Paris Prosecutors Conduct Raid on Elon Musk’s X Offices Amid Data and Child Exploitation Investigation
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Paris prosecutors raid France offices of Elon Musk’s X
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
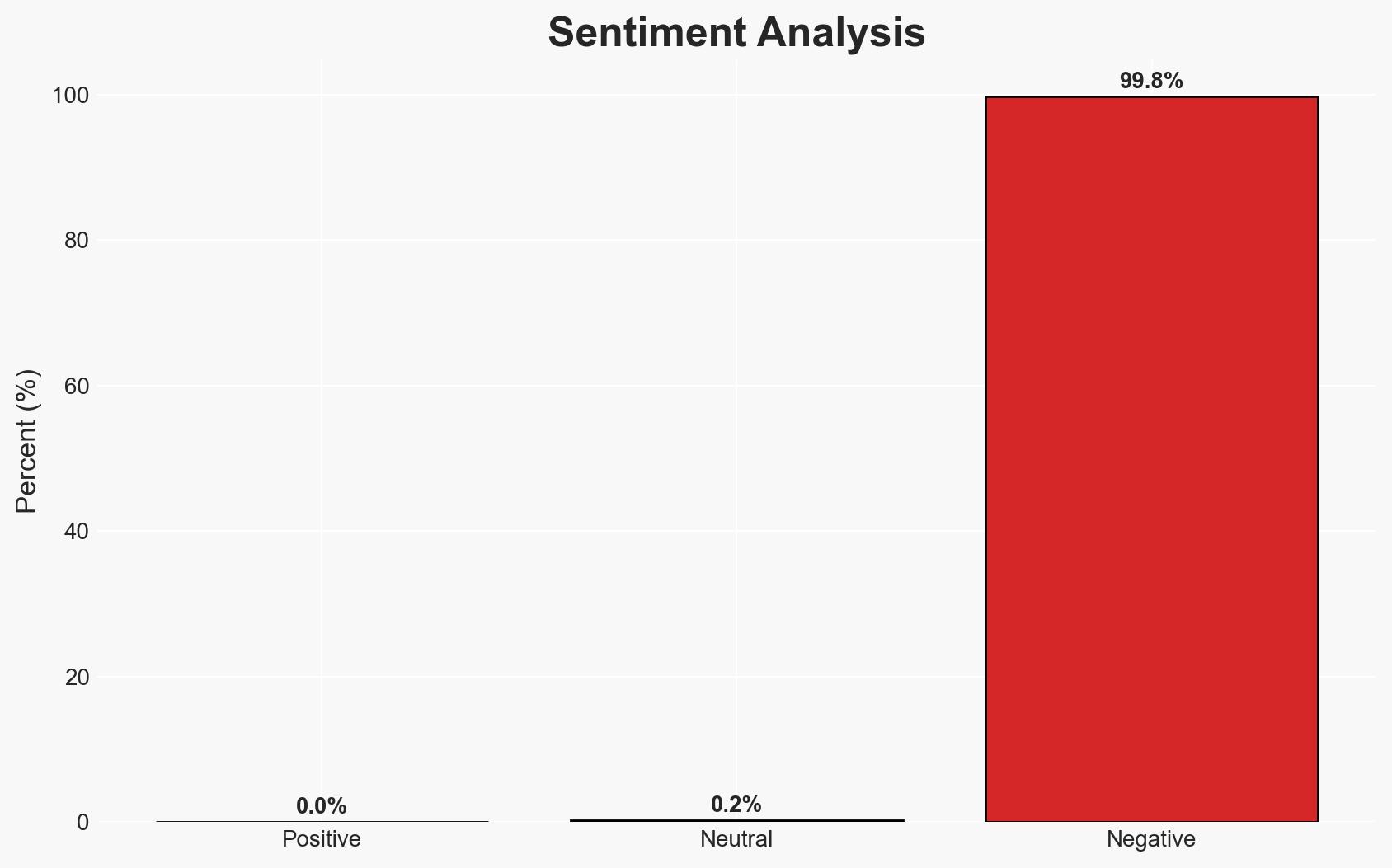
The raid on Elon Musk’s X offices in Paris by French prosecutors highlights potential legal challenges related to data extraction and child pornography. The investigation’s expansion to include Musk’s AI tool, Grok, raises significant concerns about data privacy and misuse. This situation could escalate tensions between X and European regulatory bodies, with moderate confidence in the hypothesis that legal non-compliance is a primary driver.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The raid is a legitimate legal action based on substantial evidence of wrongdoing by X, including unlawful data practices and complicity in child pornography. Supporting evidence includes the initiation of the investigation in January 2025 and its expansion to cover AI-related issues. However, uncertainties remain about the evidence’s strength and scope.
- Hypothesis B: The raid is politically motivated, as suggested by Musk and Yaccarino, aiming to target American companies. This is supported by public statements from X and its executives. Contradicting evidence includes the involvement of multiple regulatory bodies and the serious nature of the allegations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the involvement of multiple regulatory bodies and the serious nature of the allegations. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of concrete evidence supporting political motivations or a lack of substantive findings from the investigation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The investigation is based on credible evidence; European regulatory bodies are acting independently; X’s public statements reflect its genuine position.
- Information Gaps: Specific evidence supporting the allegations; detailed scope of the investigation; internal communications within X regarding data practices.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in public statements by X executives; risk of political bias influencing regulatory actions; possibility of strategic deception by involved parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could strain relations between X and European regulators, potentially leading to increased scrutiny of tech companies. The situation may also impact public trust in AI technologies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in regulatory actions against American tech firms in Europe.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: No direct implications identified, but increased regulatory focus on AI could influence future security policies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened scrutiny on data privacy and AI ethics, influencing future regulatory frameworks.
- Economic / Social: Possible impact on X’s market position and user trust, with broader implications for tech industry regulation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor developments in the investigation; engage with European regulators to understand compliance expectations; review internal data practices and AI tool usage.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen data privacy and compliance measures; develop partnerships with regulatory bodies to ensure alignment with legal standards; enhance transparency in AI operations.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Resolution with minimal penalties and improved compliance; Worst: Significant legal penalties and reputational damage; Most-Likely: Ongoing legal challenges with moderate penalties and increased regulatory scrutiny.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Elon Musk
- Linda Yaccarino
- Paris Public Prosecutor’s Office
- UK Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO)
- Ofcom
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data privacy, AI ethics, regulatory compliance, international relations, tech industry, legal investigation, cyber security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us