State-backed hackers exploit Notepad++ update system in targeted supply chain attack
Published on: 2026-02-02
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How state-sponsored attackers hijacked Notepad updates
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
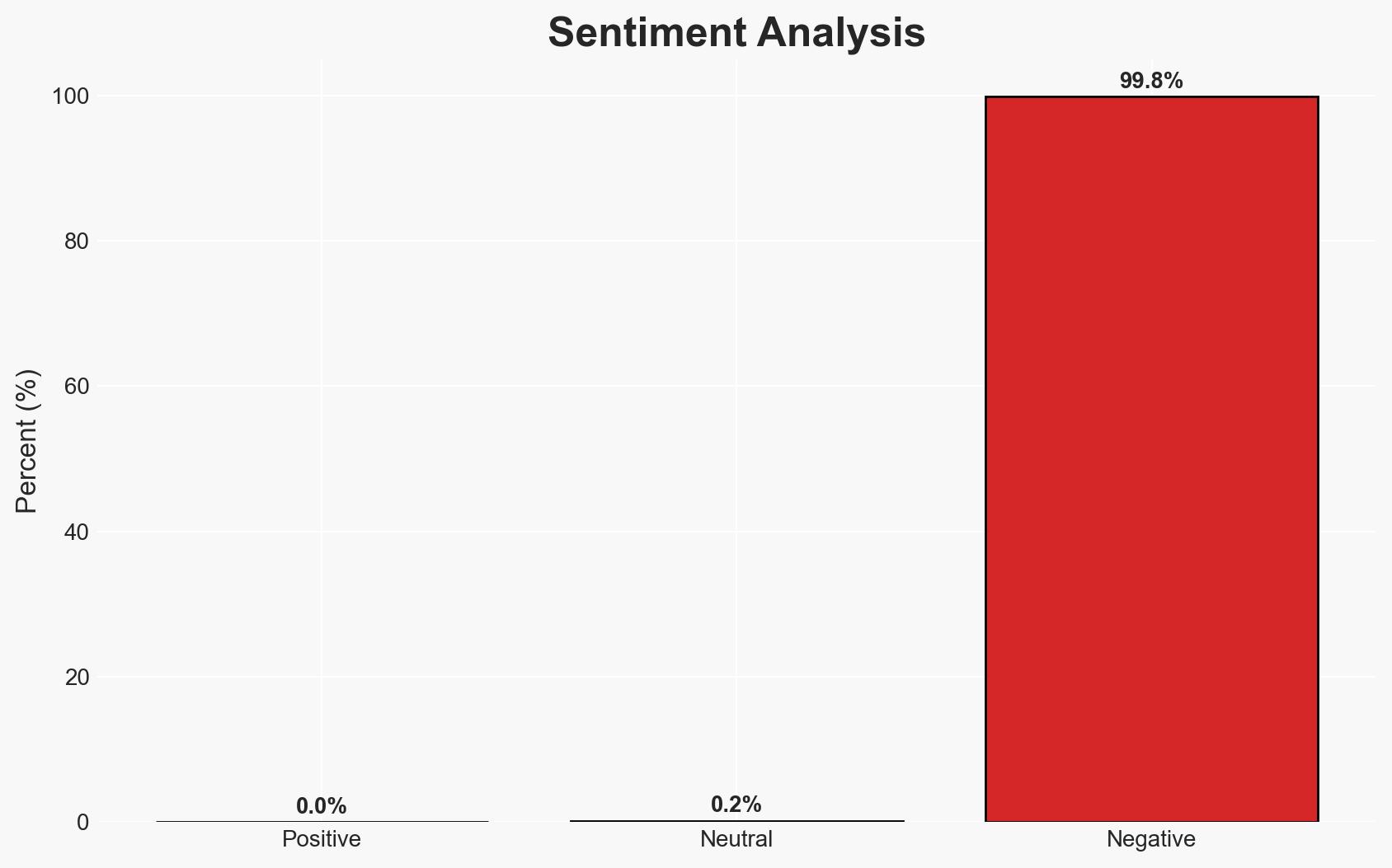
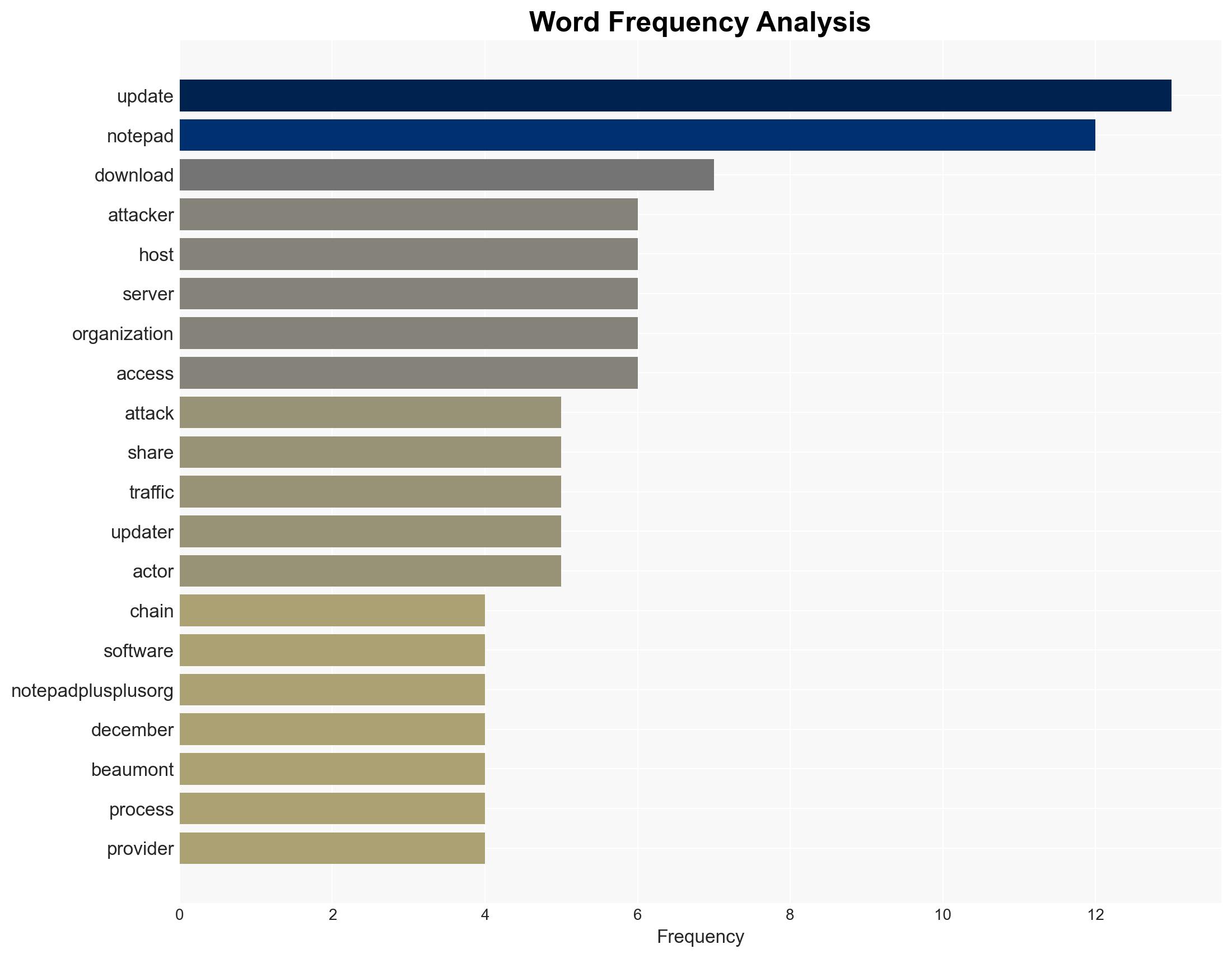
Chinese state-sponsored actors, identified as Zirconium, executed a supply chain attack on Notepad++ by compromising its update mechanism, impacting organizations in East Asia. The attack leveraged vulnerabilities in the software’s update process, allowing malicious updates to be delivered. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to confirmed technical details and partial attribution.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The attack was orchestrated by Chinese state-sponsored actors specifically targeting East Asian organizations for strategic intelligence gathering. This is supported by the targeted nature of the attacks and the attribution to Zirconium, a known Chinese threat actor.
- Hypothesis B: The attack was conducted by non-state actors or another nation-state using false flags to implicate China. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of evidence indicating alternative perpetrators and the specific targeting consistent with Chinese interests.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of the attack’s characteristics with known Chinese cyber operations and the attribution by security researchers. Indicators such as new attribution evidence or changes in targeting patterns could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers had the capability to exploit the specific vulnerabilities in Notepad++. The targeting of East Asian organizations aligns with Chinese strategic interests. The attribution to Zirconium is accurate based on current evidence.
- Information Gaps: Detailed forensic analysis of the compromised systems and direct evidence linking the attackers to the Chinese government.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Attribution bias due to historical patterns of Chinese cyber activity. Potential deception by attackers to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased tensions in cyber relations between China and affected nations, potentially prompting retaliatory measures. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in software supply chains, necessitating improved security protocols.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential diplomatic strains between China and East Asian countries, risk of retaliatory cyber actions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vigilance and security measures in targeted sectors, potential for similar attacks on other software.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and scrutiny of software supply chain security, potential for copycat attacks.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in affected sectors, potential loss of trust in software security, impacting business operations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough security audit of software supply chains, enhance monitoring of update mechanisms, and engage with affected organizations to mitigate impacts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for information sharing on cyber threats, invest in hardening software update processes, and enhance attribution capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Improved security measures prevent future attacks. Worst: Escalation of cyber conflict with significant economic impacts. Most-Likely: Continued low-level cyber skirmishes with incremental security improvements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Don Ho (Notepad++ maintainer)
- Kevin Beaumont (Security researcher)
- Zirconium (Chinese state-sponsored threat actor)
- Violet Typhoon (Alias for Zirconium)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, supply chain attack, cyber-espionage, state-sponsored actors, East Asia, software vulnerabilities, Chinese cyber operations, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us