AI Browsers: Emerging Cybersecurity Risks Demand Increased Vigilance for User Data Protection
Published on: 2026-02-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Your AI browser is a cybersecurity threat youre not prepared for
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
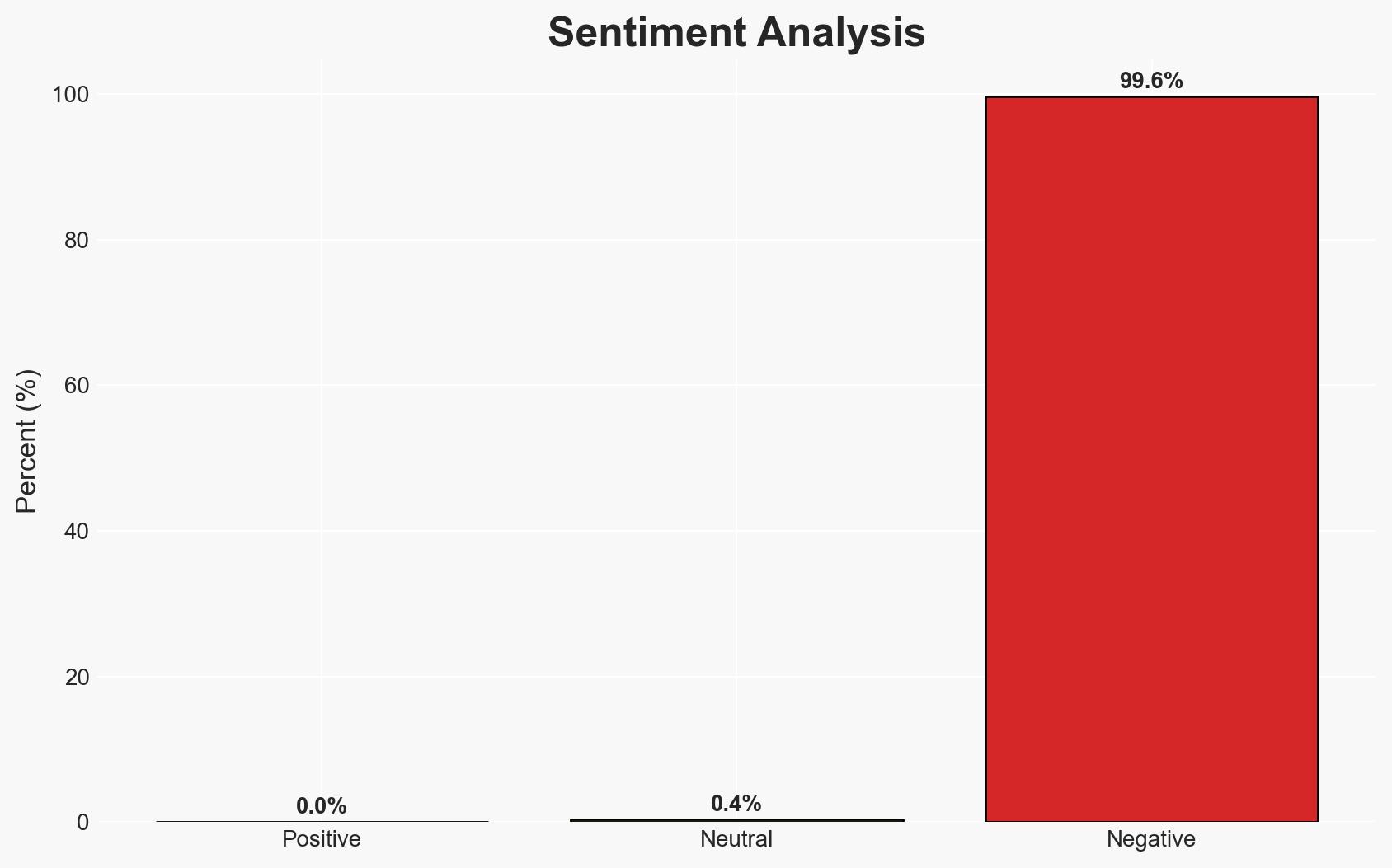
The integration of AI in web browsers introduces significant cybersecurity vulnerabilities, particularly through prompt injection attacks. These vulnerabilities pose risks to data privacy and organizational reputation, especially for regulated sectors. The most likely hypothesis is that these threats will increase as AI browsers gain popularity, with moderate confidence in this assessment due to existing evidence and potential for rapid technological evolution.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI browsers will become a primary target for cyber threat actors due to their inherent vulnerabilities, such as prompt injection, leading to increased data breaches and reputational damage. This is supported by recent incidents and warnings from cybersecurity authorities. Key uncertainties include the pace of AI adoption and the development of mitigation strategies.
- Hypothesis B: AI browsers will not significantly increase cybersecurity risks as developers will implement effective countermeasures to address vulnerabilities like prompt injection. This hypothesis is less supported due to the current lack of comprehensive solutions and the rapid adoption of AI technologies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to documented vulnerabilities and the absence of robust countermeasures. Indicators that could shift this judgment include the development of effective security protocols and a slowdown in AI browser adoption.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI browser adoption will continue to grow; prompt injection remains a significant vulnerability; organizations will not immediately implement comprehensive security measures.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the number of prompt injection incidents and the effectiveness of current mitigation strategies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on AI developers’ assurances of security; underestimation of cyber threat actors’ capabilities to exploit new technologies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI browsers could significantly impact cybersecurity landscapes, with potential ripple effects across various domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cybersecurity incidents linked to AI technologies.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities for malicious actors to conduct sophisticated cyber operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Escalation in cyber espionage and data theft incidents, challenging information integrity.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic losses due to data breaches and erosion of public trust in AI technologies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI browser vulnerabilities; develop awareness campaigns on prompt injection risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in research for robust security measures; foster partnerships between AI developers and cybersecurity experts.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Effective security measures reduce vulnerabilities; Worst: Widespread data breaches damage trust in AI; Most-Likely: Continued vulnerabilities with incremental improvements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC)
- US National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Brave
- Apple
- Perplexity Comet
7. Thematic Tags
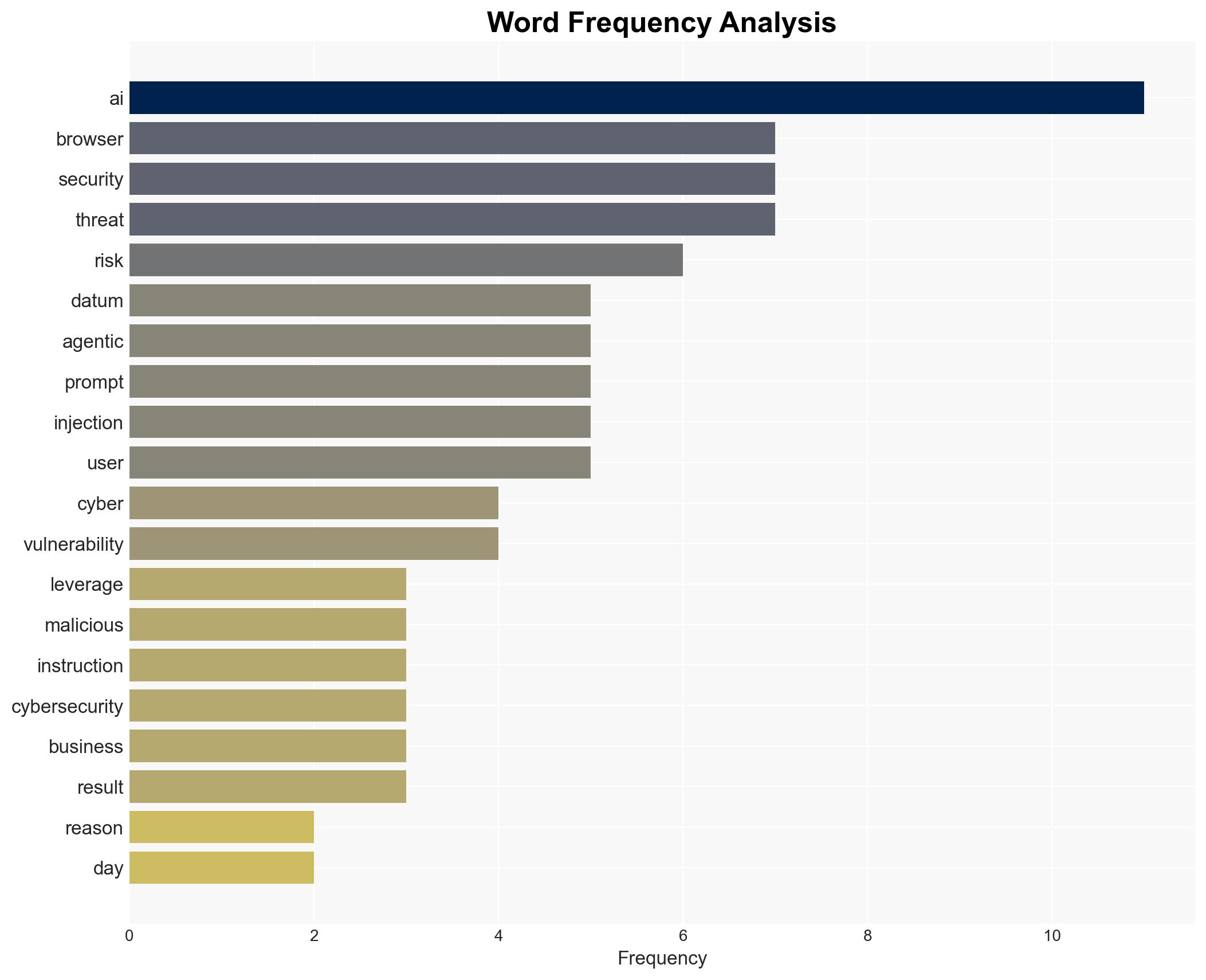
cybersecurity, AI vulnerabilities, prompt injection, data privacy, reputational risk, regulated sectors, cyber threat actors
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us