Border Shutdowns Between Pakistan and Afghanistan Disrupt Vital Trade Route for Months
Published on: 2026-02-10
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Pakistan-Afghanistan border closures paralyze trade along a key route
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
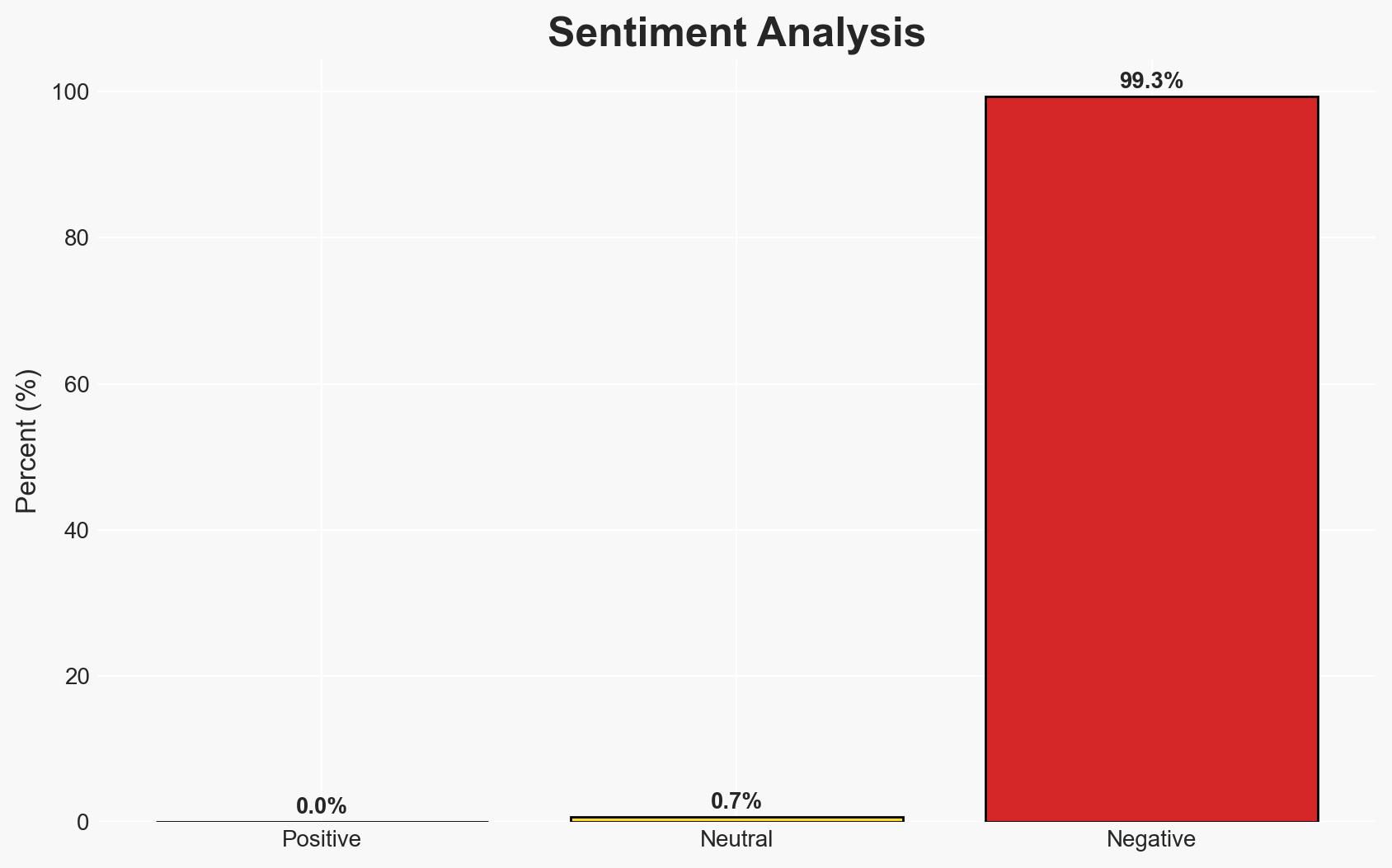
The prolonged closure of the Pakistan-Afghanistan border has severely disrupted trade and heightened tensions between the two nations, primarily due to unresolved security concerns. The most likely hypothesis is that the closure is a strategic move by Pakistan to pressure Afghanistan into addressing militancy issues. This situation affects regional trade dynamics and has significant socio-economic implications. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the complex interplay of regional security and political factors.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The border closure is primarily a security measure by Pakistan to curb cross-border militancy. Supporting evidence includes Pakistan’s accusations against Afghanistan for harboring militants and the recent surge in militant activities. Contradicting evidence is the lack of a clear resolution despite ongoing peace talks, indicating possible alternative motives.
- Hypothesis B: The closure is a political maneuver by Pakistan to exert pressure on the Taliban government for broader geopolitical gains. Supporting evidence includes the timing of the closure following failed peace talks and accusations of airstrikes. However, the economic self-harm caused by the closure contradicts this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the direct link between security concerns and the closure. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in militant activity levels or new diplomatic engagements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The border closure is directly linked to security concerns; Pakistan’s primary goal is to reduce militant threats; Afghanistan’s Taliban government has limited control over militant groups.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the internal decision-making processes of both governments; specific impacts on local economies and populations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from both Pakistani and Afghan sources; risk of manipulation in public statements to serve political agendas.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate regional instability and hinder economic recovery efforts, potentially leading to increased militancy and further geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation into broader diplomatic conflicts; strain on Pakistan-Afghanistan relations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cross-border militant activities; potential for retaliatory actions.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible use of cyber operations to influence public perception or disrupt communications.
- Economic / Social: Significant disruption to trade routes; potential for social unrest due to economic hardship.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence monitoring of border activities; engage in diplomatic dialogues to de-escalate tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for affected trade sectors; strengthen regional partnerships to address security concerns.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Rapid resolution and reopening of borders; Worst: Prolonged closure leading to economic collapse and increased militancy; Most-Likely: Gradual reopening with ongoing security tensions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
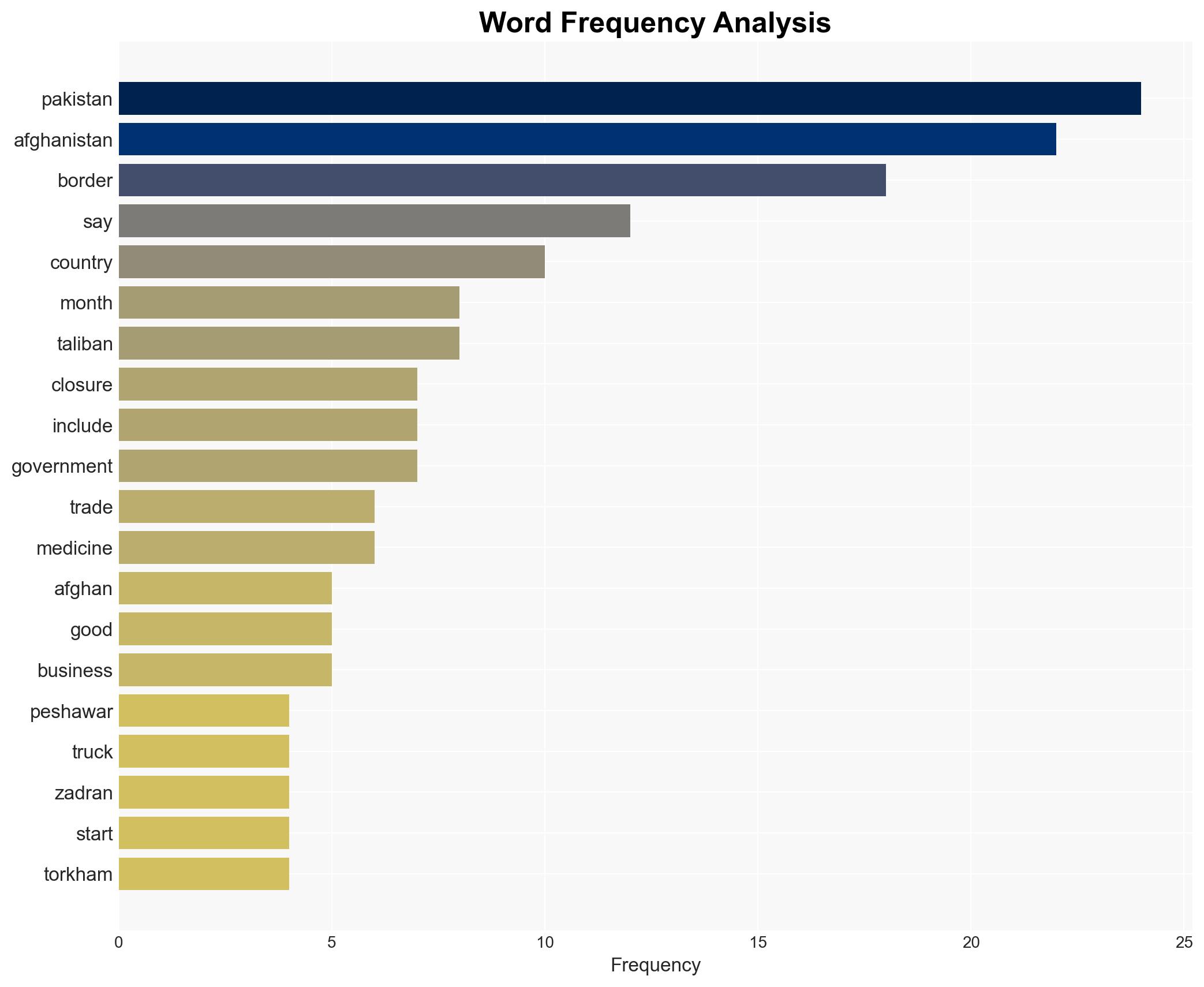
regional conflicts, border security, trade disruption, militancy, Pakistan-Afghanistan relations, geopolitical tensions, economic impact, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Conflicts Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us