Western Nations Criticized for Inadequate Support of Assyrian Christians Amid Ongoing Persecution
Published on: 2026-02-08
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
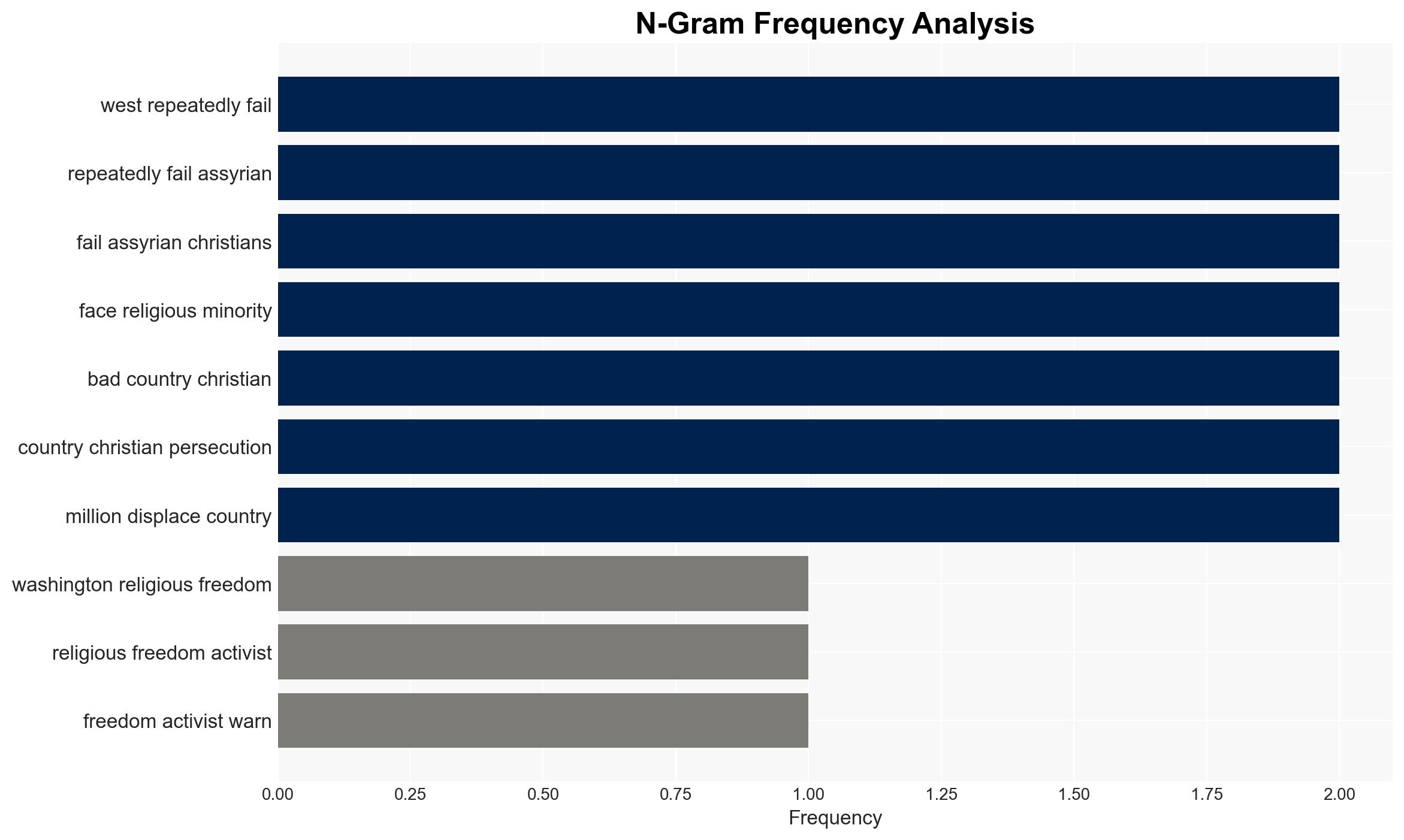
Intelligence Report: West has ‘repeatedly failed Assyrian Christians’
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
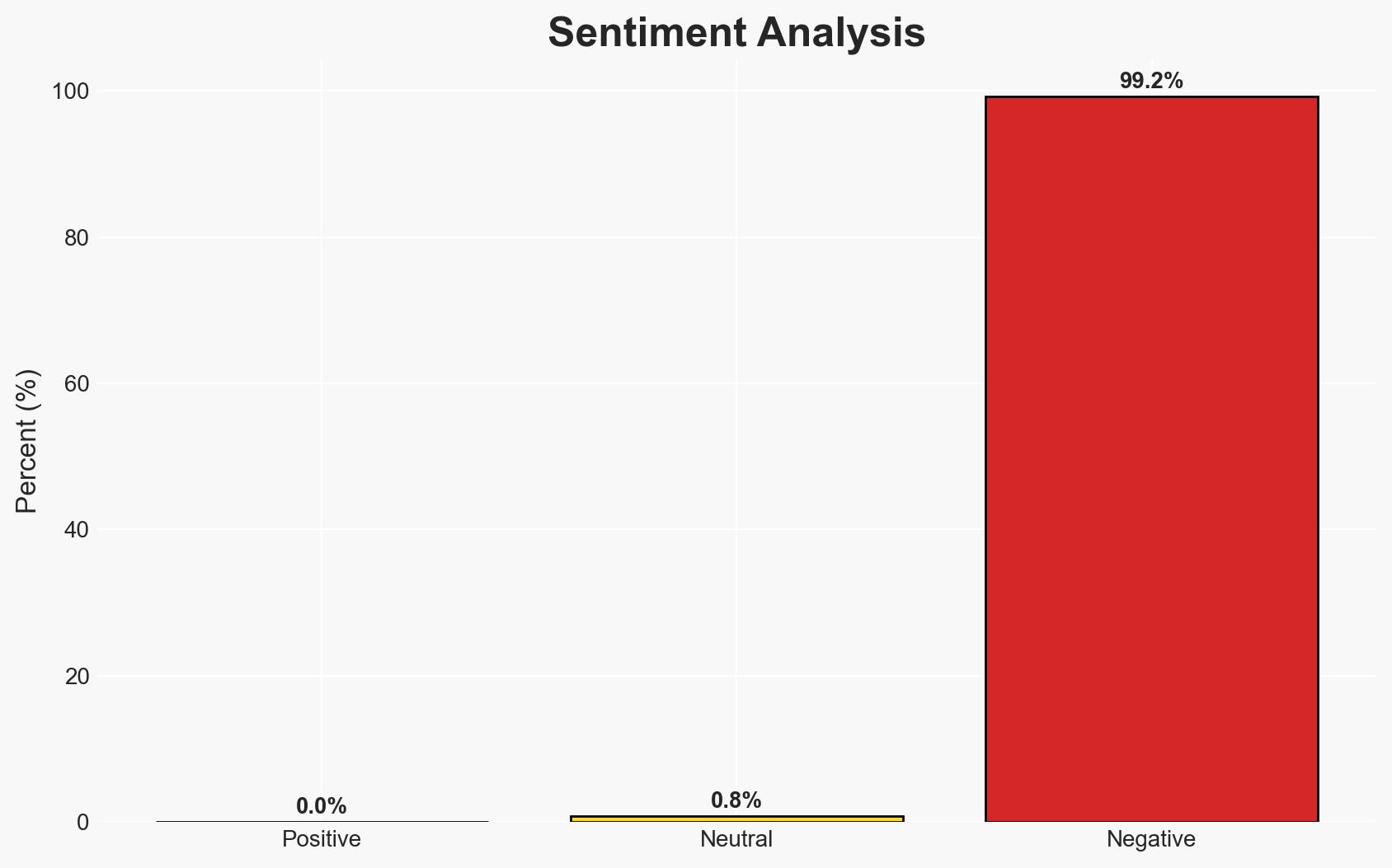
The Assyrian Christian community in the Middle East faces existential threats due to systematic persecution and lack of effective international support. The most likely hypothesis is that without significant intervention, the community will continue to decline, potentially disappearing entirely from the region. This situation affects regional stability and religious diversity, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The decline of the Assyrian Christian community is primarily due to systematic persecution by jihadist and Kurdish forces, compounded by regional instability. Evidence includes reports of violent attacks, forced conversions, and vandalism of cultural sites. Key uncertainties include the extent of international awareness and potential covert support for these actions.
- Hypothesis B: The decline is largely due to broader regional instability and economic collapse, with persecution as a secondary factor. Supporting evidence includes the general lack of security and economic opportunities affecting all minorities. Contradicting evidence includes specific targeting of Assyrian Christians.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to specific evidence of targeted persecution and cultural destruction. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in regional security dynamics or increased international intervention.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The West has the capacity and willingness to intervene effectively; regional powers are complicit or passive in persecution; international organizations can influence local dynamics.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the scale of persecution and the effectiveness of current international support efforts.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting due to advocacy positions; risk of underreporting by local governments or media manipulation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued decline of Assyrian Christians could exacerbate regional instability and diminish religious diversity, potentially fueling further sectarian conflict.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between Western nations and regional powers; potential for international diplomatic fallout.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential for increased radicalization and recruitment by extremist groups exploiting the situation.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible use of digital platforms to spread propaganda or misinformation regarding the plight of Assyrian Christians.
- Economic / Social: Further economic decline and social fragmentation in affected regions, reducing prospects for recovery and stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of the situation through intelligence and diplomatic channels; engage with regional partners to assess intervention options.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected communities; strengthen partnerships with NGOs and international bodies to provide humanitarian aid.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: International intervention stabilizes the situation, preserving the Assyrian community.
- Worst: Continued decline leads to the near-total disappearance of Assyrian Christians from the region.
- Most-Likely: Gradual decline continues with sporadic international attention and limited impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
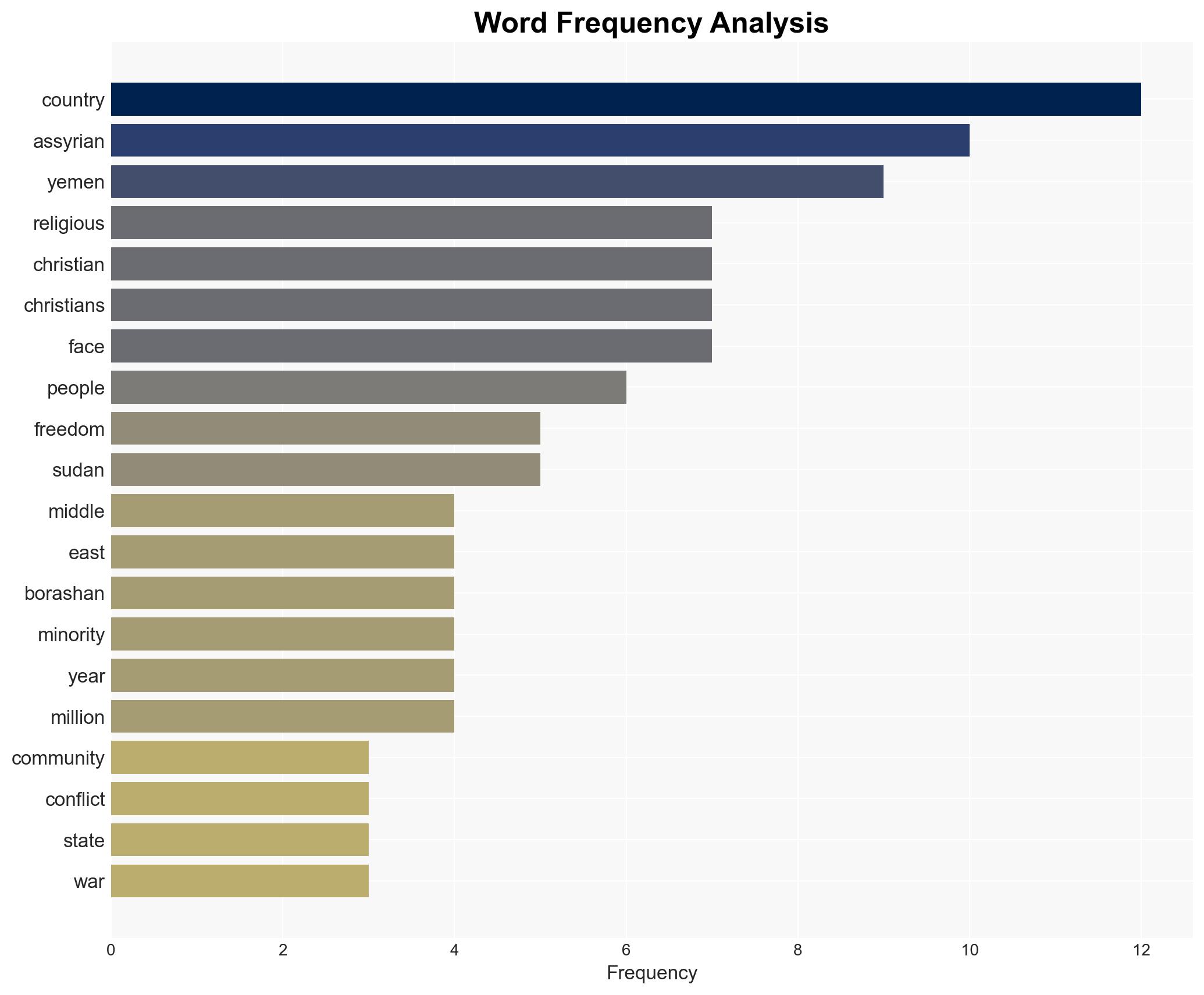
- Karmella Borashan, Assyrian International Council
- Sudan Kamal Fahmi, Set My People Free
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
regional conflicts, religious persecution, Middle East stability, minority rights, international intervention, cultural heritage, sectarian conflict, humanitarian crisis
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us