Security Risks Emerge as Malware Found in Popular OpenClaw AI Skill Extensions
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: OpenClaws AI skill extensions are a security nightmare
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
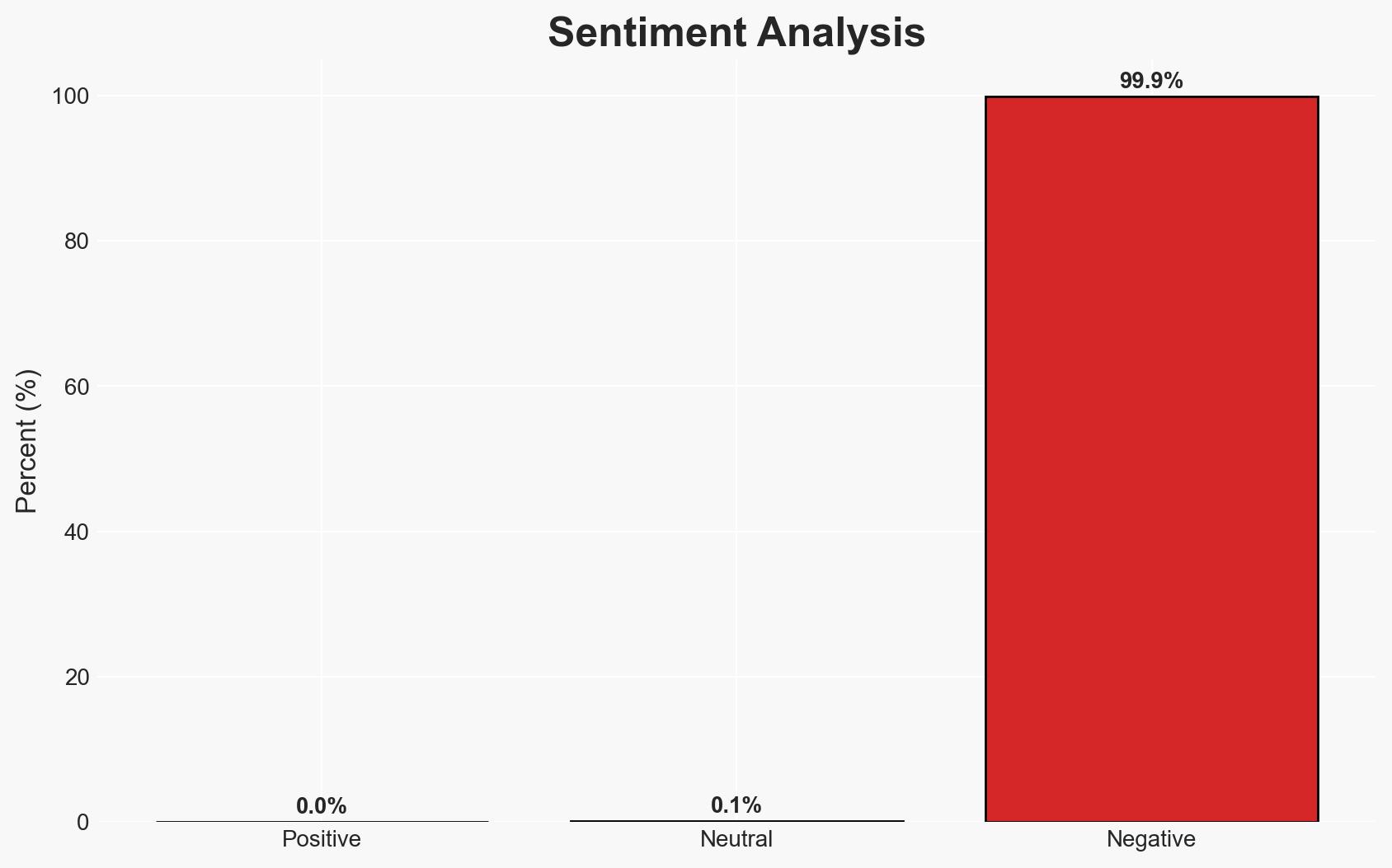
The OpenClaw AI platform is experiencing significant security vulnerabilities due to malware in user-submitted skill extensions, posing risks to users’ data and devices. The most likely hypothesis is that malicious actors are exploiting OpenClaw’s open marketplace to distribute malware, affecting users globally who utilize these AI extensions. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Malicious actors are intentionally exploiting OpenClaw’s open marketplace to distribute malware. This is supported by the discovery of hundreds of malicious skills and the platform’s insufficient vetting process. However, the extent of the actors’ coordination and motives remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The presence of malware is primarily due to inadequate security measures and oversight by OpenClaw, rather than coordinated malicious intent. While the platform’s recent security updates suggest recognition of these issues, the rapid proliferation of malware indicates potential exploitation by organized groups.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the volume and nature of the malicious skills identified, suggesting deliberate exploitation. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of systemic security improvements or identification of specific threat actors.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: OpenClaw’s user base is sufficiently large to attract malicious actors; the platform’s current security measures are inadequate; users are not fully aware of the risks associated with skill installations.
- Information Gaps: Details on the identity and motives of the actors behind the malware; comprehensive data on user impact and financial losses.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from security firms with vested interests; possible underreporting of incidents by affected users or the platform itself.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of AI platforms and marketplaces, influencing regulatory and security standards. The situation may evolve into a broader cybersecurity concern if not addressed promptly.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for regulatory action or international cooperation on cybersecurity standards for AI platforms.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber threats targeting critical infrastructure if similar vulnerabilities are exploited elsewhere.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential backlash against AI technologies, affecting public trust and adoption rates.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial losses for users and reputational damage to OpenClaw, impacting market dynamics and user engagement.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of the ClawHub marketplace, implement stricter vetting processes for skill submissions, and increase user awareness of security risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing threat analysis, and invest in platform security enhancements.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of threats and improved platform security, leading to restored user trust.
- Worst: Escalation of malware incidents causing significant financial and data losses, prompting regulatory intervention.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security measures with intermittent incidents as new vulnerabilities are discovered and exploited.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Peter Steinberger (OpenClaw creator)
- Jason Meller (1Password product VP)
- OpenSourceMalware (Malware tracking platform)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, malware distribution, open-source security, user data protection, regulatory implications, platform security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us