Ransomware Attack on SmarterTools Exploits Unpatched Vulnerability in SmarterMail System
Published on: 2026-02-09
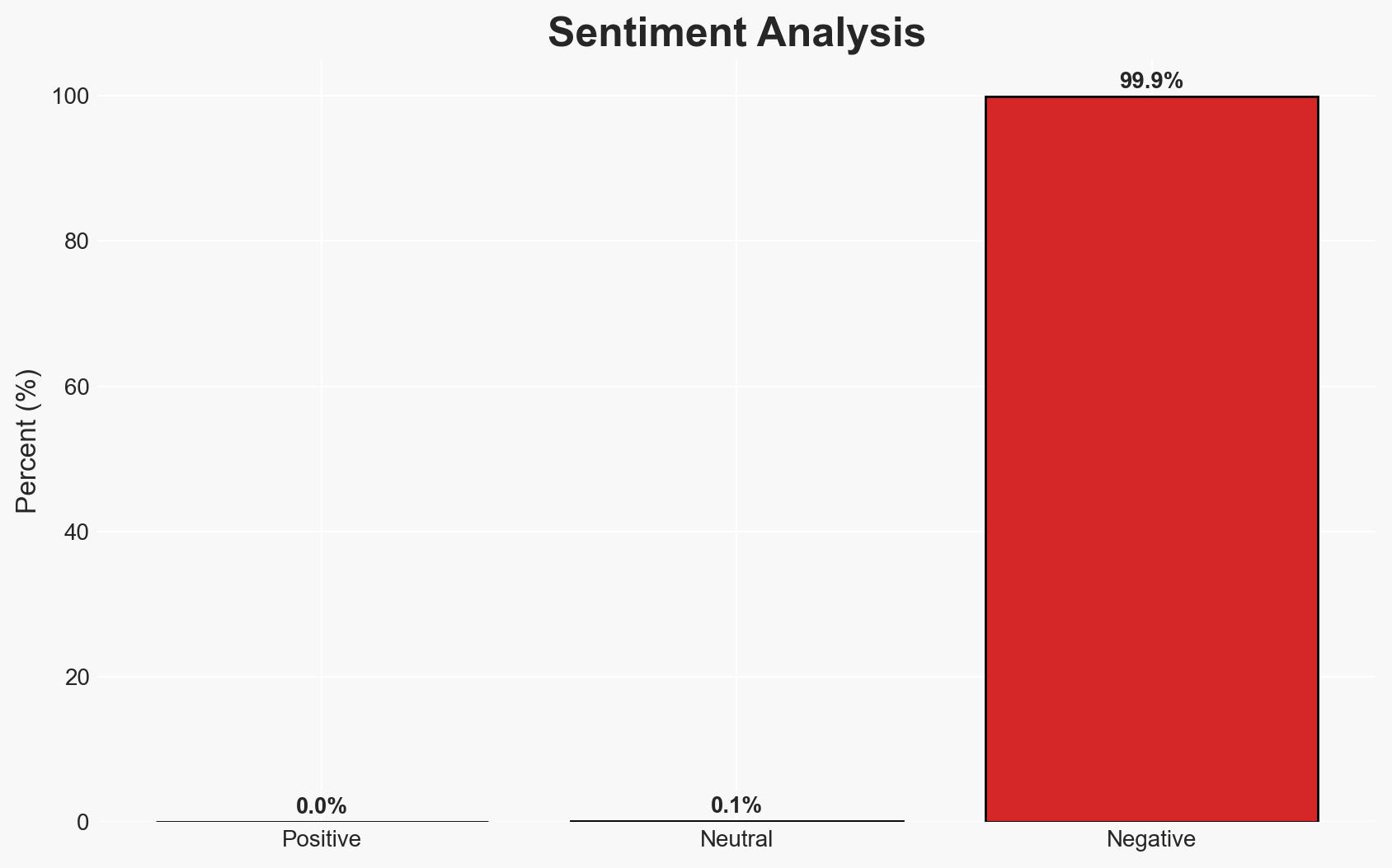
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Ransomware group breached SmarterTools via flaw in its SmarterMail deployment
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The Warlock group exploited a vulnerability in SmarterMail, leading to a breach of SmarterTools’ network. The attack primarily affected Windows servers, prompting SmarterTools to eliminate Windows and Active Directory services. The most likely hypothesis is that the group exploited CVE-2026-24423, given its recent inclusion in CISA’s catalog. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited details on the specific vulnerability exploited.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Warlock group exploited CVE-2026-24423 to breach SmarterTools. This is supported by the timing of the vulnerability’s inclusion in CISA’s catalog and its known exploitation in ransomware attacks. However, the specific vulnerability exploited was not confirmed by SmarterTools.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was due to another unknown or unreported vulnerability in SmarterMail. This hypothesis is less supported as no other vulnerabilities were reported as exploited in ransomware attacks recently.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of CVE-2026-24423 with known exploitation patterns. Confirmation of the specific vulnerability exploited would shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Warlock group consistently uses known vulnerabilities; SmarterTools’ network was adequately secured except for the unpatched VM; CVE-2026-24423 is the most likely vulnerability exploited.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the vulnerability exploited; full extent of data compromised; potential other vulnerabilities in SmarterMail.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the attack to a known group without full evidence; risk of underestimating the group’s capabilities or other vulnerabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This breach highlights vulnerabilities in enterprise software and the persistent threat of ransomware groups. The incident could lead to increased scrutiny of software security practices and influence organizational IT strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory pressure on software security standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened awareness and preparedness against ransomware threats, especially from groups like Warlock.
- Cyber / Information Space: Likely increase in cyber defense measures and patch management practices across affected sectors.
- Economic / Social: Possible financial impact on SmarterTools and affected clients; broader implications for trust in IT service providers.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a thorough forensic analysis of the breach; ensure all systems are patched; enhance monitoring for similar TTPs.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in cybersecurity training and infrastructure resilience.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: No further breaches occur, and SmarterTools strengthens its security posture.
- Worst: Additional vulnerabilities are exploited, leading to further breaches and data loss.
- Most-Likely: SmarterTools and similar companies enhance security measures, reducing the likelihood of successful future attacks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Derek Curtis, Chief Operating Officer, SmarterTools
- Warlock group (aka Gold Salem, aka Storm-2603)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, cyber-security, vulnerability management, threat intelligence, IT infrastructure, software security, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us