OpenClaw AI Bot Farm Faces Major Security Issues Amid Surge in Malware and Vulnerabilities
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: DIY AI bot farm OpenClaw is a security ‘dumpster fire’
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
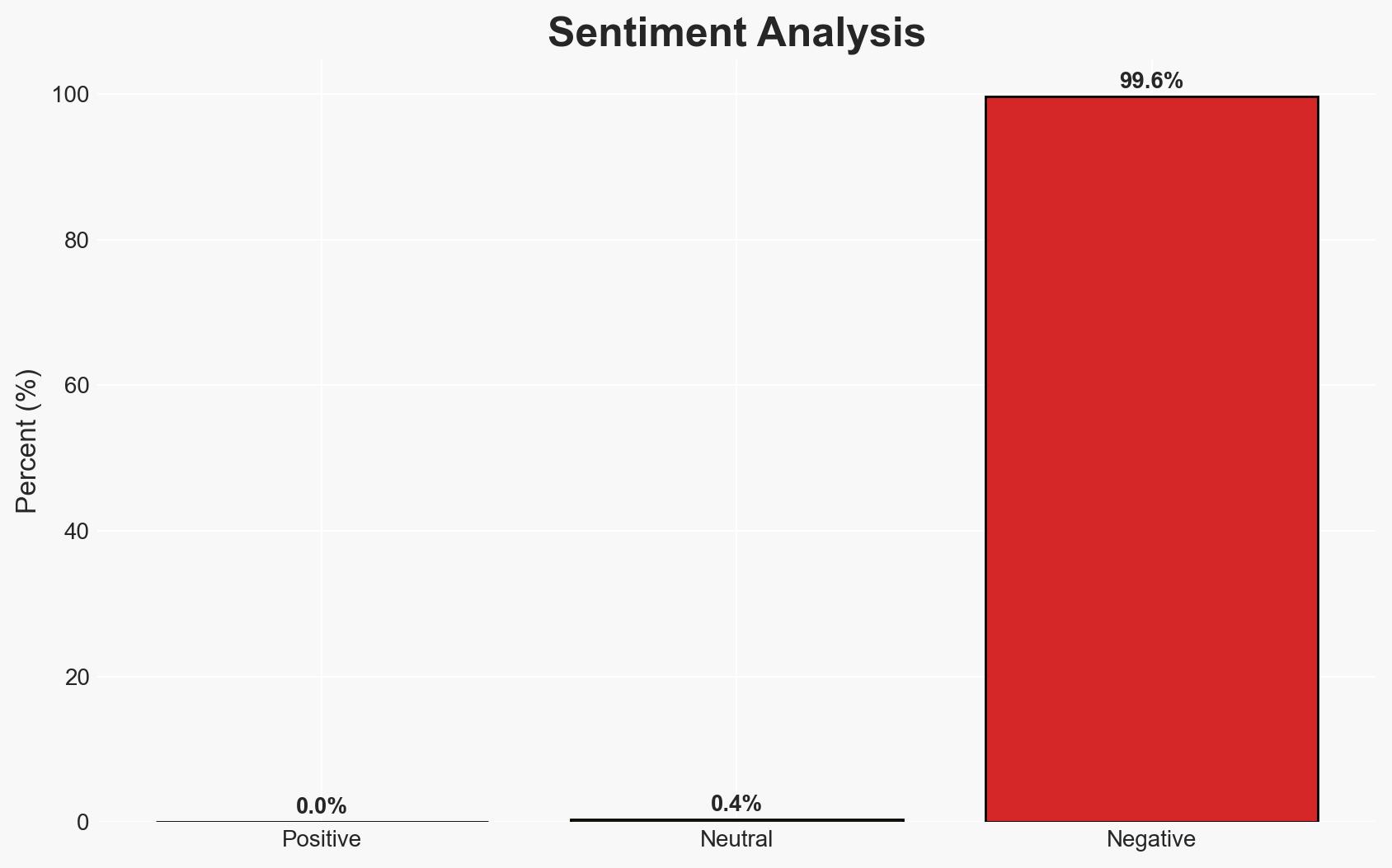
The OpenClaw project, an AI-powered personal assistant, is currently experiencing significant security vulnerabilities, including remote code execution and command injection flaws. These issues have led to the proliferation of malicious activities, such as cryptocurrency theft, posing risks to users and developers. The situation demands immediate attention to mitigate potential exploitation. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to the rapidly evolving nature of the situation and incomplete data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: OpenClaw’s security vulnerabilities are primarily due to its rapid development and deployment without adequate security measures. This is supported by the recent discovery of multiple high-impact vulnerabilities and malicious extensions. However, the lack of detailed technical analysis on the root causes remains a key uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities in OpenClaw are being deliberately exploited by malicious actors who are embedding backdoors and malicious skills to capitalize on the platform’s popularity. This is indicated by the presence of numerous malicious skills and the triviality of backdooring skills as noted by researchers. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of direct attribution to specific threat actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the evidence of rapid development and inadequate security protocols. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the identification of specific threat actors exploiting these vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: OpenClaw’s vulnerabilities are not intentionally introduced by its developers; the platform’s popularity will continue to attract both legitimate and malicious interest; current security advisories reflect the most critical issues.
- Information Gaps: Detailed technical analysis of the vulnerabilities; comprehensive threat actor attribution; full scope of malicious activities facilitated by OpenClaw.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from security researchers with vested interests; risk of deception by malicious actors embedding false information in OpenClaw’s ecosystem.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing security issues with OpenClaw could lead to broader systemic risks if not addressed, potentially impacting user trust and the integrity of AI-driven platforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory scrutiny on AI platforms, particularly concerning data privacy and security.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated risk of exploitation by cybercriminals and potentially state-sponsored actors targeting AI vulnerabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased likelihood of cyberattacks leveraging OpenClaw’s vulnerabilities, contributing to a broader threat landscape.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for users and developers; erosion of trust in AI technologies could slow adoption and innovation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit of OpenClaw; engage with cybersecurity experts to patch vulnerabilities; increase monitoring for malicious activities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing threat intelligence; implement robust security protocols and user education initiatives.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of vulnerabilities and restoration of user trust, leading to secure platform growth.
- Worst: Continued exploitation leading to significant financial and reputational damage, prompting regulatory intervention.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with ongoing challenges from emerging threats.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Simon Willison
- Andrej Karpathy
- Laurie Voss
- Jamieson O’Reilly
- Cyberstorm.MU
- Koi Security
- ZeroLeaks
- OpenSourceMalware
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, malware, digital trust, regulatory scrutiny, threat intelligence, platform security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us