Open-source Global Threat Map Provides Real-Time Visualization of Cyber Activity Worldwide
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Global Threat Map Open-source real-time situational awareness platform
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
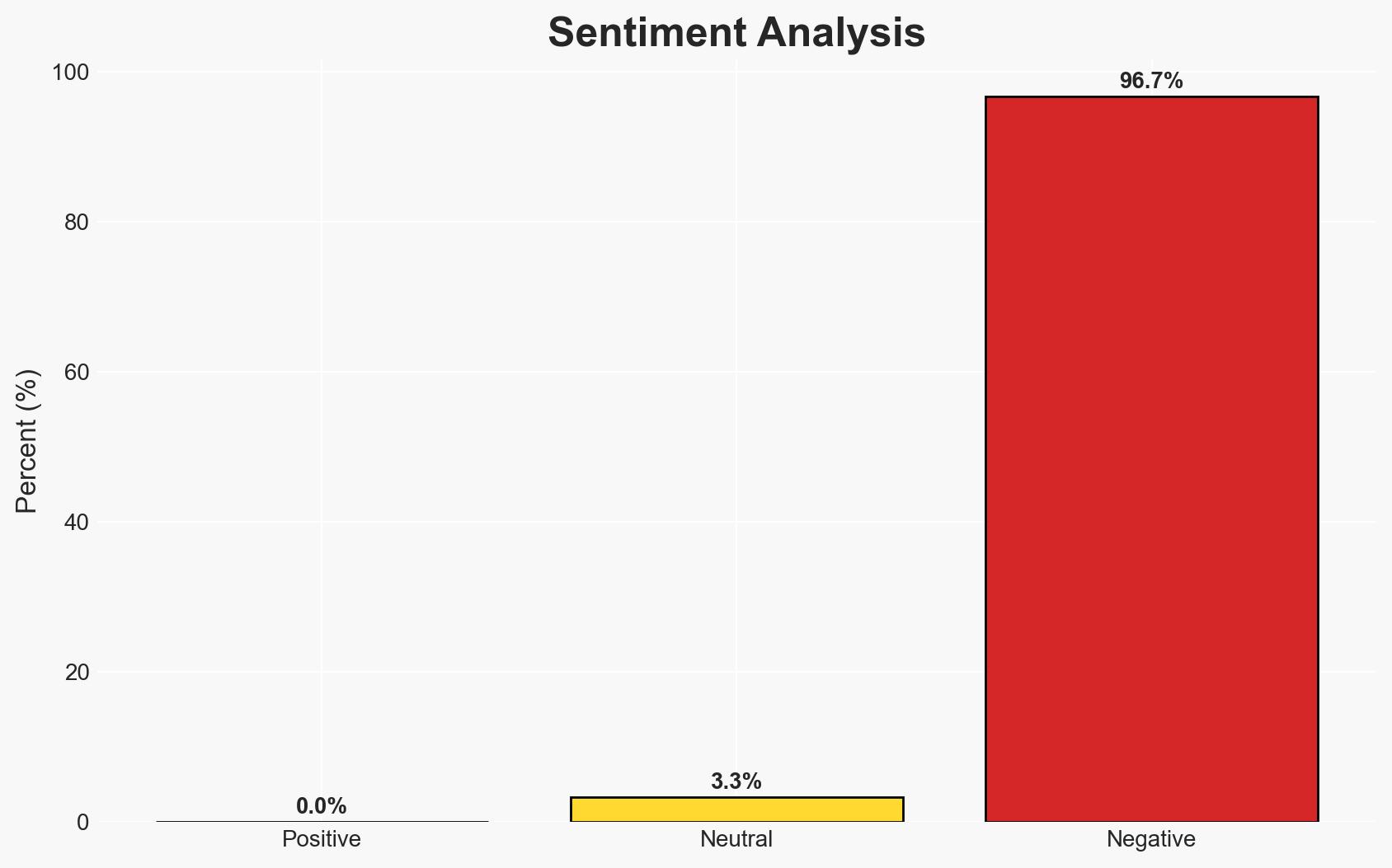
The Global Threat Map provides an open-source platform for visualizing global cyber threats, offering transparency and community-driven insights. It is most likely to be a valuable tool for security professionals seeking non-proprietary threat intelligence. However, its reliance on open data feeds introduces potential accuracy and scope limitations. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Global Threat Map enhances situational awareness by providing comprehensive and transparent threat intelligence. This is supported by the project’s open-source nature and detailed data aggregation, but contradicted by potential variability in data feed accuracy.
- Hypothesis B: The Global Threat Map may not significantly improve situational awareness due to its reliance on open data feeds, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This is supported by the known limitations of open-source data but contradicted by the platform’s transparency and community involvement.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the project’s transparency and the ability for users to verify and modify data sources. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of significant inaccuracies in the data feeds or the emergence of more reliable proprietary alternatives.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The open data feeds are reasonably accurate and comprehensive; users have the technical capability to assess and modify the data; the community will actively maintain and update the platform.
- Information Gaps: Specific accuracy metrics for the data feeds; user engagement and modification statistics; comparative analysis with proprietary platforms.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in community-maintained data sources; risk of manipulation by malicious actors contributing false data; cognitive bias towards trusting open-source transparency without verification.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The Global Threat Map could influence the cyber threat landscape by democratizing access to threat intelligence and encouraging collaborative analysis. However, reliance on open data may lead to inconsistent threat assessments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased transparency could pressure governments to improve their own threat intelligence sharing practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced situational awareness could improve defensive measures but may also expose vulnerabilities if data is inaccurate.
- Cyber / Information Space: The platform could become a target for cyber-attacks aiming to disrupt or manipulate data feeds.
- Economic / Social: Broader access to threat intelligence could empower smaller organizations lacking resources for proprietary solutions, potentially leveling the playing field.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Encourage security teams to integrate the Global Threat Map into their threat intelligence processes while cross-referencing with other sources for validation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with other open-source projects to enhance data accuracy and coverage; invest in community engagement to ensure active maintenance.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: The platform becomes a leading tool for threat intelligence, fostering global collaboration. Worst: Data inaccuracies lead to mistrust and reduced usage. Most-Likely: The platform gains moderate adoption, supplementing existing tools.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Prosper Otemuyiwa, creator of Global Threat Map
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, open-source intelligence, threat intelligence, transparency, community collaboration, data accuracy, situational awareness
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us