Insights from a Special Forces Perspective on the 2025 NSS and 2026 NDS Implications for Operations
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The 2025 National Security Strategy and the 2026 National Defense Strategy Through the Eyes of a Special Forces Soldier
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
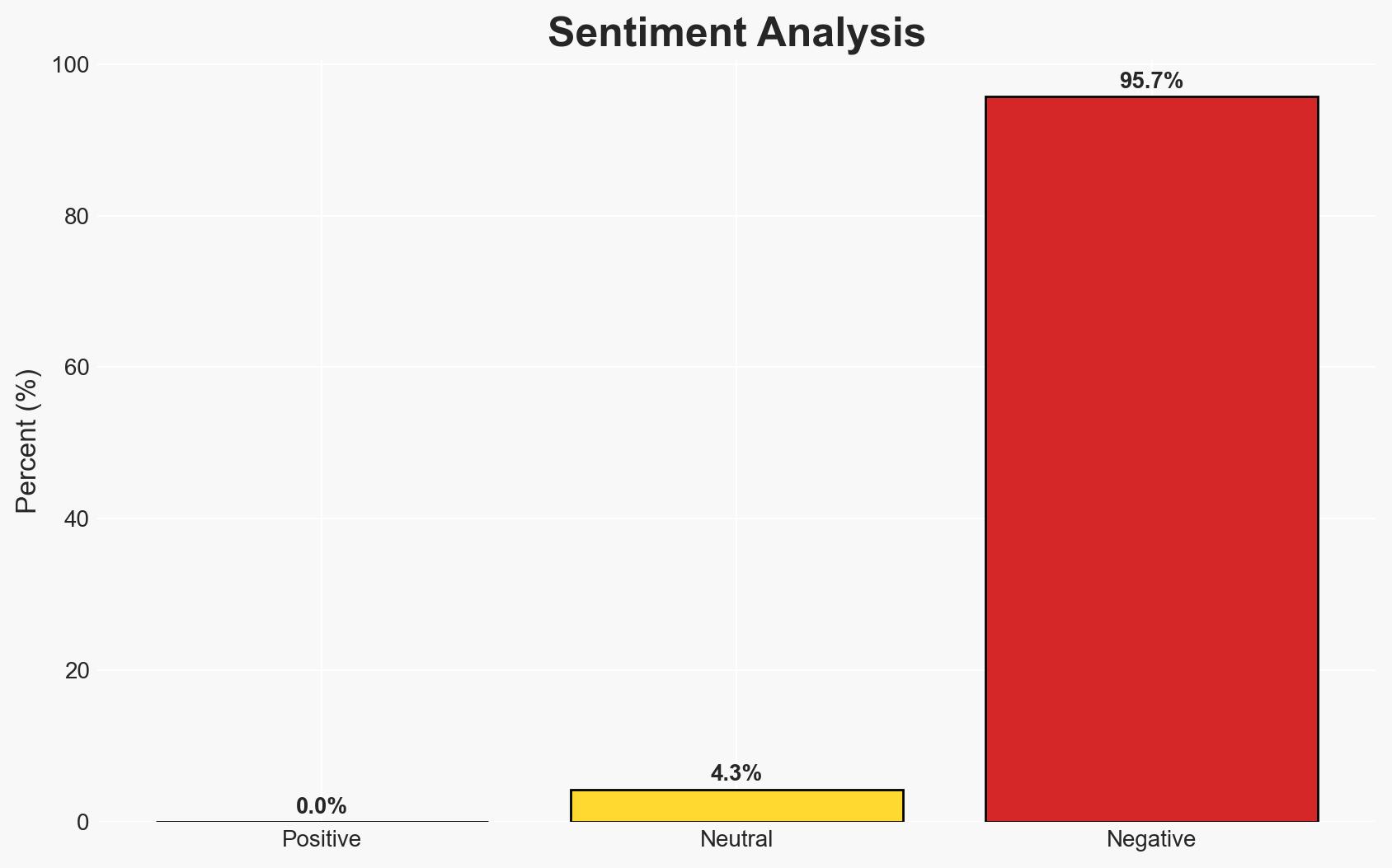
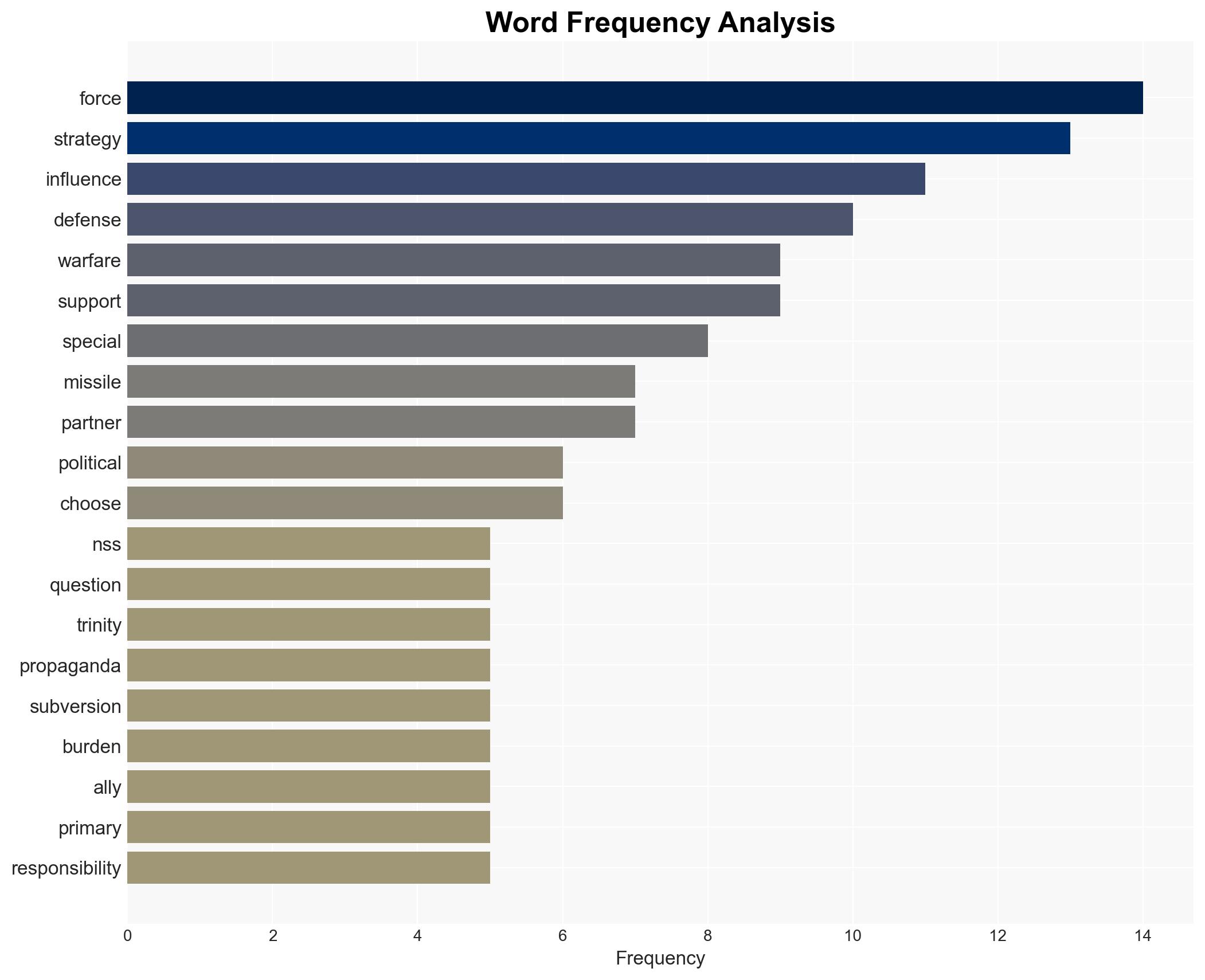
The 2025 National Security Strategy (NSS) and the 2026 National Defense Strategy (NDS) emphasize a shift towards homeland defense and regional burden-sharing, potentially altering the operational focus of U.S. Special Forces. This strategic pivot may require Special Forces to enhance capabilities in irregular warfare and influence operations. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited visibility into specific operational plans and regional responses.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The NSS and NDS will lead to a reduced forward presence of U.S. forces, with Special Forces taking on more roles in irregular warfare and influence operations to compensate. This is supported by the emphasis on homeland defense and regional burden-sharing but lacks clarity on specific operational changes.
- Hypothesis B: Despite the strategic shift, U.S. Special Forces will maintain a significant forward presence to ensure global stability and rapid response capabilities. This hypothesis is contradicted by the stated focus on homeland defense and regional burden-sharing.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the explicit strategic focus on homeland defense and the expectation of allies taking primary responsibility in their regions. Indicators such as changes in deployment patterns or increased training for irregular warfare could shift this assessment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The U.S. will successfully negotiate increased burden-sharing with allies; Special Forces have the capacity to adapt to new roles; the strategic environment will remain relatively stable.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on how Special Forces missions will be adjusted; regional allies’ willingness and capability to assume greater defense responsibilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on stated strategic documents without considering real-world constraints; possible underestimation of adversaries’ adaptive strategies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The strategic shift could lead to a reallocation of resources and a potential gap in global rapid response capabilities, impacting U.S. influence and deterrence posture.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased reliance on allies may lead to geopolitical shifts and realignment of regional power dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential vulnerabilities in global counter-terrorism efforts if regional partners are unable to fill the gap effectively.
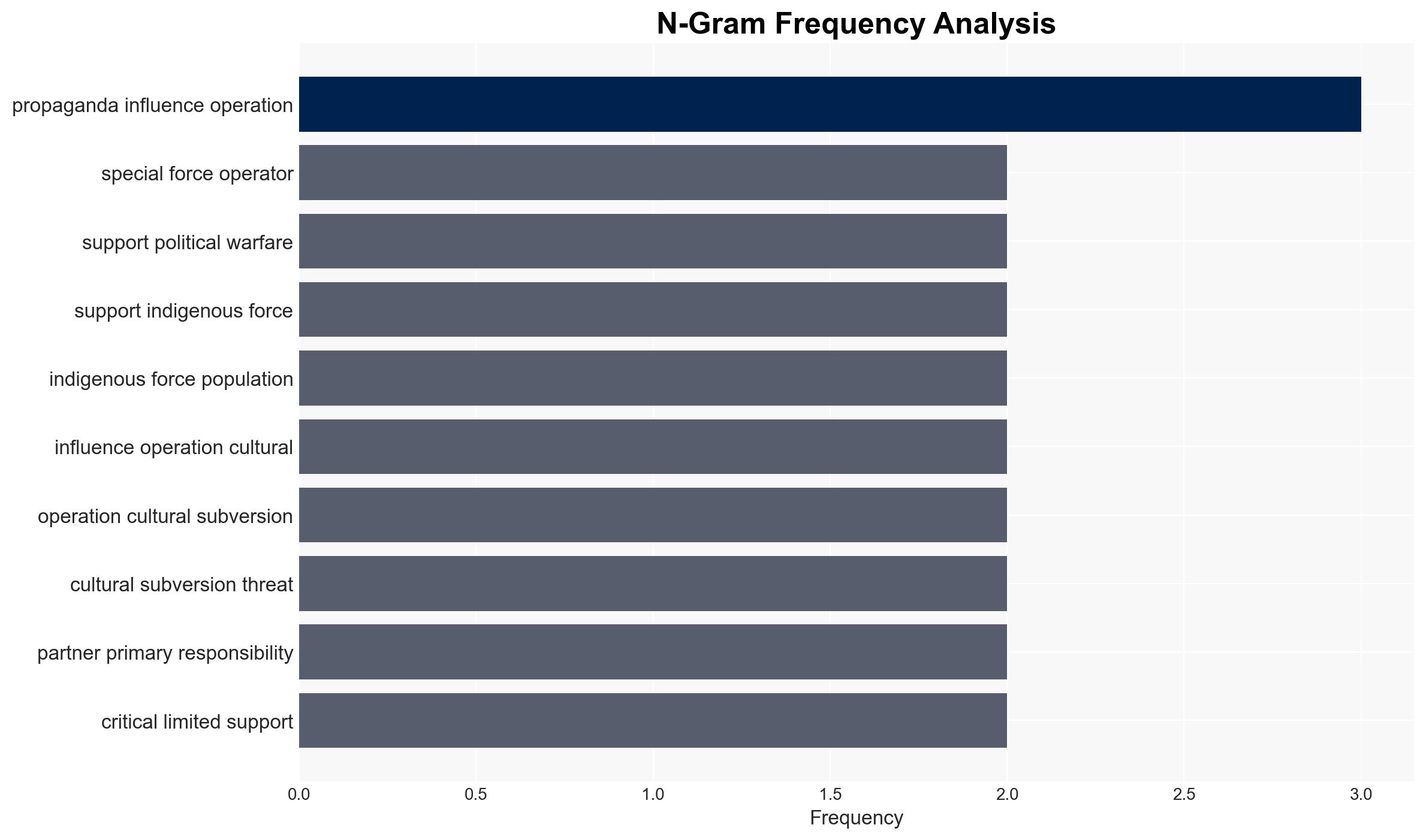
- Cyber / Information Space: Emphasis on countering propaganda and influence operations may lead to increased cyber and information warfare activities.
- Economic / Social: Changes in defense spending priorities could impact domestic industries and social programs.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive assessment of ally capabilities and readiness; enhance intelligence sharing and coordination mechanisms.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop training programs focused on irregular warfare and influence operations; strengthen regional partnerships and capacity-building initiatives.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful burden-sharing leads to enhanced global stability and reduced U.S. resource strain.
- Worst: Allies fail to meet expectations, leading to security vacuums and increased adversary influence.
- Most-Likely: Gradual transition with mixed results, requiring ongoing U.S. support and adjustments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, national security strategy, defense strategy, special forces, irregular warfare, homeland defense, burden-sharing, influence operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us