SSHStalker Botnet Targets Legacy Linux Systems Using IRC for Command and Control Operations
Published on: 2026-02-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: SSHStalker Botnet Uses IRC C2 to Control Linux Systems via Legacy Kernel Exploits
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
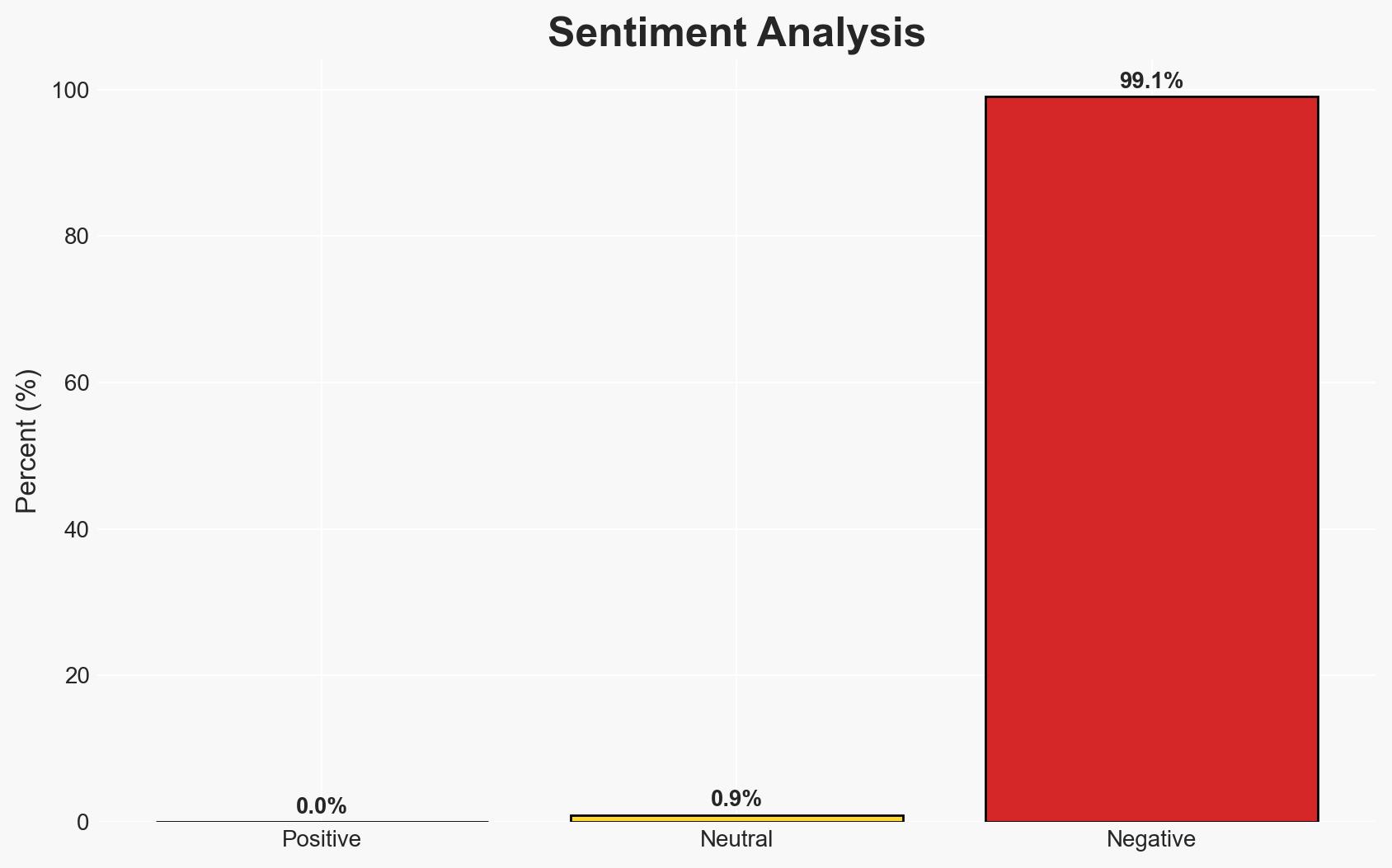
The SSHStalker botnet represents a novel threat by leveraging legacy Linux kernel exploits and IRC-based command-and-control to compromise and control systems. Unlike typical botnets, it maintains dormant access, suggesting potential strategic use. This development poses a moderate threat to outdated infrastructure and legacy systems, with moderate confidence in the assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: SSHStalker is primarily a strategic access tool designed for future exploitation or testing, supported by its dormant behavior and lack of immediate post-exploitation activities. Uncertainties include the ultimate intent and identity of the operators.
- Hypothesis B: SSHStalker is an opportunistic tool for gathering compromised systems for eventual monetization through traditional cybercriminal activities. This is contradicted by the absence of typical monetization behaviors such as DDoS or cryptocurrency mining.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the botnet’s dormant nature and sophisticated use of legacy exploits, indicating a strategic rather than opportunistic intent. Indicators such as a shift to active exploitation or monetization could alter this assessment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The operators have advanced technical capabilities; the targeted systems are primarily legacy and unpatched; the IRC C2 method is chosen for stealth and persistence.
- Information Gaps: The identity and ultimate objectives of the operators; the full scope of the compromised infrastructure; potential connections to state or non-state actors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating the threat due to the use of older exploits; deception risk in the apparent dormancy masking other activities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The SSHStalker botnet could evolve into a significant threat if leveraged for strategic cyber operations or if its capabilities are enhanced. Its current dormant state suggests potential for future activation, posing risks to unpatched systems.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for use in state-sponsored cyber operations targeting geopolitical adversaries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk to critical infrastructure reliant on legacy systems, necessitating enhanced monitoring.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlights vulnerabilities in legacy systems and the need for updated security protocols.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on organizations reliant on outdated technology, increasing costs for security upgrades.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of IRC traffic and legacy system vulnerabilities; conduct awareness campaigns on patching outdated systems.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in upgrading legacy infrastructure security.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Botnet remains dormant and is dismantled. Worst: Activation for strategic cyberattacks. Most-Likely: Continued dormancy with periodic testing, requiring ongoing vigilance.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
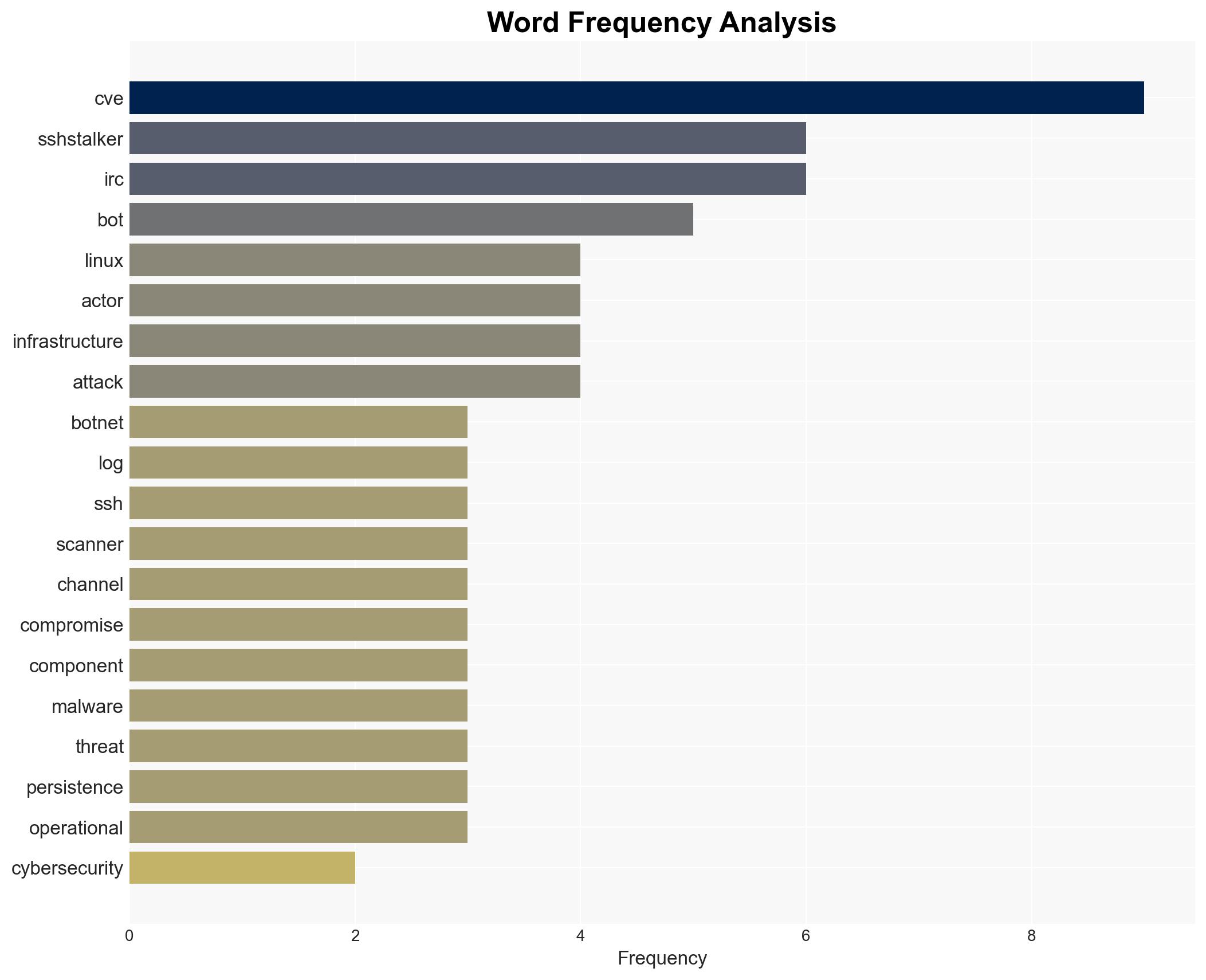
cybersecurity, botnet, legacy systems, IRC, Linux exploits, strategic cyber operations, infrastructure vulnerability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us