Children in Middle East and North Africa face escalating violence and crises in early 2026
Published on: 2026-02-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 2026 brings no respite to children living in violence and conflict in the Middle East and North Africa
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
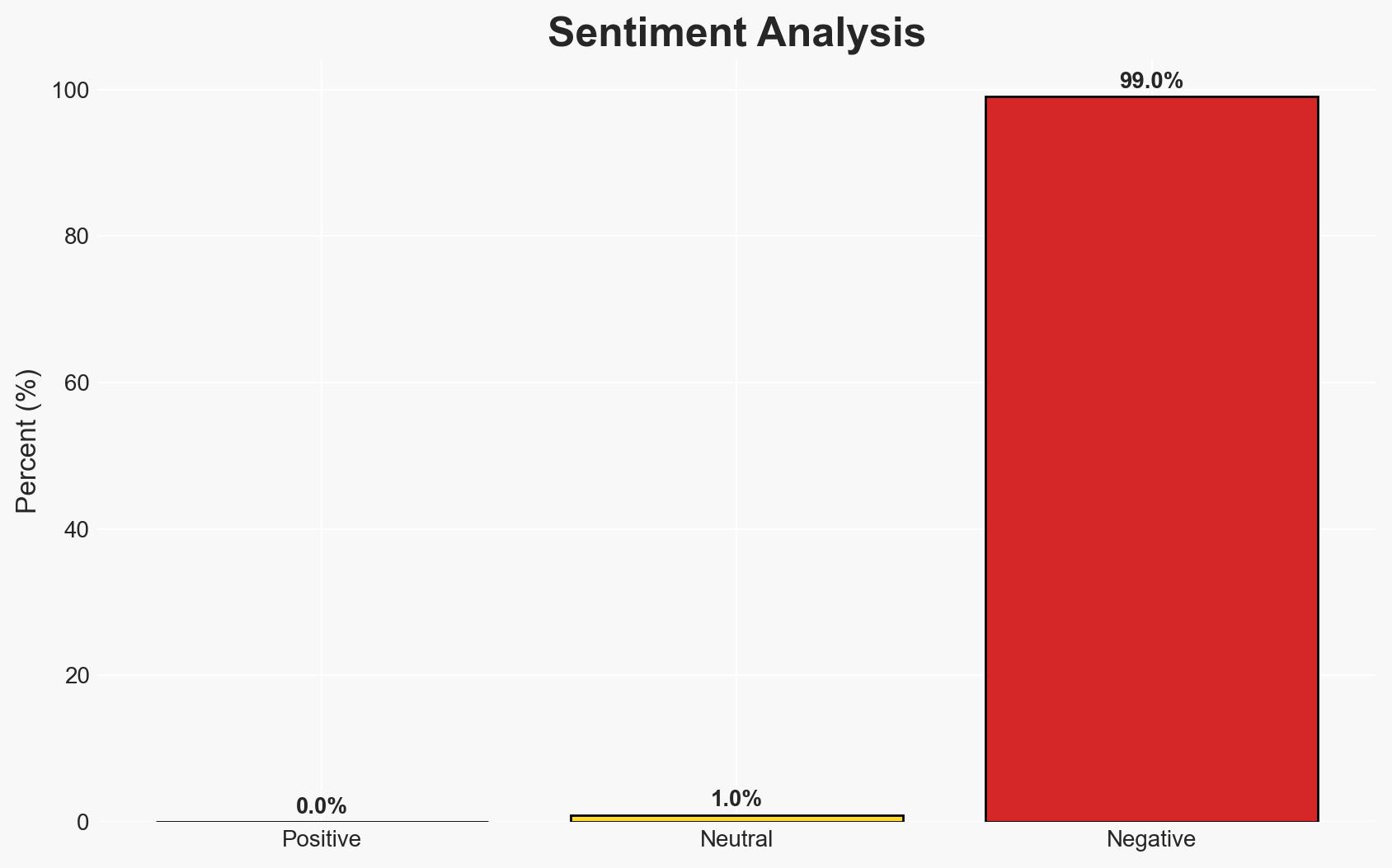
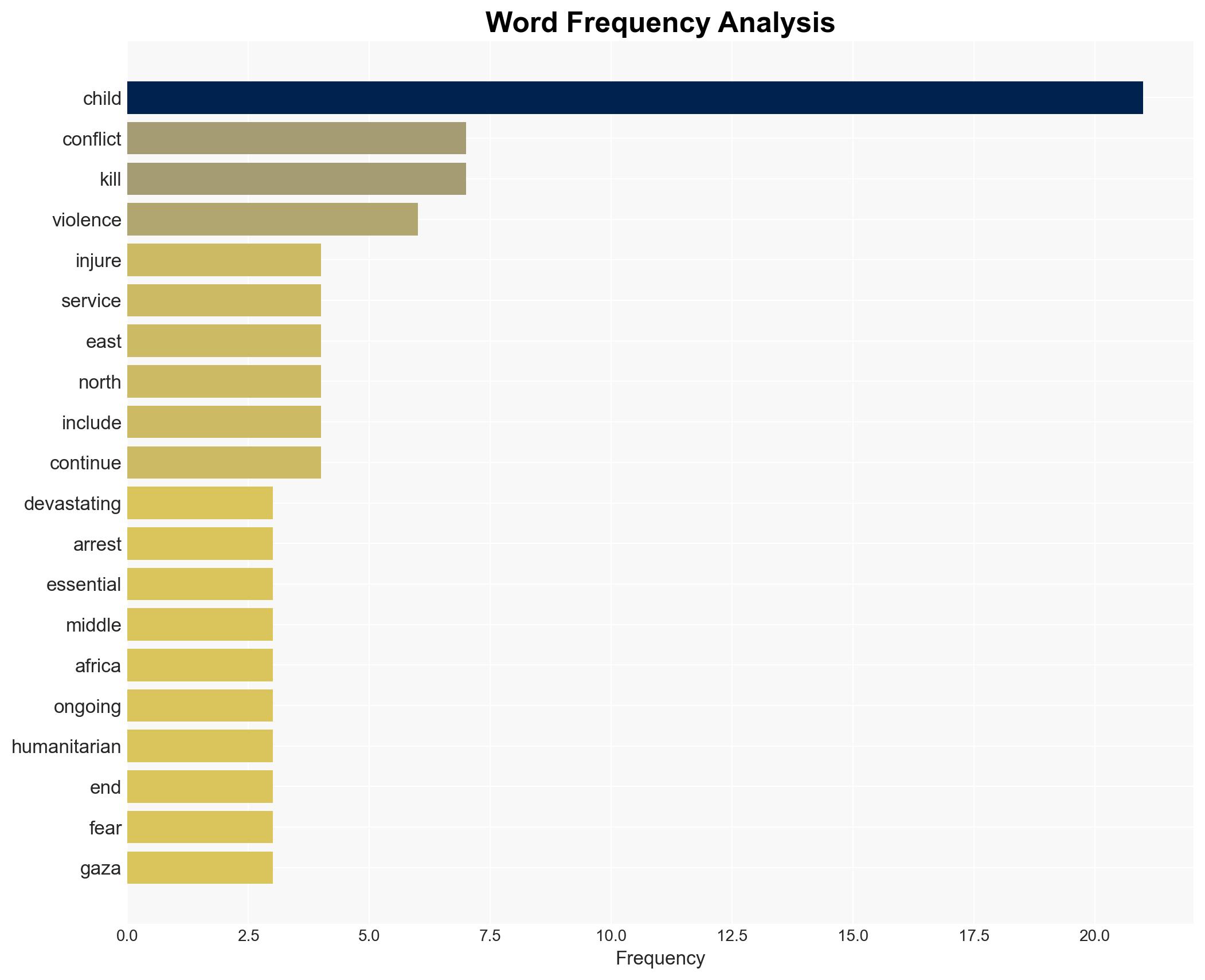
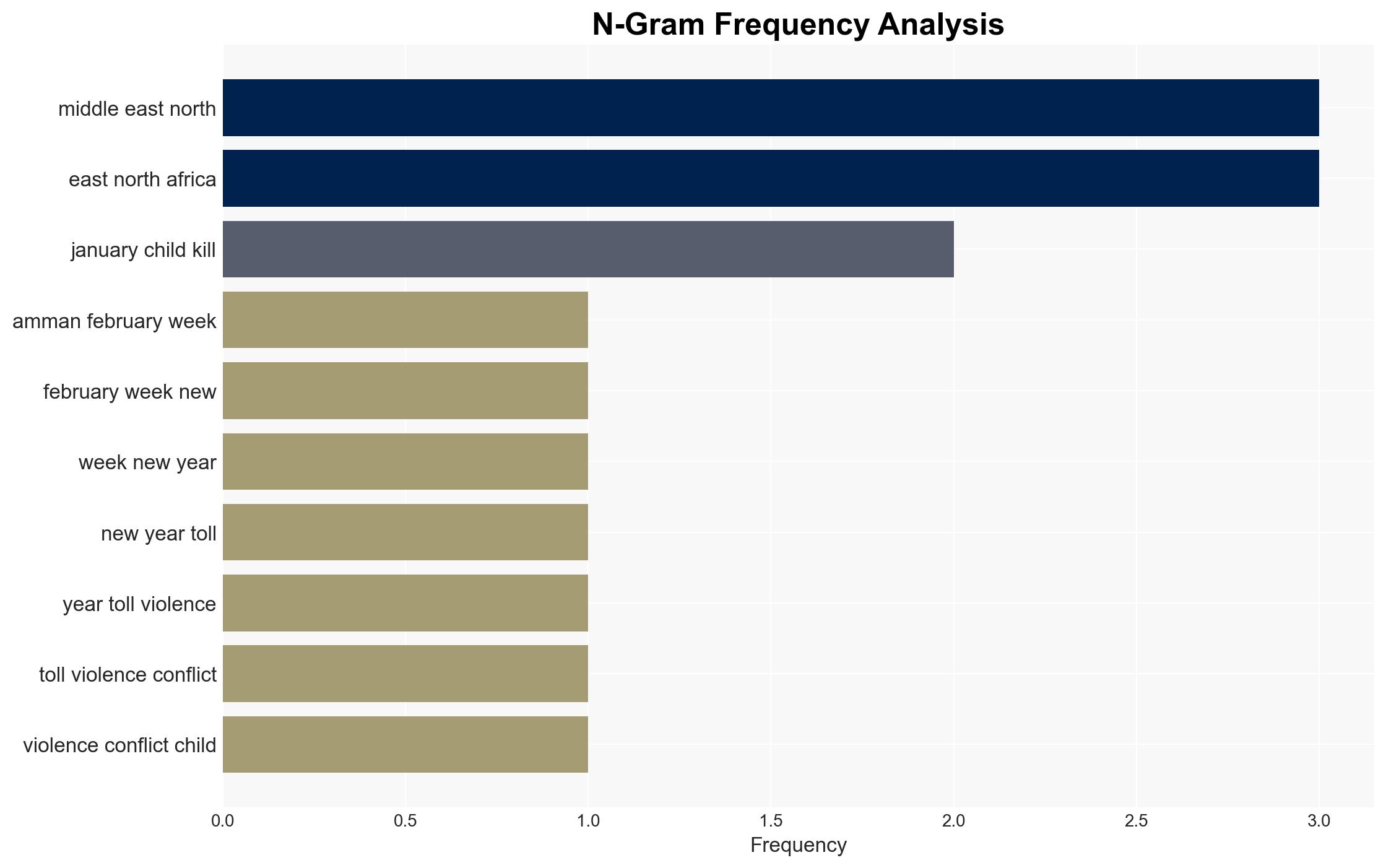
The ongoing conflicts and crises in the Middle East and North Africa continue to severely impact children, with significant casualties and disruptions to essential services. The situation is particularly dire in Syria, Sudan, Iran, and the Gaza Strip. The most likely hypothesis is that these conditions will persist or worsen without significant intervention. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited data on potential mitigating actions by regional actors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The violence and humanitarian crises affecting children in the region will persist or worsen due to entrenched conflicts and inadequate international response. This is supported by ongoing violence in Syria, Sudan, and the Gaza Strip, and the lack of effective ceasefires or peace processes. Key uncertainties include potential shifts in international diplomatic efforts or unforeseen regional developments.
- Hypothesis B: There will be a significant improvement in the situation for children due to increased international intervention and successful peace negotiations. This is contradicted by the current lack of substantial international engagement and the continuation of hostilities in key areas.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported given the ongoing violence and lack of effective international intervention. Indicators such as new peace agreements or increased humanitarian aid could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Conflicts in the region will remain unresolved in the short term; international response will continue to be limited; regional actors will not significantly alter their current strategies.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of current humanitarian efforts and the internal political dynamics of key countries like Iran and Sudan.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from conflict zones; manipulation of casualty figures by involved parties to influence international opinion.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continuation of violence and humanitarian crises could exacerbate regional instability, increase refugee flows, and strain international aid resources. These conditions may also foster environments conducive to radicalization and terrorism.
- Political / Geopolitical: Prolonged conflicts could lead to increased regional tensions and involvement of external powers.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Deteriorating conditions may provide fertile ground for extremist recruitment and operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting humanitarian organizations or spreading disinformation.
- Economic / Social: Continued instability may lead to economic decline and further social fragmentation, impacting long-term recovery prospects.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of conflict zones, enhance coordination with international humanitarian agencies, and advocate for ceasefires.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected populations, strengthen partnerships with regional actors, and support diplomatic efforts for conflict resolution.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful peace negotiations lead to reduced violence and improved humanitarian access.
- Worst: Escalation of conflicts results in further casualties and displacement.
- Most-Likely: Continued violence with periodic humanitarian interventions offering limited relief.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, conflict, humanitarian crisis, Middle East, North Africa, child protection, international intervention, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us