US Forces Intercept Venezuela-Linked Oil Tanker in Indian Ocean Amid Expanded Sanctions Enforcement
Published on: 2026-02-09
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: US Boards Sanctioned Venezuela-Linked Oil Tanker in Indian Ocean
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
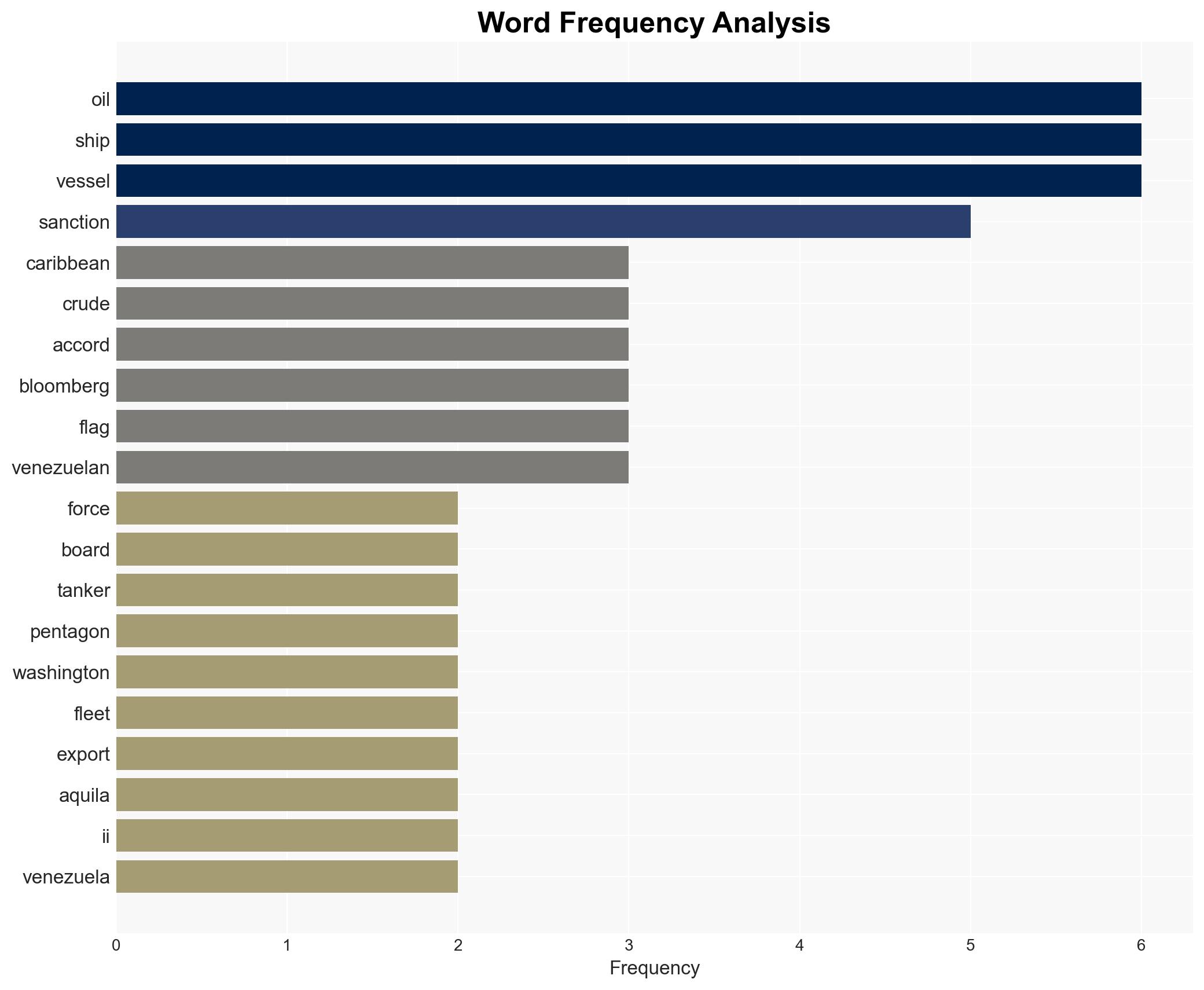
The US has expanded its enforcement of sanctions against Venezuela-linked oil shipments by intercepting the Aquila II in the Indian Ocean. This action underscores Washington’s commitment to a global crackdown on sanctioned crude exports. The operation affects geopolitical relations and global oil markets, with moderate confidence in the assessment that the US will continue aggressive enforcement actions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The US is expanding its geographic scope of enforcement to deter future violations of sanctions by Venezuela-linked vessels. This is supported by the interception of the Aquila II far from the Caribbean and the Pentagon’s statements about a global crackdown. However, the lack of detailed operational data introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The interception of the Aquila II is an isolated incident driven by specific intelligence rather than a broader strategic shift. This is contradicted by the Pentagon’s public statements and recent similar actions, but the absence of a clear pattern of global interceptions could support this view.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to consistent US policy statements and actions indicating a strategic expansion of enforcement. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include a decrease in similar interceptions or changes in US policy rhetoric.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The US has sufficient intelligence and resources to sustain global enforcement; Venezuela-linked vessels will continue to attempt sanctions evasion; geopolitical tensions will not significantly alter US enforcement capabilities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed operational data on the interception and the decision-making process; comprehensive tracking of other Venezuela-linked vessels globally.
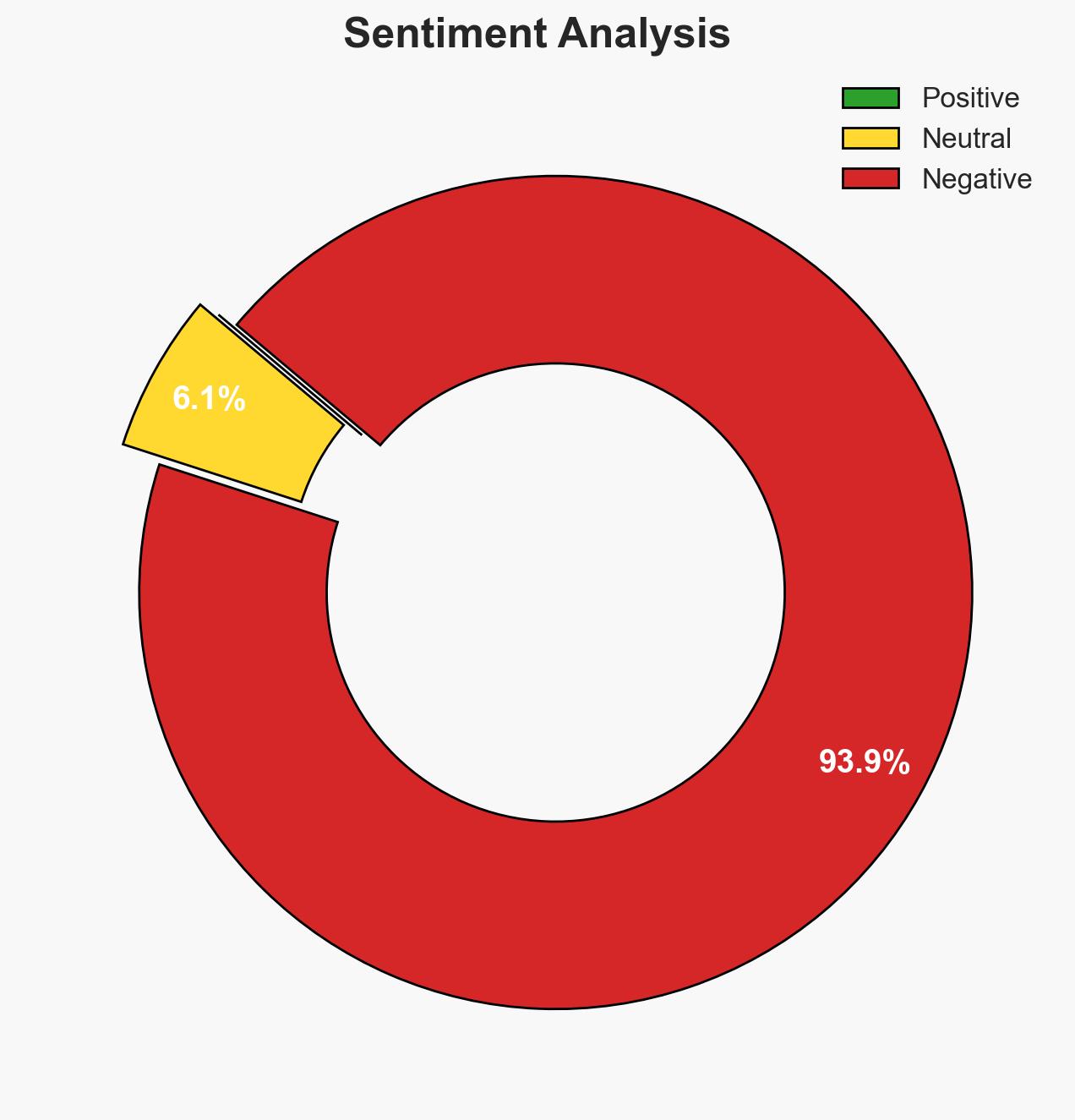
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in US public statements to project strength; risk of deception by vessels using false flags and misleading signals.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and impact global oil markets. The US’s aggressive enforcement may provoke responses from affected nations and entities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on US-China relations if Chinese interests are affected; increased diplomatic friction with Venezuela and its allies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of retaliatory actions against US interests; potential for increased maritime security incidents.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting US maritime enforcement capabilities; disinformation campaigns by affected states.
- Economic / Social: Disruption in oil supply chains; potential economic impact on countries reliant on Venezuelan crude.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance maritime surveillance and intelligence sharing; engage diplomatically with key stakeholders to mitigate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen partnerships with allied nations for coordinated enforcement; develop resilience measures for potential retaliatory actions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful deterrence of sanctions evasion with minimal geopolitical fallout.
- Worst: Escalation of geopolitical tensions leading to broader conflict or economic instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued enforcement actions with periodic diplomatic and economic challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth
- Linnet Marguerite Ltd
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, sanctions, maritime security, geopolitical tensions, oil trade, US-Venezuela relations, global enforcement, energy security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us