Docker Addresses Severe Vulnerability in Ask Gordon AI, Enabling Code Execution via Image Metadata
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Docker Fixes Critical Ask Gordon AI Flaw Allowing Code Execution via Image Metadata
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
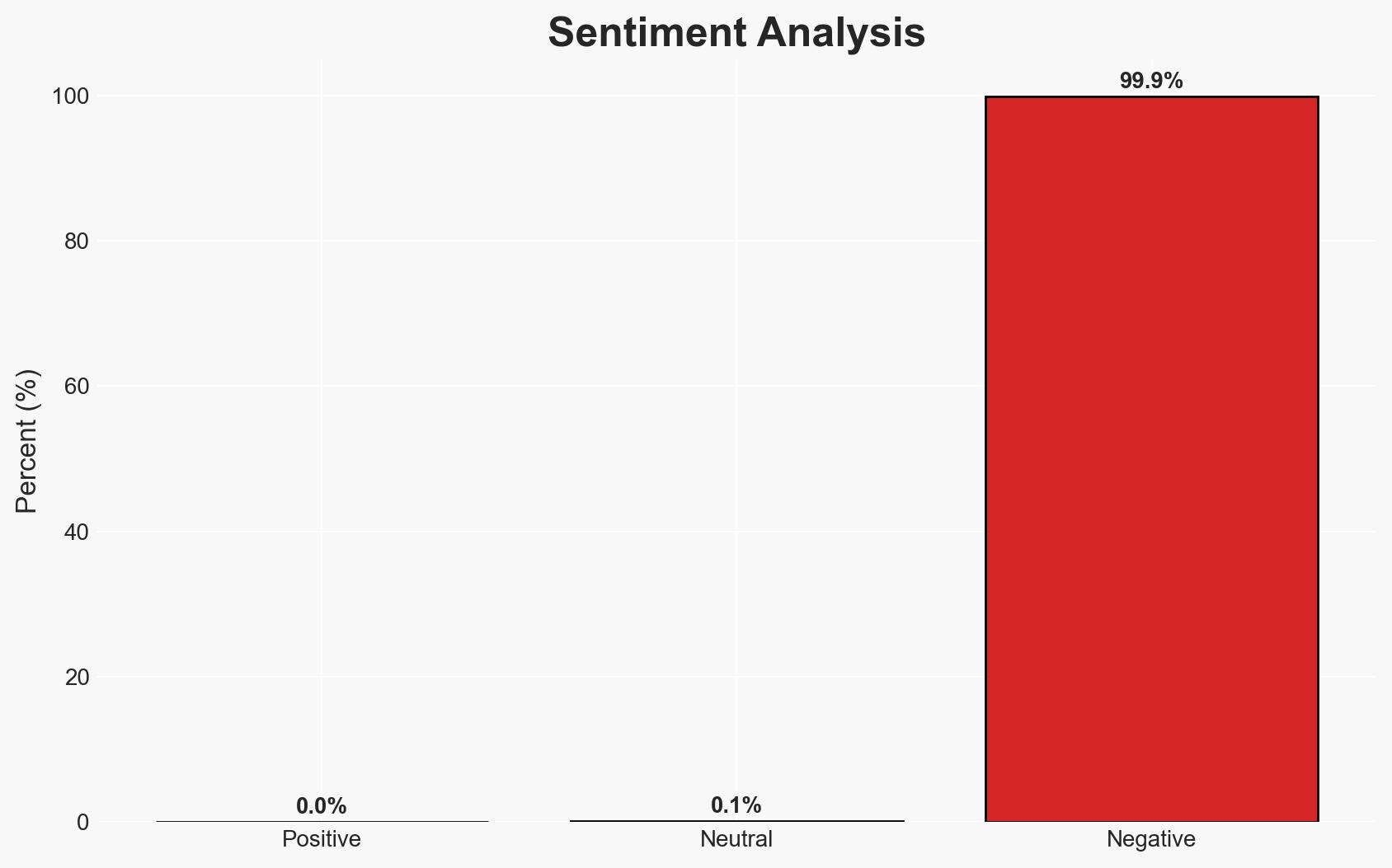
The recent patch of a critical vulnerability in Docker’s Ask Gordon AI highlights significant risks in AI-driven environments where metadata is treated as executable commands. This flaw, if exploited, could lead to remote code execution and data exfiltration, impacting cloud and desktop systems. The most likely hypothesis is that this vulnerability was a result of oversight in AI metadata handling, with moderate confidence due to limited information on potential exploitation attempts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerability was an unintended oversight in the design of Ask Gordon AI’s metadata processing, leading to a critical security flaw. This is supported by the lack of validation in metadata handling and the subsequent patch release. However, there is uncertainty regarding the extent of exploitation prior to the patch.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerability was intentionally introduced by a malicious insider or through compromised development processes. There is no direct evidence supporting this, but the sophistication of the attack vector suggests a deep understanding of Docker’s architecture.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the immediate response and patching by Docker, indicating a likely oversight rather than malicious intent. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of insider involvement or targeted exploitation campaigns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The vulnerability was not widely exploited before patching; Docker’s patch effectively mitigates the risk; the flaw was an oversight rather than intentional.
- Information Gaps: Details on any exploitation incidents; insights into Docker’s internal security review processes; information on potential insider threats.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Possible underestimation of the vulnerability’s exploitation scope; reliance on Docker’s self-reported data; potential manipulation of public perception by affected parties.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development underscores the critical need for robust security protocols in AI-driven systems, particularly those interfacing with cloud and local environments. Over time, similar vulnerabilities could be exploited by state or non-state actors, influencing broader security dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased scrutiny on AI and software security could lead to regulatory changes or international cybersecurity agreements.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential for exploitation by cybercriminals or terrorist groups to disrupt critical infrastructure or exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlights vulnerabilities in AI systems, potentially leading to increased cyber espionage activities.
- Economic / Social: Could impact trust in AI technologies, affecting adoption rates and innovation in the tech industry.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough review of AI metadata handling protocols; enhance monitoring for unusual activity in Docker environments; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess potential risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI and cybersecurity firms to improve resilience; invest in training for secure AI development practices; establish a rapid response team for future vulnerabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further exploitation occurs, and security measures are strengthened industry-wide.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Limited exploitation occurs, prompting increased focus on AI security without major incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Docker
- Noma Labs
- Sasi Levi (Security Research Lead at Noma Labs)
- The Hacker News
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, Docker, metadata exploitation, remote code execution, data exfiltration, software security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us