South Korea Attributes Coupang Data Breach to Management Oversight, Not Cyberattack Sophistication
Published on: 2026-02-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: S Korea Blames Coupang Data Breach on Management Failure Not Sophisticated Attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
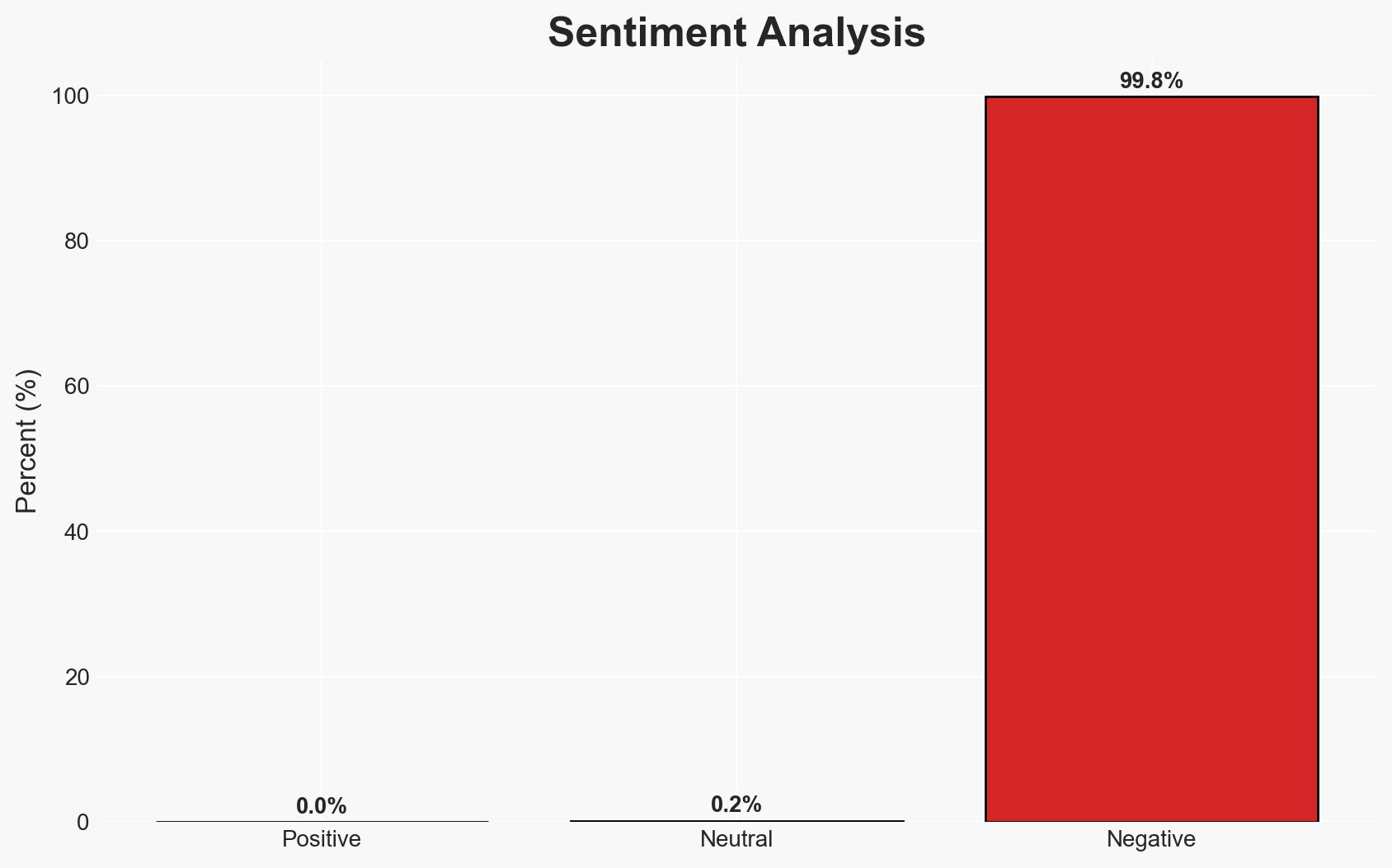
The South Korean government attributes the Coupang data breach to management failures rather than a sophisticated cyberattack, implicating a former employee in exploiting authentication vulnerabilities. This incident has significant implications for Coupang’s operational security and its regulatory relationship with South Korean authorities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, pending further investigation results.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The breach was primarily due to internal management failures, with a former employee exploiting known vulnerabilities. Evidence includes the government’s findings on lax oversight and the employee’s prior knowledge of the system. However, uncertainties remain regarding the potential involvement of additional actors.
- Hypothesis B: The breach was a more sophisticated attack possibly involving external actors, with the former employee acting as a scapegoat. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of evidence of external involvement and the government’s focus on internal failures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the government’s detailed findings on management failures and the employee’s role. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of external actor involvement or additional breaches.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Coupang’s internal security protocols were inadequate; the former employee acted alone; the breach did not involve financial data.
- Information Gaps: Details on whether other employees or external actors were involved; full scope of data accessed or compromised.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in government reporting to downplay external threats; Coupang’s statements may understate the breach’s impact to mitigate reputational damage.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny of foreign companies in South Korea and impact Coupang’s market position and investor confidence. The breach highlights vulnerabilities in corporate cybersecurity practices, potentially prompting broader industry reforms.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strained US-South Korea trade relations due to perceived regulatory overreach.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential for increased cyber threats if vulnerabilities are not addressed.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened awareness and potential regulatory changes in cybersecurity standards.
- Economic / Social: Possible consumer trust erosion in Coupang, affecting its market share and economic performance.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive security audit of Coupang’s systems; enhance monitoring of regulatory developments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms; implement robust employee exit protocols and continuous security training.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Enhanced security and restored trust; Worst: Further breaches and regulatory penalties; Most-Likely: Incremental security improvements with ongoing regulatory challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Choi Woo-hyuk, Deputy Minister for Cyber Security and Network Policy
- South Korean Science Ministry
- Coupang Inc.
- Former Coupang engineer (name not provided)
7. Thematic Tags
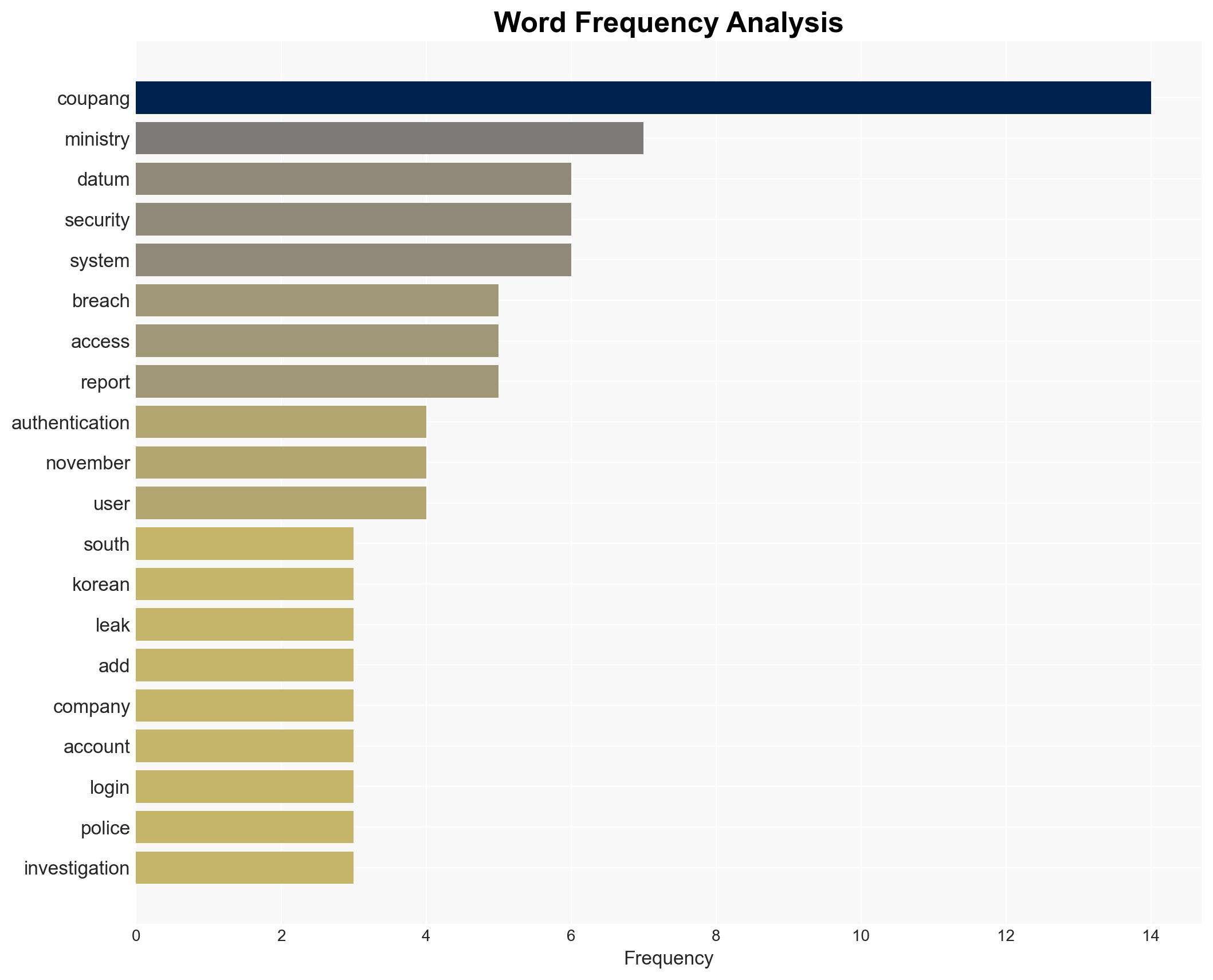
cybersecurity, data breach, regulatory compliance, US-South Korea relations, corporate governance, information security, e-commerce
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us