Russia Launches Largest Missile and Drone Assault on Ukrainian Energy Infrastructure, NATO Responds
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: NATO scrambles fighters as Russia launches major strike on Ukrainian energy targets
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
Russia has conducted a significant strike on Ukraine’s energy infrastructure, deploying a large number of missiles and drones. This action is likely intended to degrade Ukraine’s energy capabilities during winter, increasing civilian hardship and pressuring the Ukrainian government. The most supported hypothesis is that this is part of a broader strategy to weaken Ukraine’s resolve and force concessions. The overall confidence level in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Russia’s strike is primarily aimed at crippling Ukraine’s energy infrastructure to weaken civilian morale and force political concessions. This is supported by the timing during winter and the focus on non-military targets. However, the exact strategic objectives remain unclear.
- Hypothesis B: The strike is a demonstration of military capability intended to deter Western support for Ukraine by showcasing Russia’s ability to escalate the conflict. The involvement of NATO fighters suggests a potential deterrence or escalation management strategy. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of direct military targets.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific targeting of energy infrastructure and the timing with winter conditions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Russian military rhetoric or actions targeting Western interests directly.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Russia aims to weaken Ukraine’s civilian infrastructure to gain leverage; NATO’s response is primarily defensive; Ukraine’s energy infrastructure is vulnerable to further attacks.
- Information Gaps: Detailed Russian strategic objectives; the extent of damage to Ukraine’s energy infrastructure; NATO’s internal deliberations on escalation management.
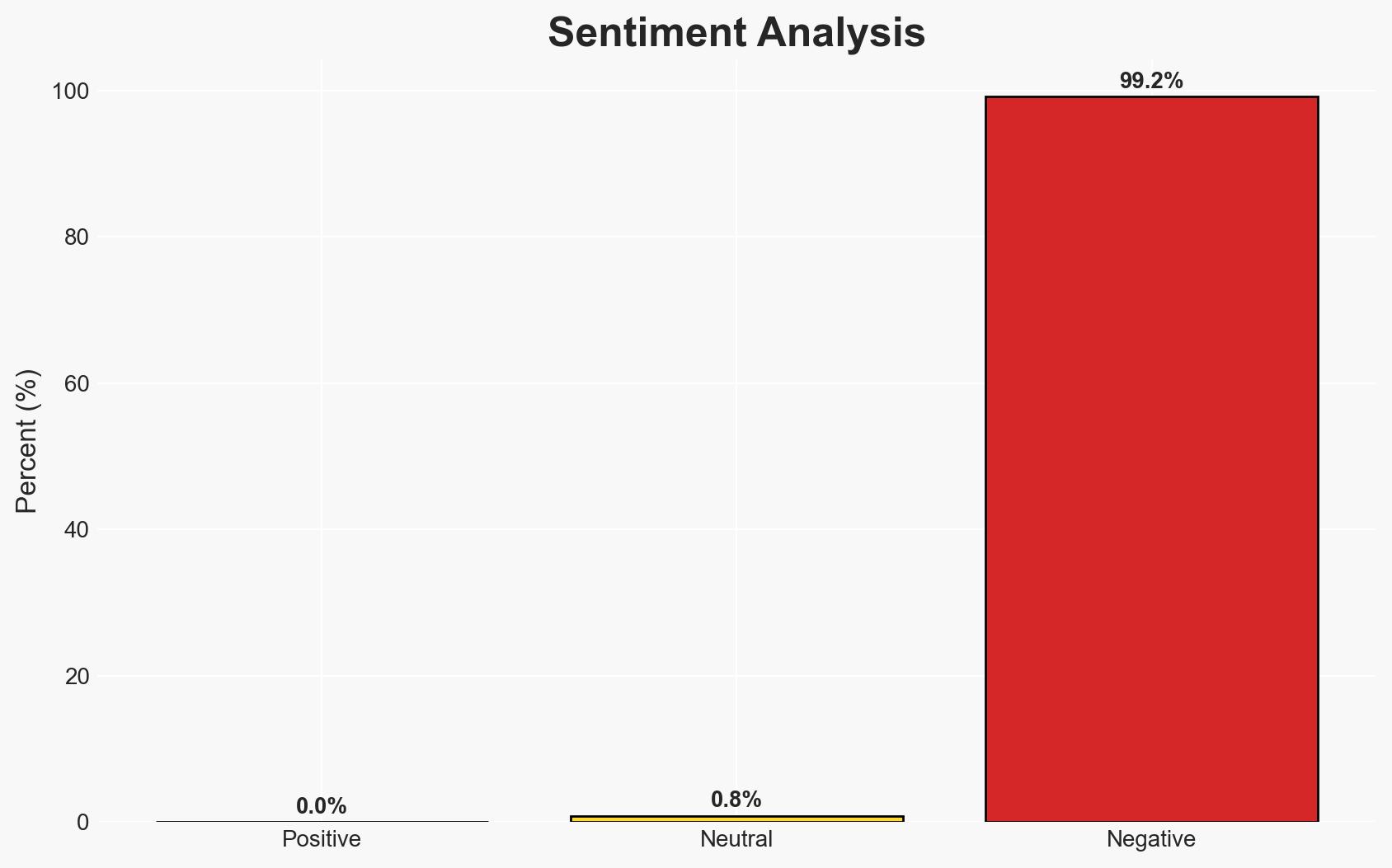
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Ukrainian and Russian reporting; risk of underestimating Russia’s willingness to escalate; possible manipulation of casualty and damage figures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased civilian hardship in Ukraine, potentially affecting political stability and public support for the government. It may also influence NATO’s strategic posture and readiness.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased Western support for Ukraine; risk of further escalation if NATO becomes more directly involved.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened threat environment in Ukraine; potential for increased Russian cyber operations against Ukrainian infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in Russian disinformation campaigns; potential for cyber retaliation by Ukraine or its allies.
- Economic / Social: Economic strain on Ukraine due to energy shortages; potential for increased migration pressures if civilian conditions worsen.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of Russian military movements; increase support for Ukrainian air defense capabilities; prepare contingency plans for NATO escalation management.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen Ukraine’s energy infrastructure resilience; bolster NATO’s eastern flank defenses; engage in diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: De-escalation through diplomatic channels, leading to a reduction in hostilities.
- Worst: Further escalation resulting in direct NATO-Russia confrontation.
- Most-Likely: Continued low-intensity conflict with periodic escalations targeting civilian infrastructure.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
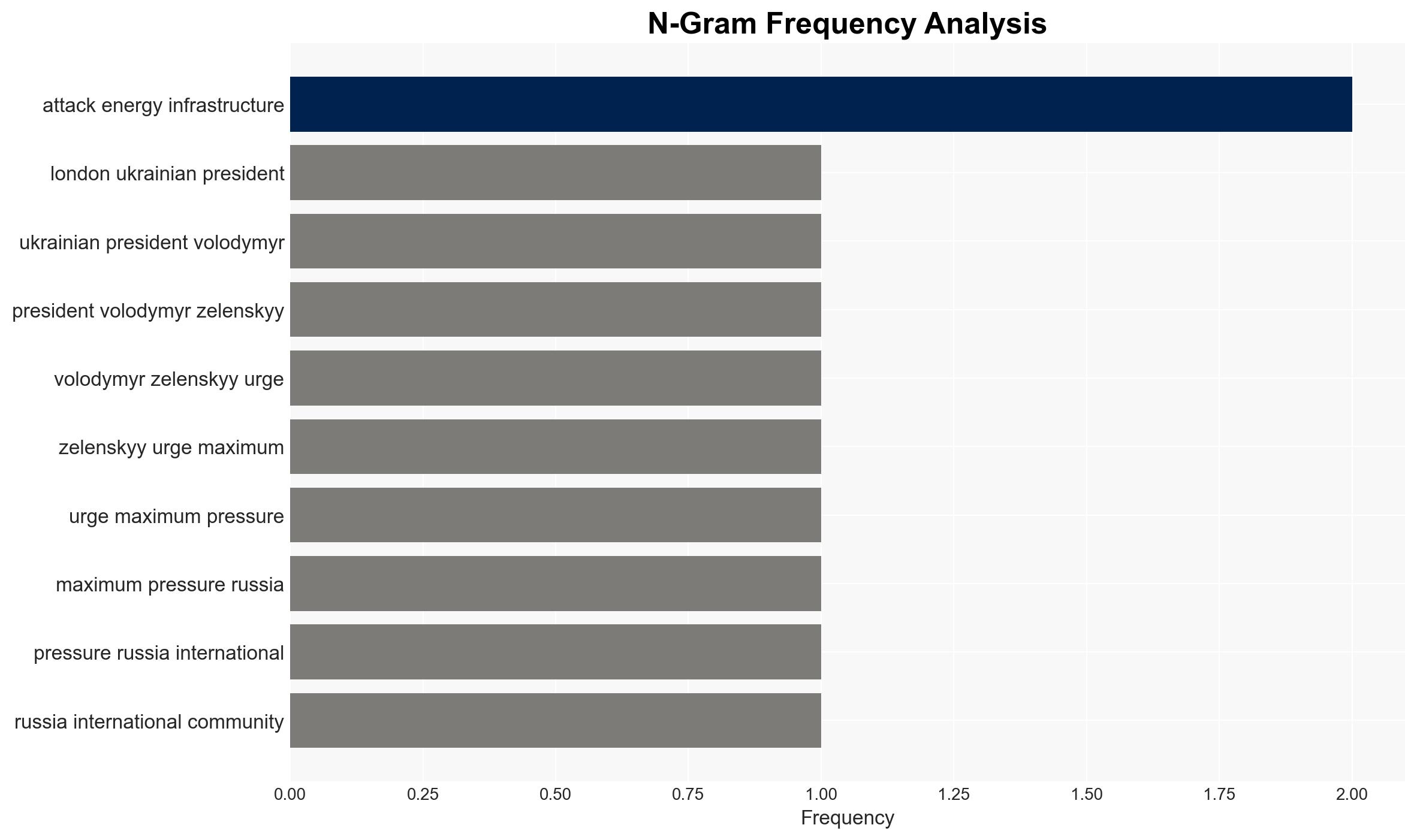
- Volodymyr Zelenskyy, Ukrainian President
- Denys Shmyhal, Ukrainian Energy Minister
- DTEK, Ukraine’s largest private energy firm
- Ukrenergo, Ukraine’s state energy company
- Russian Defense Ministry
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
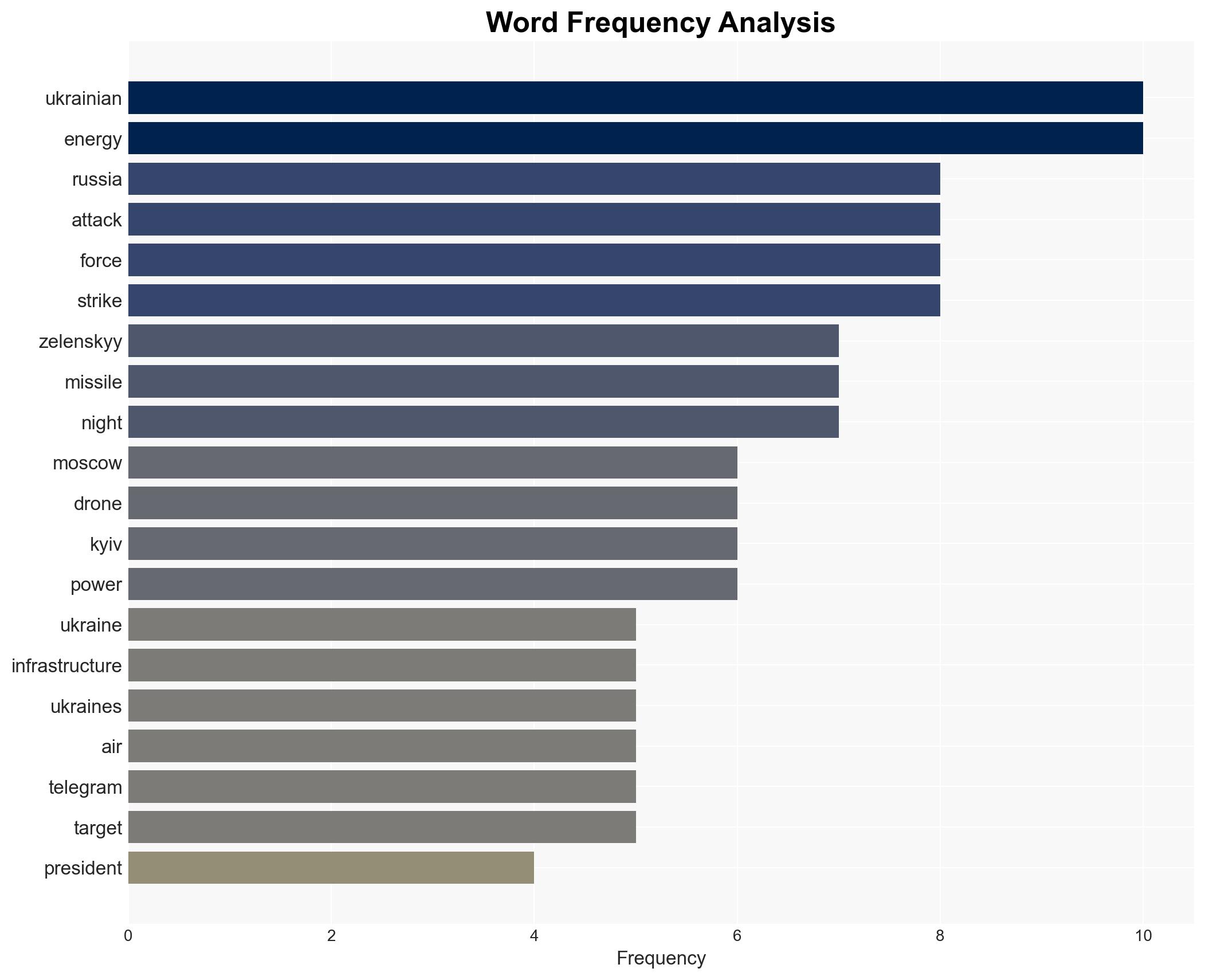
regional conflicts, energy infrastructure, military escalation, NATO response, civilian impact, Russian strategy, Ukraine conflict, winter operations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us