Microsoft Alerts on Rise of Python-Based Infostealers Targeting macOS Through Deceptive Ads and Installers
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Microsoft Warns Python Infostealers Target macOS via Fake Ads and Installers
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
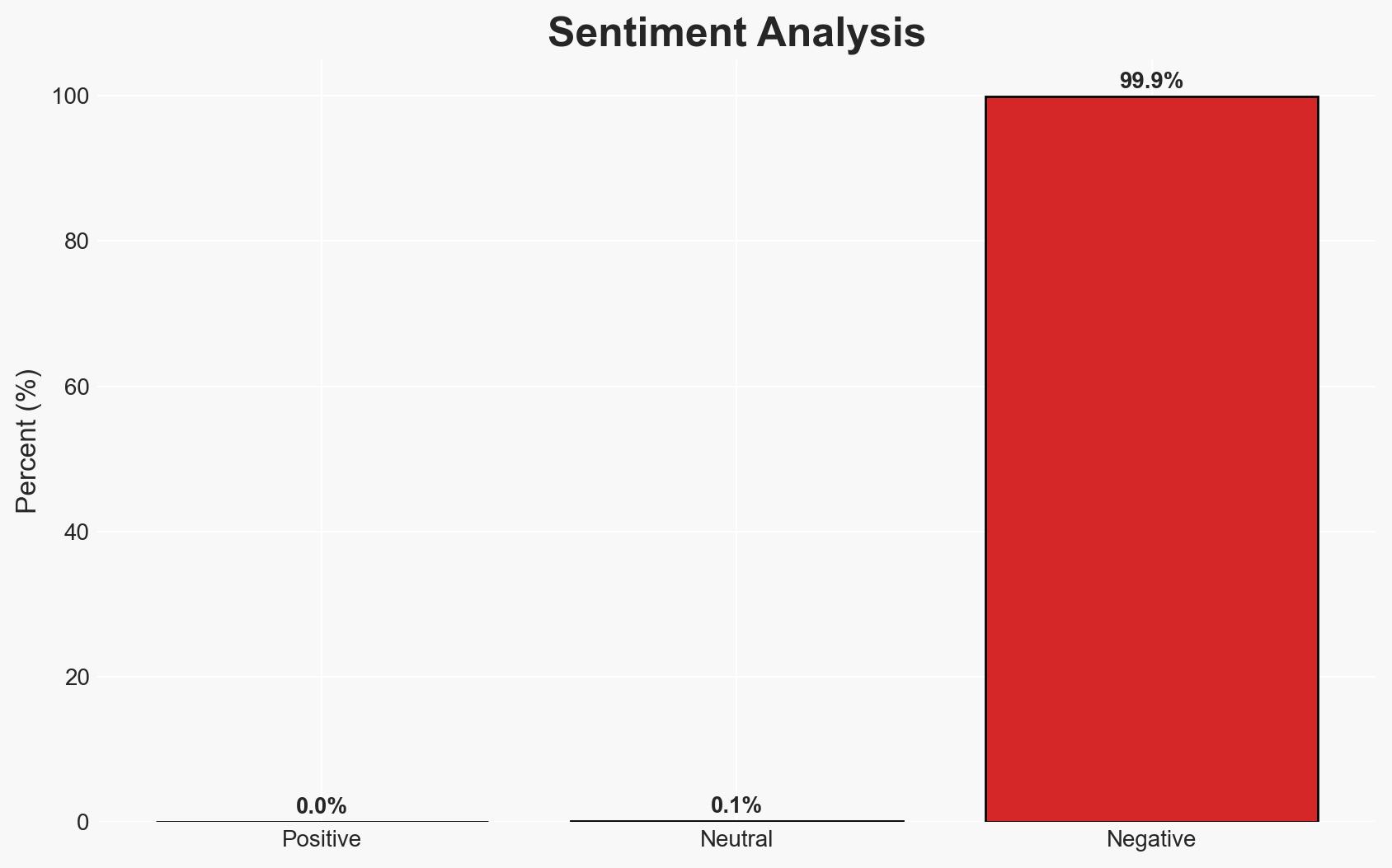
Microsoft has identified a significant expansion of Python-based infostealer malware campaigns targeting macOS environments, leveraging social engineering and trusted platforms for distribution. The primary affected parties include macOS users and organizations with macOS infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that these campaigns are driven by financially motivated threat actors exploiting cross-platform capabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to the evolving nature of the threat and limited visibility into all threat actor motivations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The campaigns are primarily financially motivated, targeting macOS users to steal sensitive information such as credentials and financial data. Supporting evidence includes the use of phishing and malvertising techniques, as well as the targeting of financial and cryptocurrency accounts. Key uncertainties include the full scope of targeted sectors and potential state-sponsored involvement.
- Hypothesis B: The campaigns are part of a broader cyber-espionage effort aimed at gathering intelligence from macOS users, potentially involving state-sponsored actors. This is less supported due to the focus on financial data and the use of common cybercrime tactics. However, the use of sophisticated techniques like fileless execution suggests a higher level of capability.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the clear financial motivations and typical cybercrime methodologies observed. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of targeting specific sectors for intelligence purposes or links to known state-sponsored groups.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The threat actors are primarily financially motivated; macOS is increasingly targeted due to its growing user base; Python’s cross-platform nature is a key enabler for these campaigns.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of the threat actors; comprehensive understanding of the targeted sectors; full scope of the malware’s capabilities.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in overestimating financial motivations without considering espionage; reliance on vendor-reported data which may have inherent biases or limitations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The expansion of infostealer campaigns to macOS could lead to increased targeting of Apple users, impacting both personal and organizational data security. This development may prompt a broader reassessment of macOS security postures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state-sponsored involvement is identified, impacting international relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Elevated threat environment for macOS users, necessitating enhanced security measures and awareness.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in cybercrime tactics, leveraging cross-platform capabilities and trusted platforms for distribution.
- Economic / Social: Potential financial losses for individuals and businesses; erosion of trust in digital platforms and advertising networks.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance user education on social engineering tactics; implement monitoring for suspicious network activity and access to sensitive data on macOS systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in cross-platform security solutions and resilience measures.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Effective mitigation reduces threat impact; Worst: Escalation to state-sponsored campaigns; Most-Likely: Continued financial targeting with incremental sophistication.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft Defender Security Research Team
- LevelBlue/Trustwave
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, macOS, infostealers, social engineering, Python malware, financial cybercrime, cross-platform threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us