Surge in Defense Spending Fuels Opportunities for Innovative Startups in Europe
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The rush for Europe’s 920 billion warchest
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
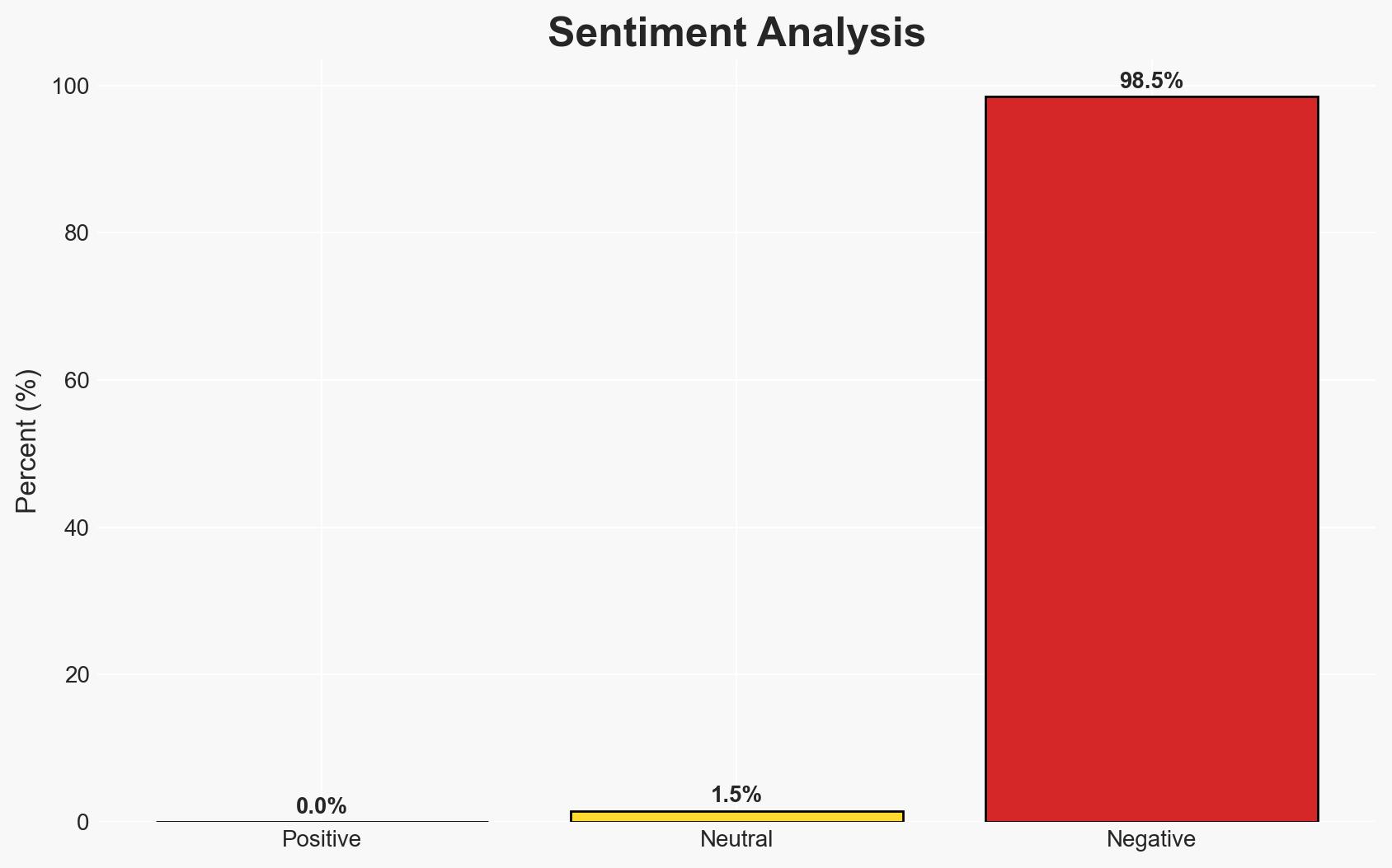
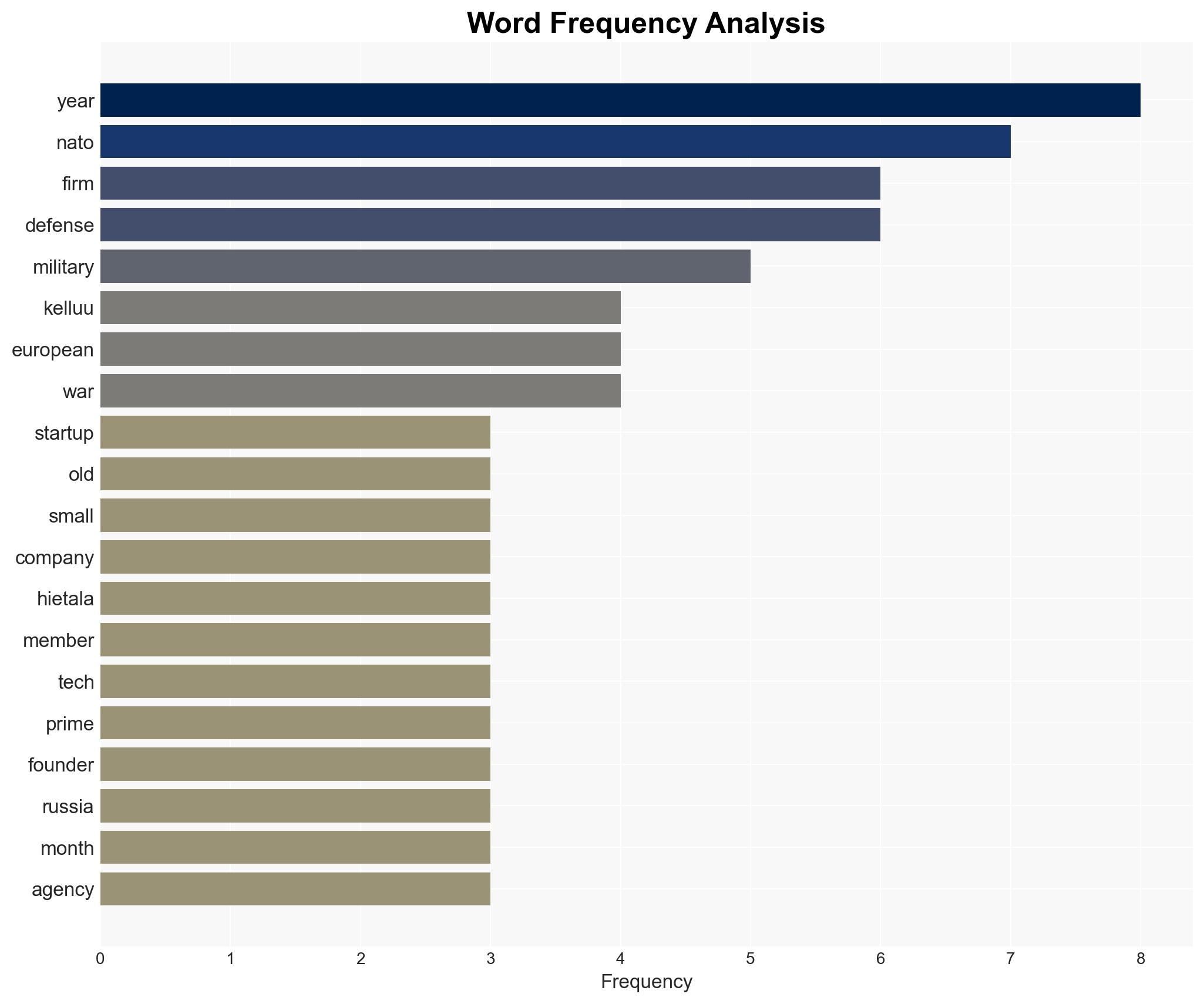
The integration of small defense tech firms like Kelluu into NATO’s procurement processes indicates a shift towards rapid innovation and diversification of suppliers, driven by geopolitical tensions and technological advancements. This development primarily affects European defense markets and NATO military capabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the uncertainty surrounding the specific impacts on traditional defense contractors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: NATO’s increased engagement with small tech firms will lead to a significant diversification of defense suppliers, enhancing military adaptability and innovation. This is supported by the establishment of DIANA and increased venture capital investments. However, the long-term sustainability of these firms in a traditionally prime-dominated market remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The shift towards smaller firms is a temporary response to immediate geopolitical pressures and will not substantially alter the dominance of traditional defense contractors. This hypothesis is supported by the entrenched position and resources of the primes, but contradicted by NATO’s strategic initiatives to integrate new technologies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to NATO’s proactive measures and the rising interest from investors, which indicate a structural shift. Indicators such as sustained investment levels and successful integration of small firms into military operations could further support this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: NATO will continue to prioritize rapid technological integration; geopolitical tensions with Russia will persist; small firms can scale effectively to meet military needs; traditional primes will not significantly adapt their strategies.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the unnamed NATO member purchasing Kelluu’s airships and the extent of integration into military operations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from NATO sources promoting DIANA’s success; lack of transparency from defense firms regarding capabilities and scalability.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to a more agile and responsive military procurement process, potentially reducing reliance on traditional primes. However, it may also introduce risks related to the reliability and scalability of new suppliers.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased NATO resilience against Russian aggression; potential friction with traditional defense contractors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities; potential vulnerabilities if new technologies are not robustly tested.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased risk of cyber espionage targeting emerging tech firms; potential for misinformation campaigns against new defense initiatives.
- Economic / Social: Growth in the defense tech sector; potential job creation in small firms; economic shifts away from traditional primes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor developments in NATO’s procurement strategies; engage with small tech firms to assess capabilities and readiness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with emerging defense tech firms; invest in resilience measures to mitigate potential supply chain disruptions.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful integration of small firms enhances NATO capabilities. Worst: New suppliers fail to meet military needs, leading to operational gaps. Most-Likely: Gradual integration with mixed success, prompting ongoing adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Janne Hietala, CEO of Kelluu
- Defence Innovation Accelerator for the North Atlantic (DIANA)
- NATO Innovation Fund
- Unnamed NATO member purchasing Kelluu’s airships
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, defense innovation, NATO procurement, small tech firms, geopolitical tensions, defense market dynamics, military adaptability, venture capital in defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us