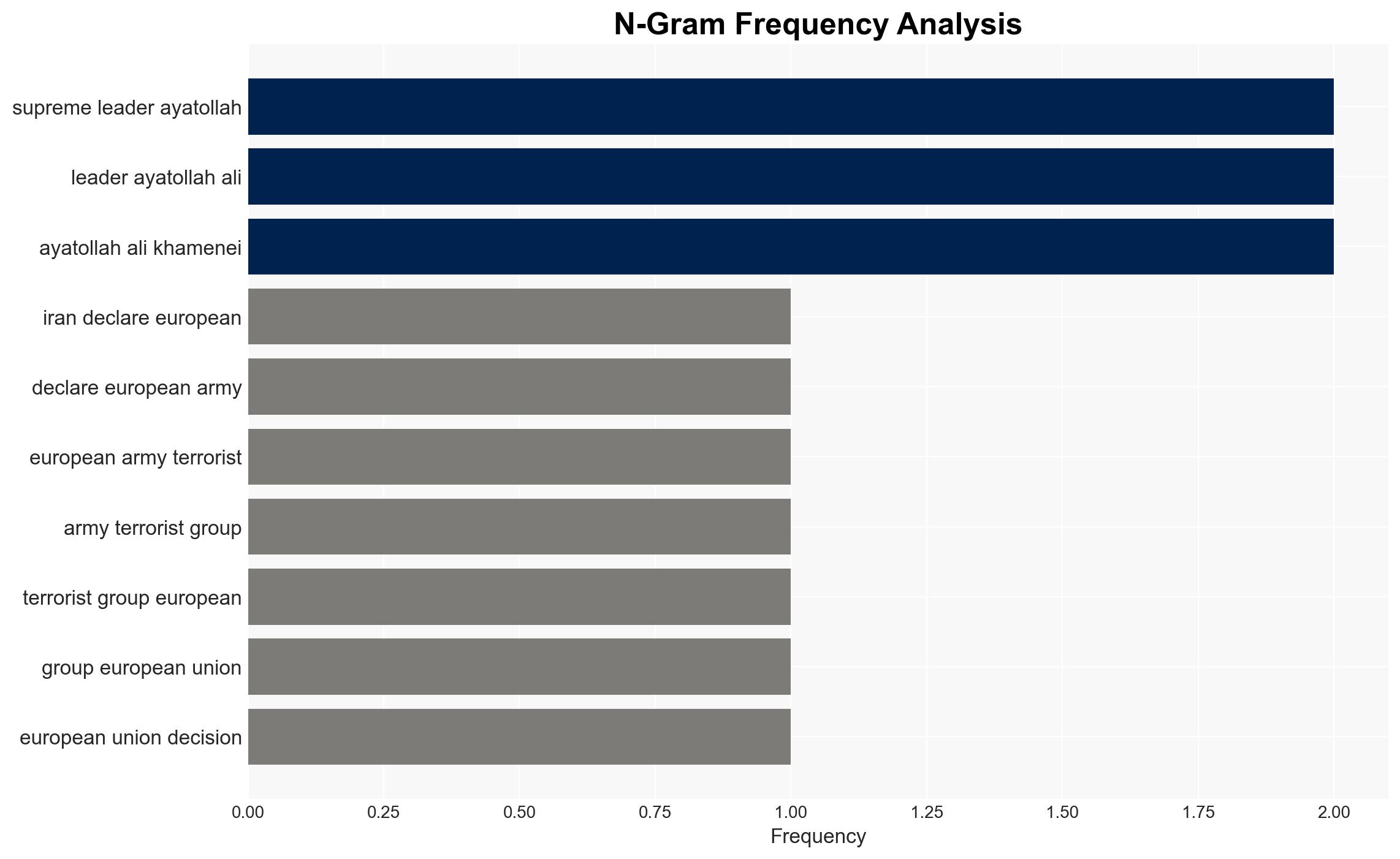
- Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, Supreme Leader of Iran
- Kaja Kallas, EU Foreign Policy Chief
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC)
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, geopolitical tensions, EU-Iran relations, counter-terrorism, military strategy, diplomatic negotiations, regional security, economic sanctions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us