McLaren Health Care Settles $14M Class Action for Data Breach Affecting 2.8M Patients; Claims Due April 29, 2…
Published on: 2026-02-07
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: McLaren Health Care 14M Data Breach Class Action Settlement Claim Up To 5000 By April 29 202628 Million Patients Affected
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
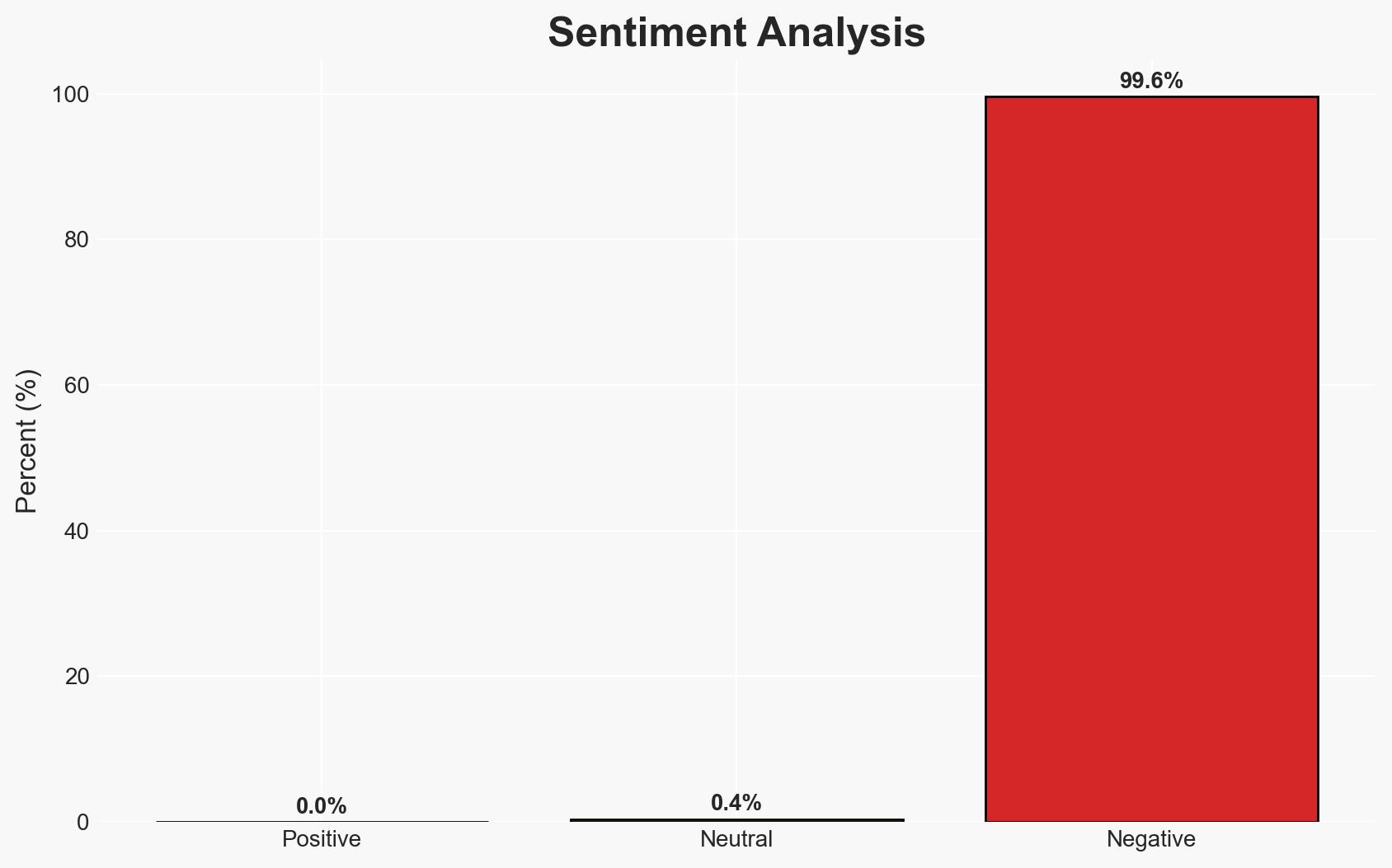
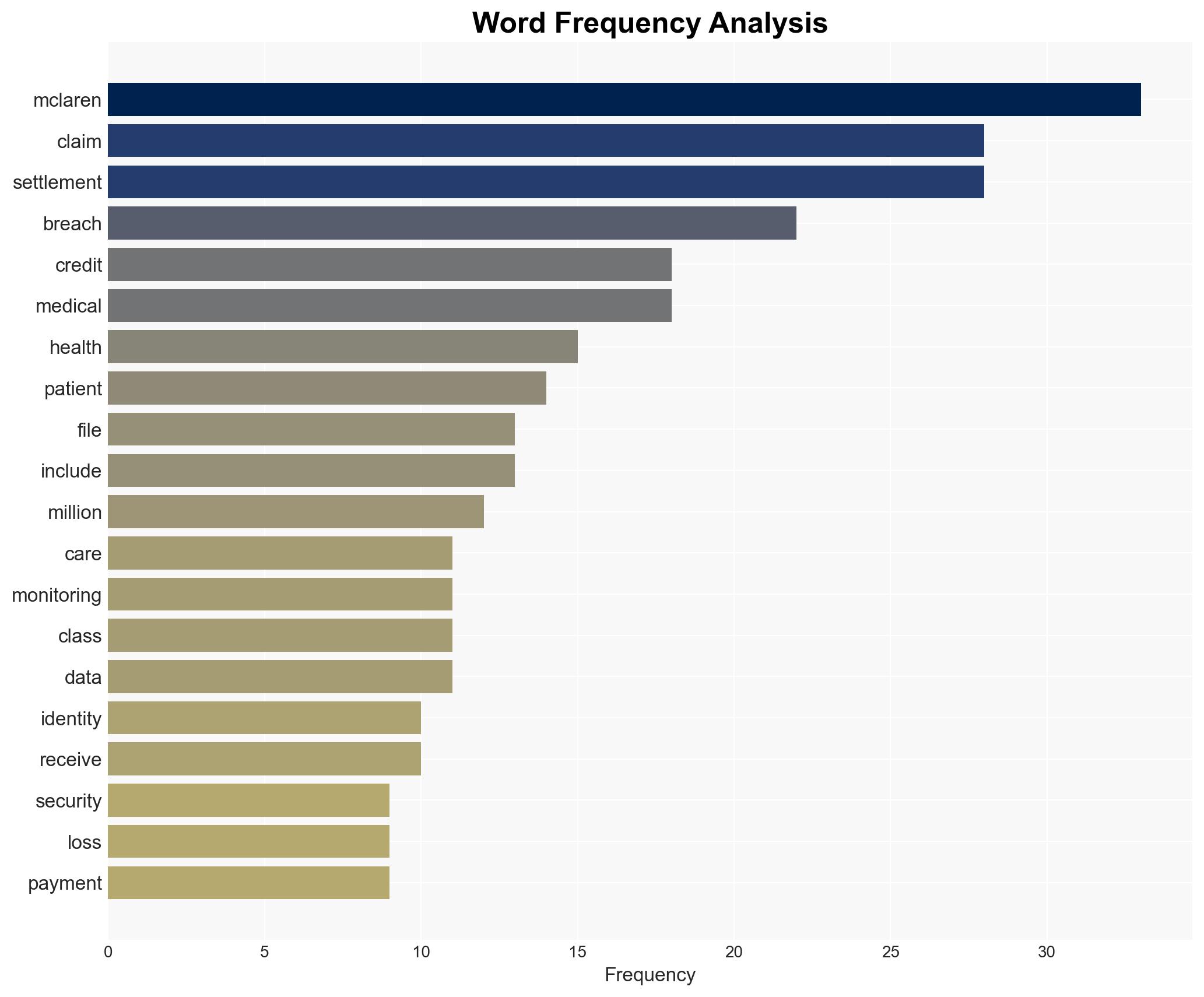
The McLaren Health Care data breach settlement highlights significant vulnerabilities in healthcare cybersecurity, affecting approximately 2.8 million patients. The most likely hypothesis is that inadequate cybersecurity measures allowed two separate ransomware attacks, leading to a $14 million settlement. This situation poses ongoing risks for identity theft and medical fraud. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breaches were primarily due to insufficient cybersecurity protocols and outdated infrastructure at McLaren Health Care. This is supported by the occurrence of two breaches within a year, indicating systemic vulnerabilities. However, specific details on security measures in place at the time are lacking.
- Hypothesis B: The breaches were the result of sophisticated and targeted cyber-attacks by external actors, possibly exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities. While the involvement of the ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group suggests a high level of sophistication, there is limited information on the specific tactics used.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the repeated nature of the breaches, suggesting internal security failings. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include revelations of advanced persistent threat (APT) involvement or new vulnerabilities exploited.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: McLaren Health Care had inadequate cybersecurity measures; the breaches involved similar tactics; the settlement amount reflects the scale of the breach and potential damages.
- Information Gaps: Specific cybersecurity measures in place at McLaren; detailed attack vectors and methods used by the attackers; potential insider involvement.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in publicly available information due to McLaren’s interest in minimizing reputational damage; possible deception by attackers in masking their methods or affiliations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased scrutiny of healthcare cybersecurity practices and potential regulatory changes. The breaches may incentivize other cybercriminals to target similar vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory oversight and legislative action on healthcare cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of further cyberattacks on healthcare infrastructure, possibly by state-sponsored actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased awareness and potential for improved cybersecurity measures within the healthcare sector.
- Economic / Social: Financial strain on McLaren Health Care and affected individuals; potential loss of trust in healthcare providers.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive cybersecurity audit of McLaren Health Care; enhance monitoring of patient data for signs of fraud.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in updated cybersecurity infrastructure and staff training.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strengthened cybersecurity measures prevent future breaches; patient trust is restored.
- Worst: Continued breaches lead to severe financial and reputational damage; regulatory penalties imposed.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity with ongoing challenges in fully securing patient data.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
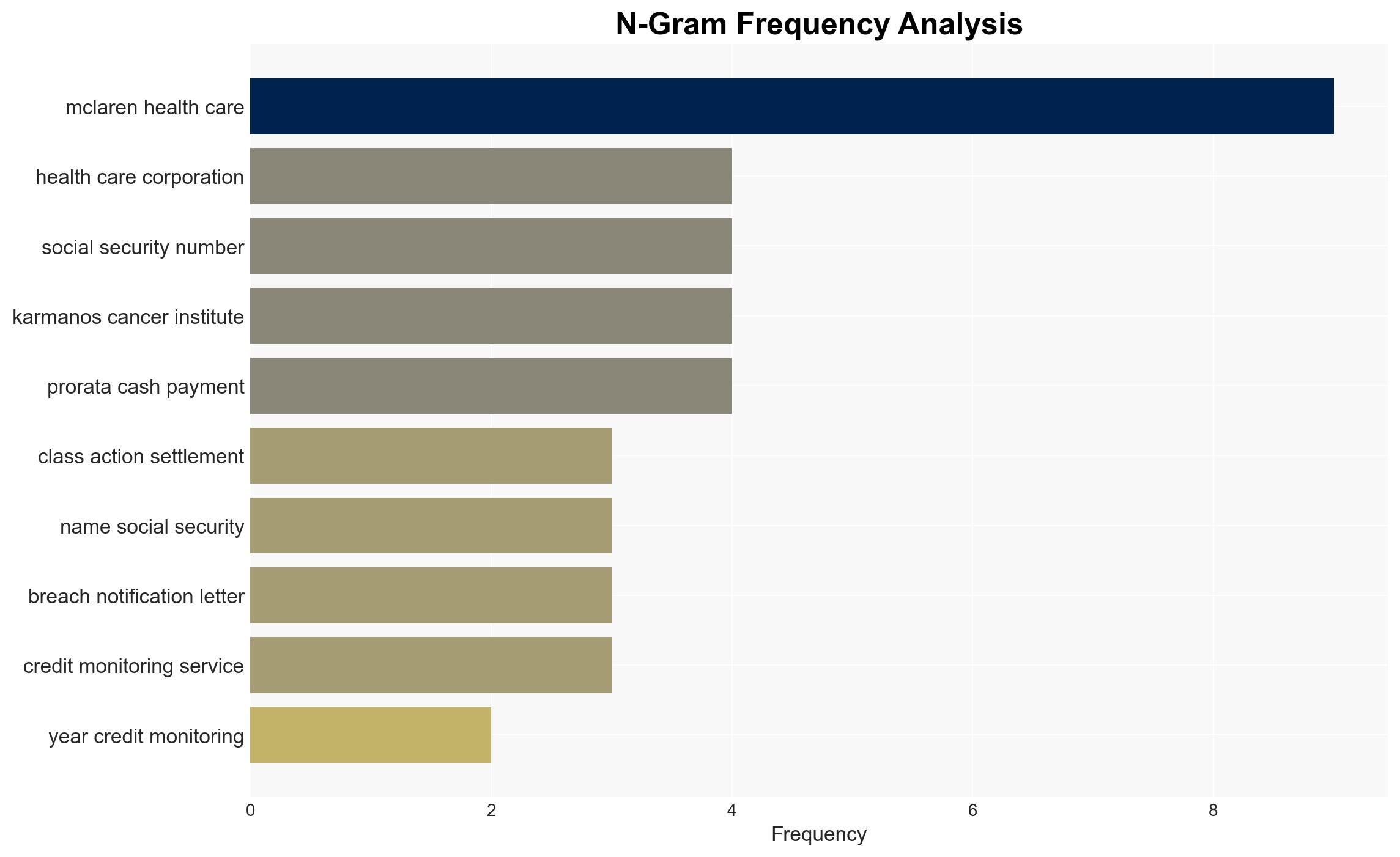
- McLaren Health Care Corporation
- ALPHV/BlackCat ransomware group
- Judge B. Chris Christenson
- Karmanos Cancer Institute
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, healthcare data breach, ransomware, identity theft, regulatory compliance, patient data protection, cybercrime
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us