BridgePay reveals ransomware attack as cause of significant service disruption across payment systems
Published on: 2026-02-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Payments platform BridgePay confirms ransomware attack behind outage
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
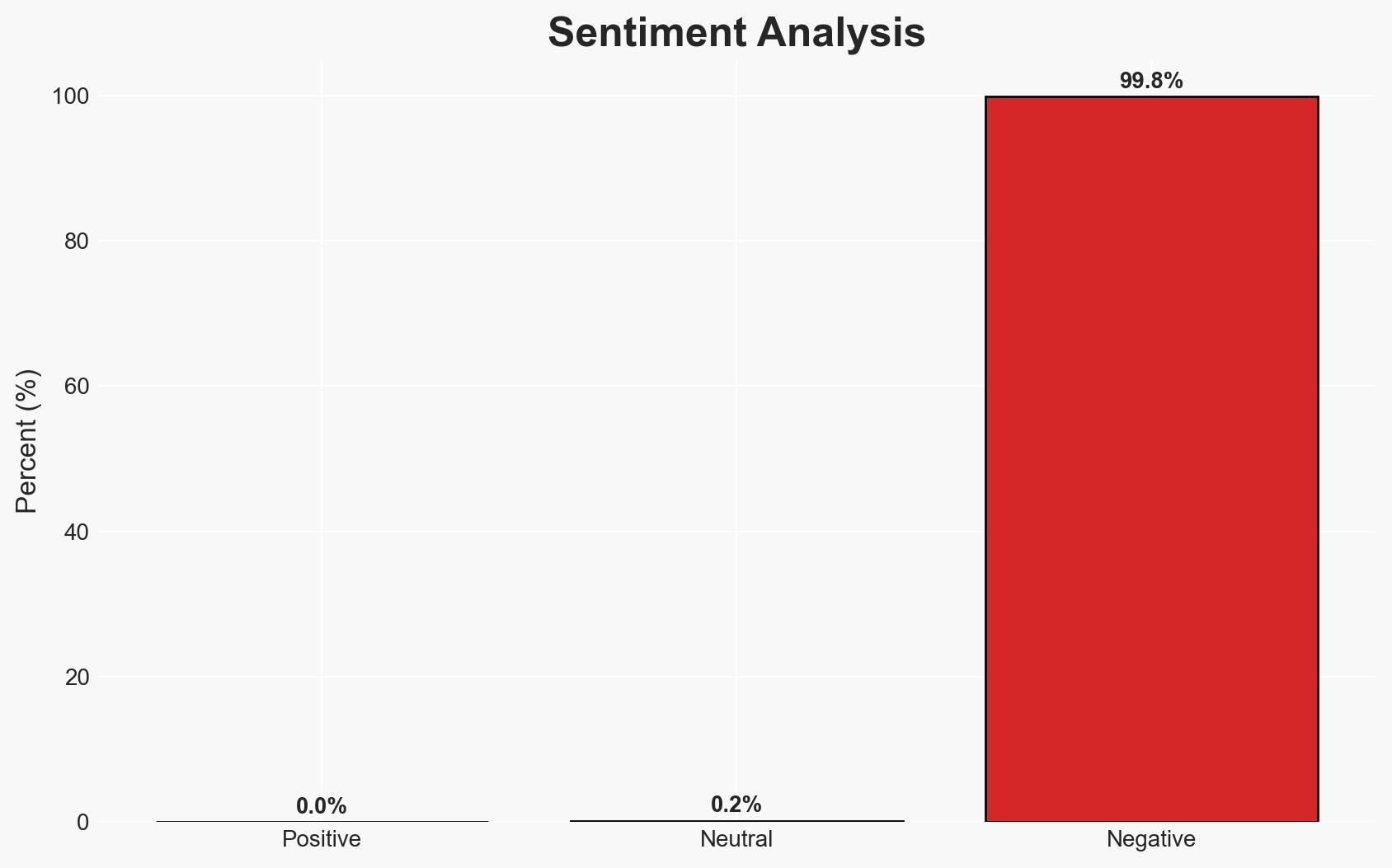
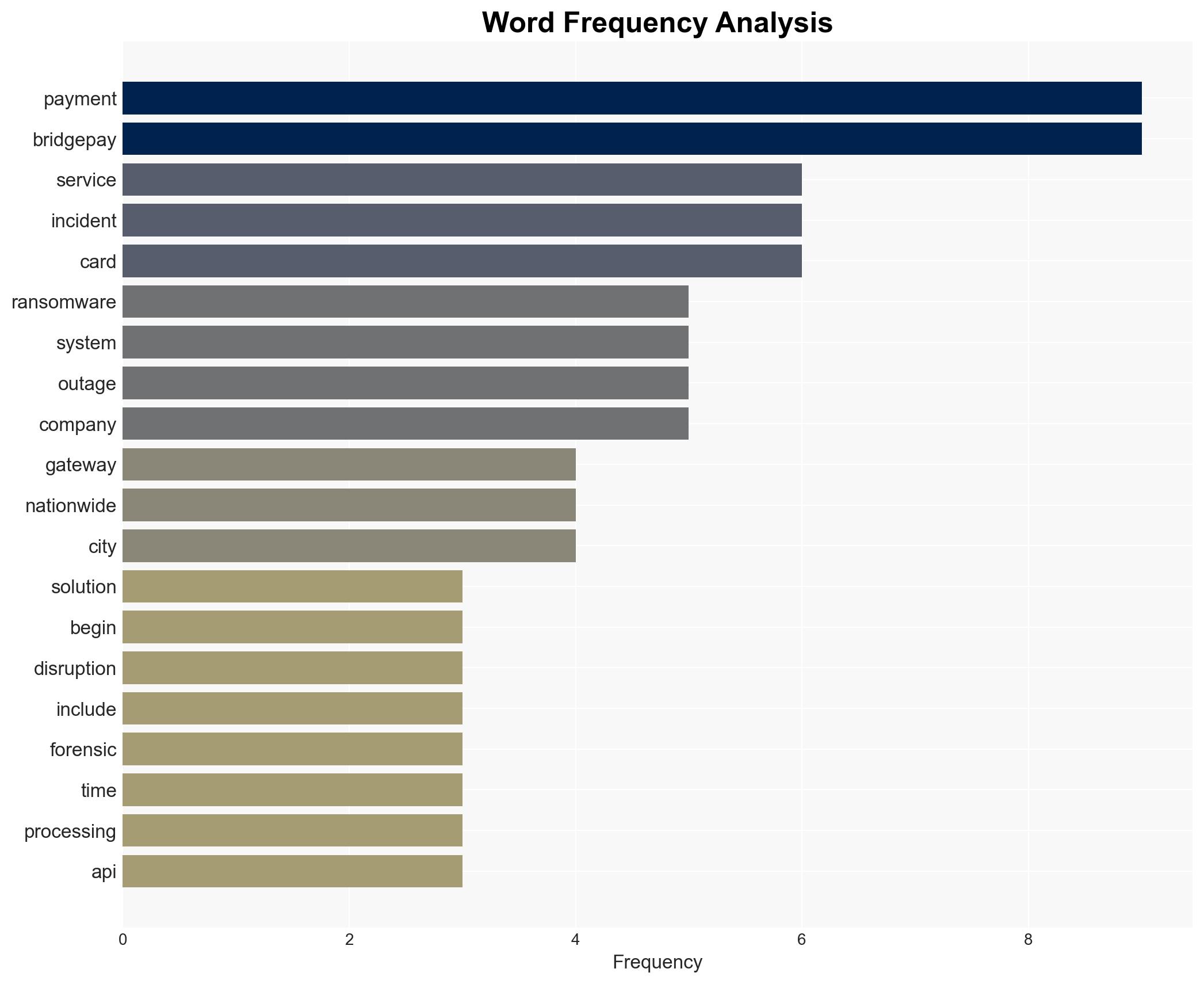
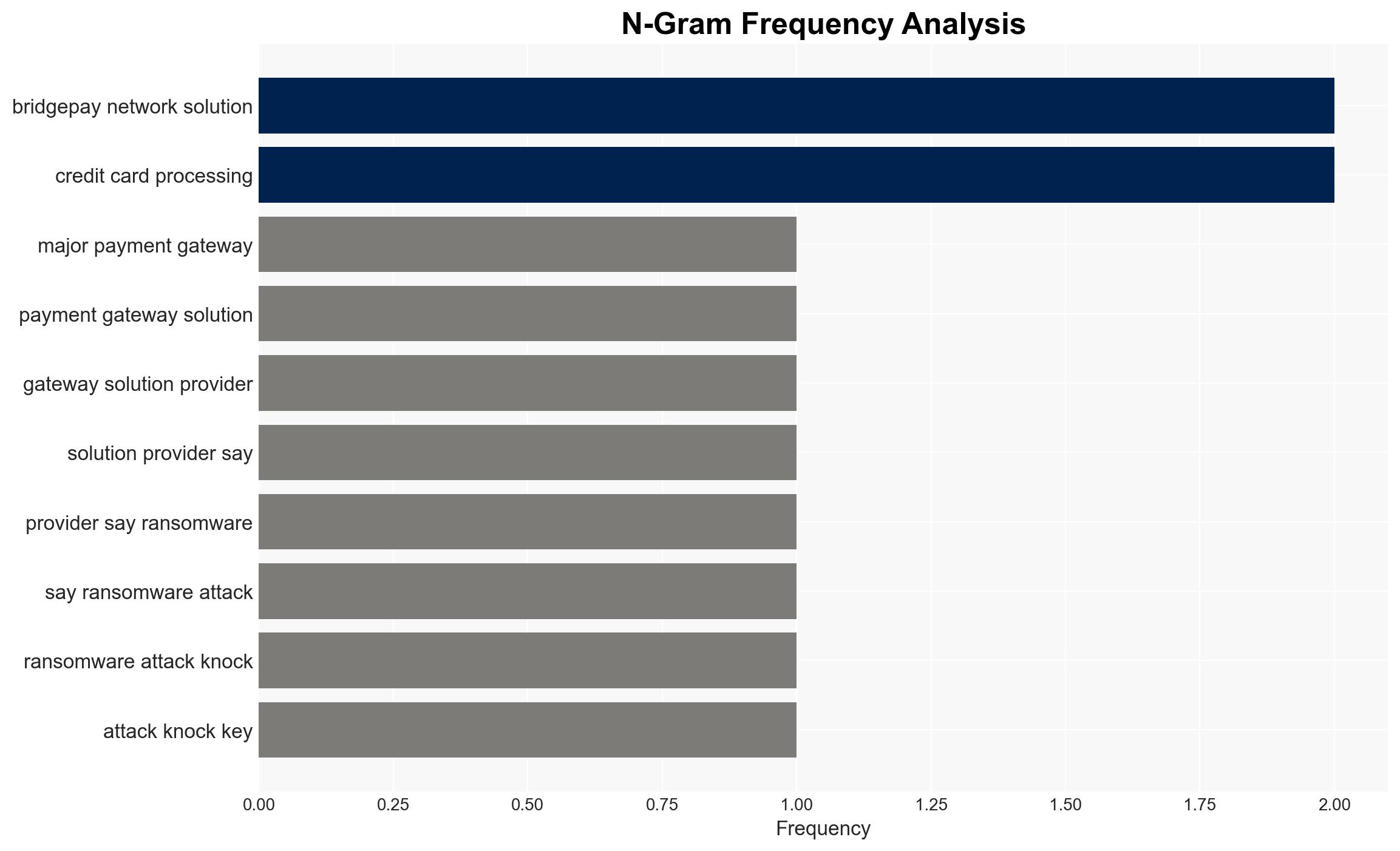
The ransomware attack on BridgePay has caused a nationwide disruption of payment processing services, affecting numerous merchants and organizations. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in critical financial infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that the attack was financially motivated, targeting BridgePay’s systems to extract a ransom. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the current lack of specific details about the attackers.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The ransomware attack was financially motivated, aiming to extort payment from BridgePay by disabling its services. This is supported by the widespread disruption and the typical modus operandi of ransomware groups. However, the specific group involved has not been identified, leaving some uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The attack could be part of a broader campaign to disrupt U.S. financial infrastructure, possibly with geopolitical motivations. This is less supported due to the lack of evidence linking the attack to state-sponsored actors or broader geopolitical tensions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the nature of the attack and its alignment with common ransomware tactics. Identification of the ransomware group or further forensic evidence could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attack was conducted by a financially motivated group; BridgePay’s public statements are accurate; the disruption is limited to BridgePay’s systems.
- Information Gaps: Identity of the ransomware group; specific vulnerabilities exploited; full scope of data accessed or encrypted.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in BridgePay’s public communications to downplay the incident; lack of independent verification of forensic findings.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The incident could lead to increased scrutiny of payment processing security and potential regulatory responses. If similar attacks occur, confidence in digital payment systems may erode, impacting consumer behavior and economic stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory oversight and international cooperation on cybersecurity.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar attacks on critical infrastructure, though no direct terrorism link is evident.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on cybersecurity measures and potential for misinformation about the attack’s impact.
- Economic / Social: Short-term economic disruptions for affected businesses; potential long-term trust issues with digital payment systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of payment systems for similar threats; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess vulnerabilities; communicate transparently with stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including backup systems and incident response plans; foster partnerships with cybersecurity firms and law enforcement.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid recovery with no further incidents, leading to strengthened cybersecurity measures.
- Worst: Repeated attacks causing significant financial and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Gradual recovery with increased cybersecurity focus and minor regulatory changes.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- BridgePay Network Solutions
- Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
- U.S. Secret Service
- Lightspeed Commerce
- ThriftTrac
- City of Palm Bay, Florida
- City of Frisco, Texas
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, financial infrastructure, digital payments, critical infrastructure, law enforcement, economic disruption
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us