Evolving Authentication Strategies for 2026: Emphasizing Phishing-Resistant Solutions Amid Rising Threats
Published on: 2026-02-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Authentication in 2026 – moving beyond foundational MFA to tackle the new era of attacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
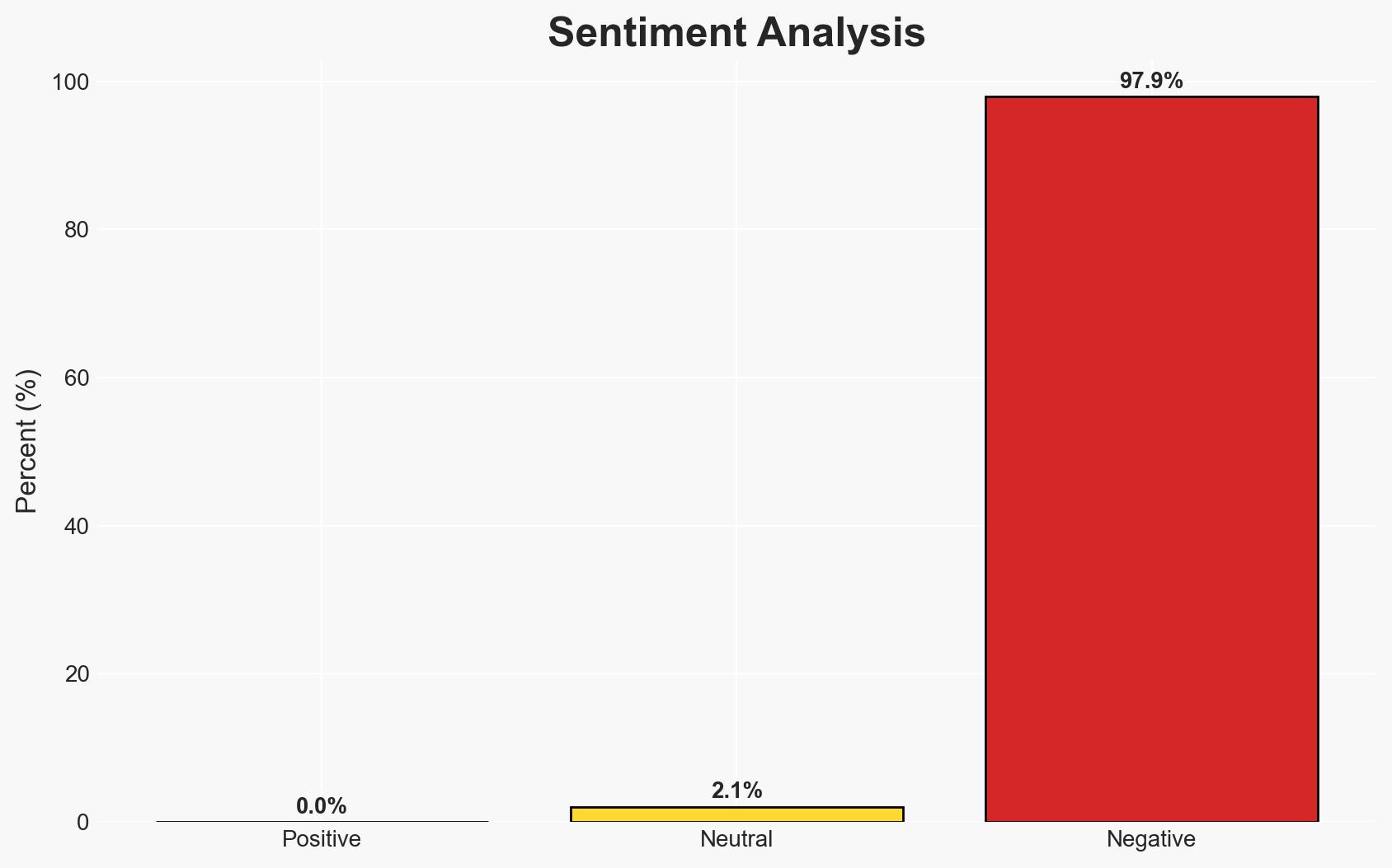
The shift towards phishing-resistant authentication methods in 2026 is driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, particularly social engineering attacks that bypass traditional MFA. Organizations are increasingly adopting advanced authentication technologies to mitigate these risks. This development affects enterprise security strategies globally, with moderate confidence in the assessment due to evolving threat landscapes and technological adoption rates.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Organizations are moving towards phishing-resistant authentication due to a genuine increase in sophisticated cyber threats, particularly social engineering. This is supported by the reported growth in phishing-resistant methods and the doubling of AI tool security assessments. However, the extent of threat sophistication and actual adoption rates remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The shift towards advanced authentication methods is primarily driven by market trends and vendor influence rather than a significant increase in threat sophistication. While the adoption of new technologies is evident, the actual threat level may not have increased proportionally, suggesting possible overestimation of risks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in phishing-resistant authentication adoption and the reported rise in social engineering attacks. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new data on threat actor capabilities or changes in organizational security incidents.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations have the resources to implement new authentication technologies; threat actors will continue to develop more sophisticated social engineering tactics; current data accurately reflects industry trends.
- Information Gaps: Detailed statistics on the success rate of new authentication methods in preventing breaches; comprehensive data on the financial impact of adopting these technologies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data from security vendors promoting their solutions; risk of over-reliance on industry reports without independent verification.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The adoption of phishing-resistant authentication methods could lead to a more secure digital environment, but also drive threat actors to innovate further. This evolution will interact with broader dynamics in cybersecurity and enterprise risk management.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased focus on cyber defense could influence international cybersecurity policies and collaborations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced authentication methods may reduce the effectiveness of cyber-terrorism tactics, necessitating new countermeasures.
- Cyber / Information Space: The shift may lead to a temporary decrease in successful phishing attacks, but could also trigger new attack vectors targeting authentication systems.
- Economic / Social: Organizations may face increased costs for implementing new technologies, impacting economic stability and potentially leading to disparities in security capabilities across sectors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor adoption rates of phishing-resistant methods; engage with cybersecurity experts to assess organizational readiness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technology providers; invest in employee training to recognize and counter social engineering tactics.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of new methods reduces breach incidents significantly.
- Worst: Threat actors quickly adapt, rendering new methods less effective.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security posture with ongoing adaptation by both defenders and attackers.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
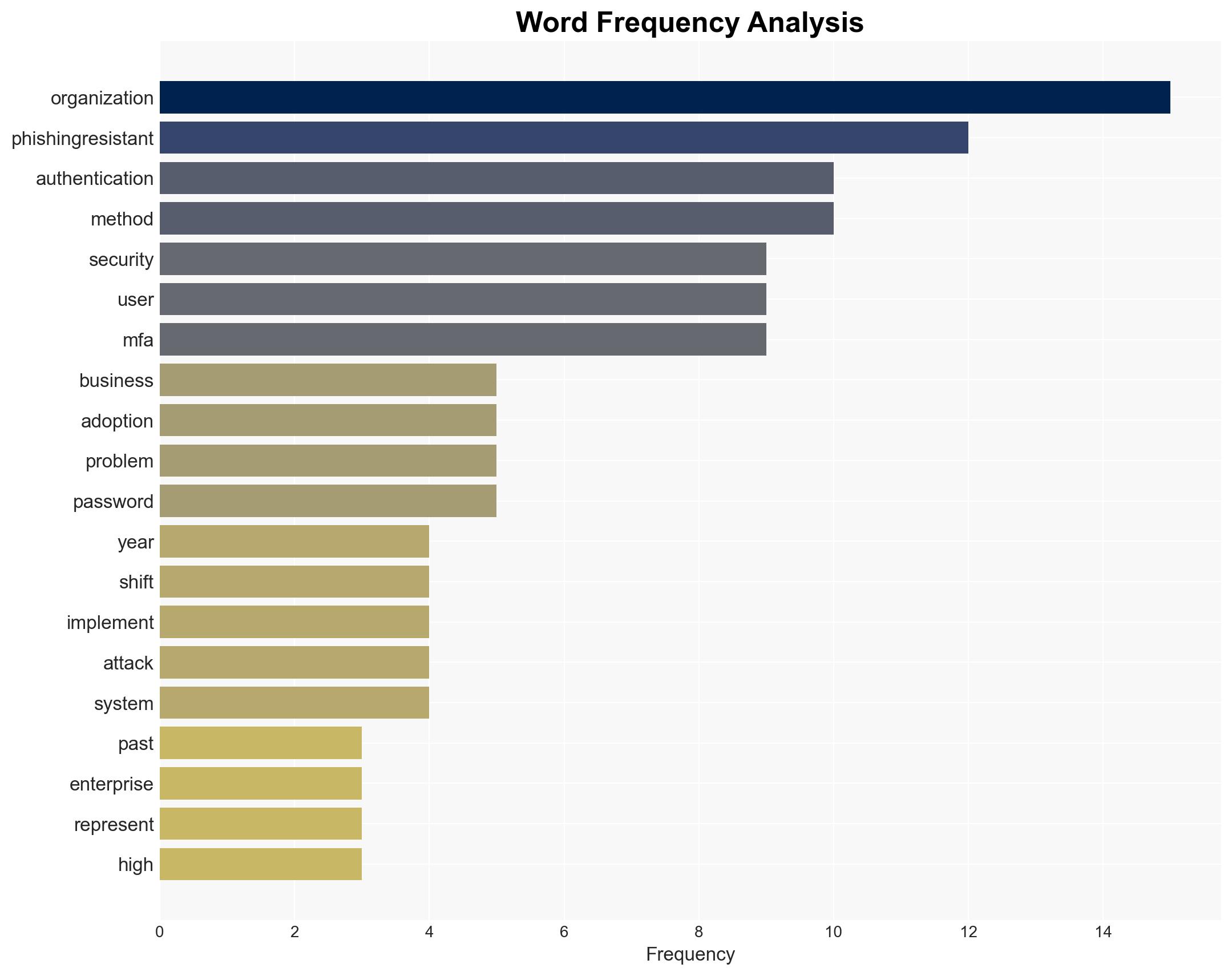
cybersecurity, phishing-resistant authentication, social engineering, enterprise security, MFA, technology adoption, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us