OIG audit uncovers security vulnerabilities in web applications at major Southeastern hospital
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: OIG audit reveals web app security weaknesses at large hospital
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
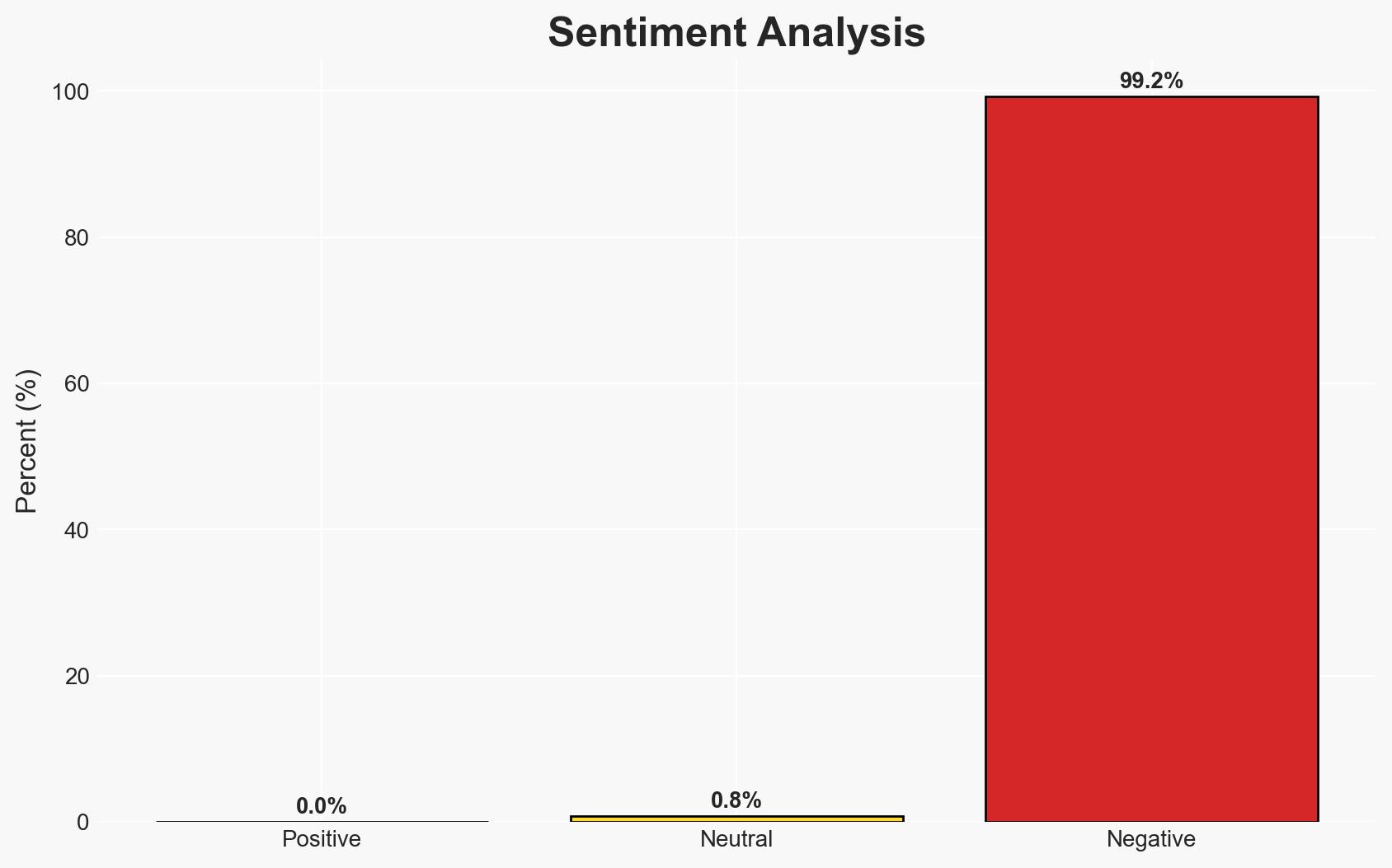
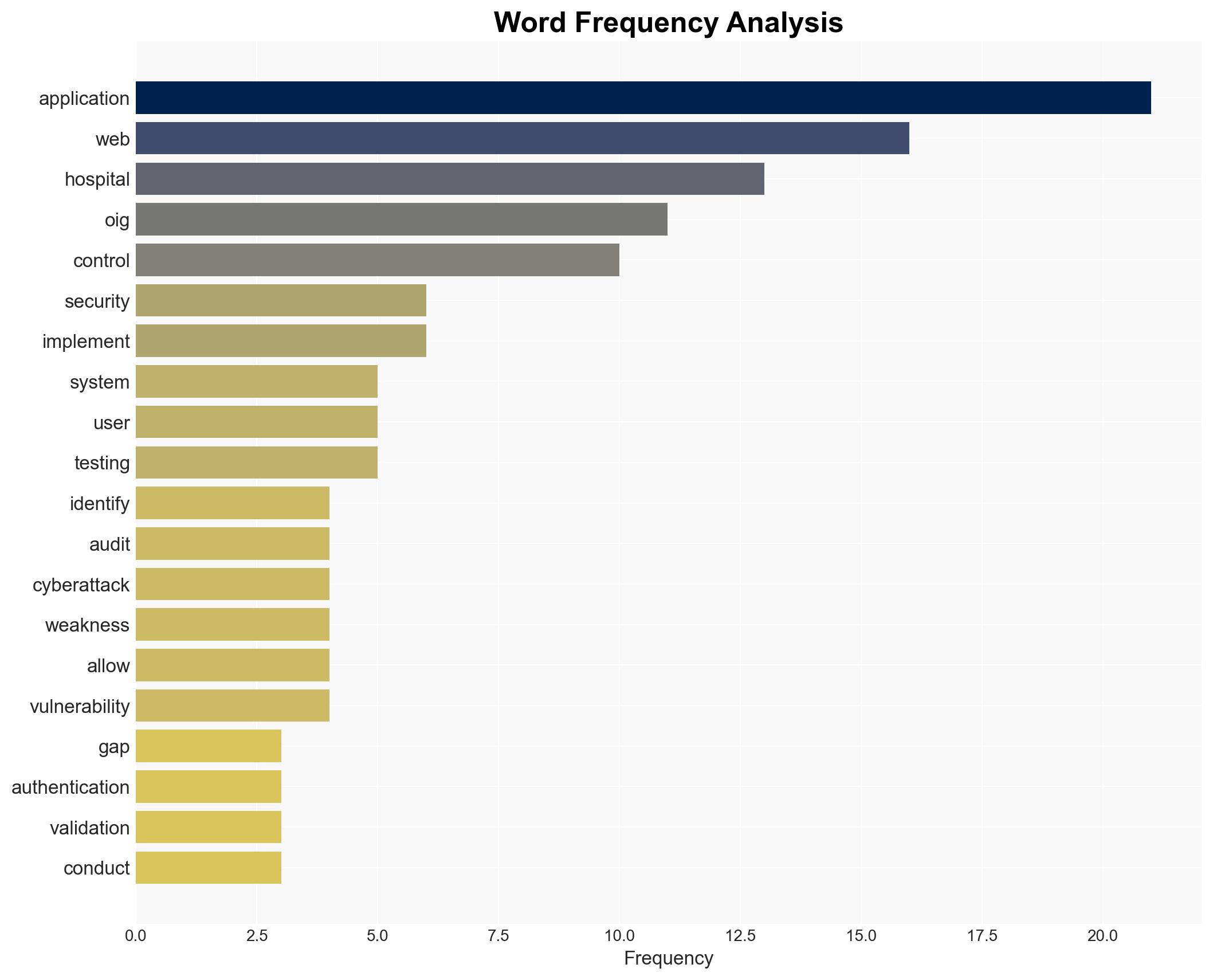
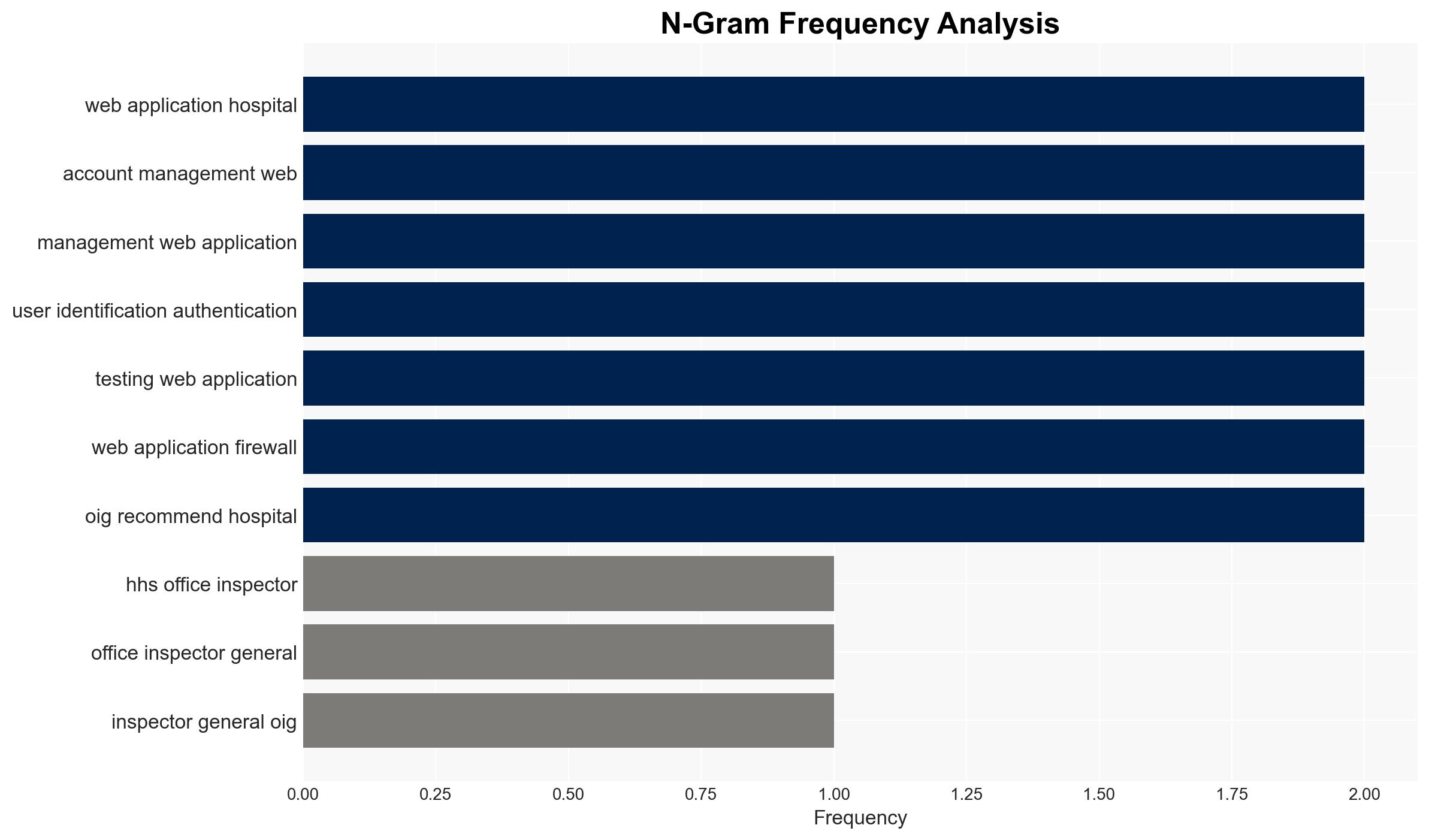
The OIG audit identified significant web application security weaknesses at a large Southeastern hospital, primarily in user identification and authentication controls. These vulnerabilities pose a risk to patient data security and hospital operations. The most likely hypothesis is that these weaknesses are due to insufficient cybersecurity measures and oversight. The affected parties include the hospital, its network, and potentially patients. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The security weaknesses are primarily due to inadequate cybersecurity measures and oversight within the hospital’s IT infrastructure. Supporting evidence includes identified gaps in authentication and validation controls and successful simulated phishing attacks. Key uncertainties include the extent of management awareness and resource allocation for cybersecurity.
- Hypothesis B: The vulnerabilities are a result of external factors, such as sophisticated threat actors targeting the hospital. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of evidence indicating targeted external attacks and the presence of internal control weaknesses.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported, as the identified gaps align with internal control deficiencies rather than external threats. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of coordinated external attacks or improvements in internal cybersecurity measures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The hospital’s IT staff are aware of the vulnerabilities; the hospital has the resources to address these issues; the vulnerabilities are not currently being exploited by external actors.
- Information Gaps: Detailed information on the hospital’s cybersecurity budget and staffing; specific details on the hospital’s response to the audit findings.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in OIG’s reporting due to reliance on contracted testing; risk of hospital underreporting vulnerabilities to protect reputation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The identified security weaknesses could lead to data breaches, impacting patient privacy and hospital operations. Over time, this could undermine trust in the hospital’s ability to protect sensitive information.
- Political / Geopolitical: Limited direct implications unless vulnerabilities are exploited by state-sponsored actors.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyberattacks targeting healthcare infrastructure, potentially affecting patient care.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for exploitation of vulnerabilities by cybercriminals, leading to data breaches and ransomware attacks.
- Economic / Social: Financial impact on the hospital due to potential fines and loss of patient trust; broader implications for healthcare sector cybersecurity standards.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive review of cybersecurity controls; implement immediate fixes to identified vulnerabilities; enhance user authentication protocols.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop a robust cybersecurity strategy; invest in staff training and awareness programs; establish partnerships with cybersecurity firms for regular audits.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Hospital addresses vulnerabilities, enhancing security posture. Worst: Exploitation of vulnerabilities leads to significant data breach. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements with ongoing risk of minor breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, healthcare, data protection, vulnerability assessment, risk management, information security, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us