Italy’s government advances legislation for stricter immigration controls, including potential naval blockades
Published on: 2026-02-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Italy approves new bill to tighten immigration enable ‘naval blockades’
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
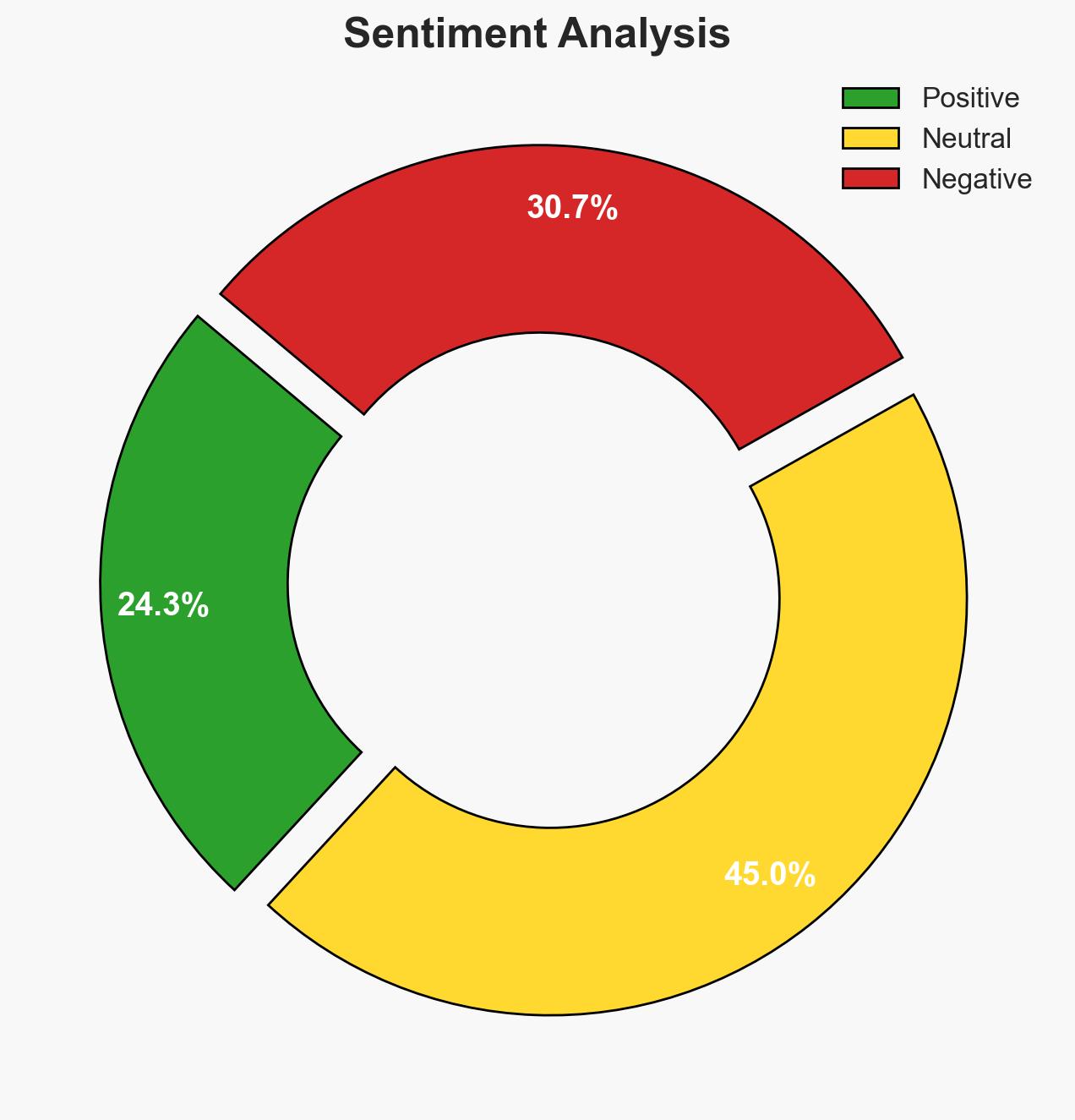
Italy’s government, led by Premier Giorgia Meloni, has approved a bill to enforce stricter immigration controls, including potential naval blockades. This move aligns with recent EU migration policy changes and could significantly impact migration patterns and humanitarian operations in the Mediterranean. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate due to potential legal and operational challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The bill is primarily a deterrent aimed at reducing illegal immigration and enhancing national security. Supporting evidence includes the bill’s provisions for naval blockades and stricter border surveillance. Contradicting evidence includes potential legal challenges and humanitarian opposition.
- Hypothesis B: The bill is a political maneuver to consolidate domestic support by appearing tough on immigration. Supporting evidence includes the timing of the bill following EU policy changes and potential public support for stricter immigration controls. Contradicting evidence includes the operational focus on security threats.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the detailed security measures outlined in the bill. However, indicators such as public opinion shifts or legal challenges could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Italian government has the capacity to enforce naval blockades effectively; EU support will mitigate potential legal challenges; public support for stricter immigration controls will remain stable.
- Information Gaps: Details on the operational implementation of naval blockades; specific agreements with third countries for offshore processing; potential EU responses to legal challenges.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in government statements emphasizing security threats; risk of manipulation in public discourse to justify stringent measures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The approval of this bill could lead to increased tensions in the Mediterranean and strain Italy’s relations with humanitarian organizations and neighboring countries. It may also set a precedent for other EU nations considering similar measures.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for diplomatic friction with countries affected by naval blockades and offshore processing agreements.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced border controls may reduce immediate security threats but could push migrant routes to less secure areas.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased propaganda and misinformation campaigns from both pro- and anti-immigration groups.
- Economic / Social: Possible impact on Italy’s labor market and social services due to changes in migration patterns.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor legal challenges and public opinion; engage with EU partners to ensure compliance with international law.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with affected countries to manage migration flows; enhance capabilities for maritime surveillance and humanitarian response.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective reduction in illegal immigration with minimal legal or diplomatic fallout.
- Worst: Significant legal challenges and humanitarian crises, leading to international condemnation.
- Most-Likely: Gradual implementation with ongoing legal and diplomatic negotiations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Giorgia Meloni – Premier of Italy
- Antonio Tajani – Italian Foreign Minister
- Italian Government (Conservative)
- European Union
- Humanitarian Organizations (various)
7. Thematic Tags
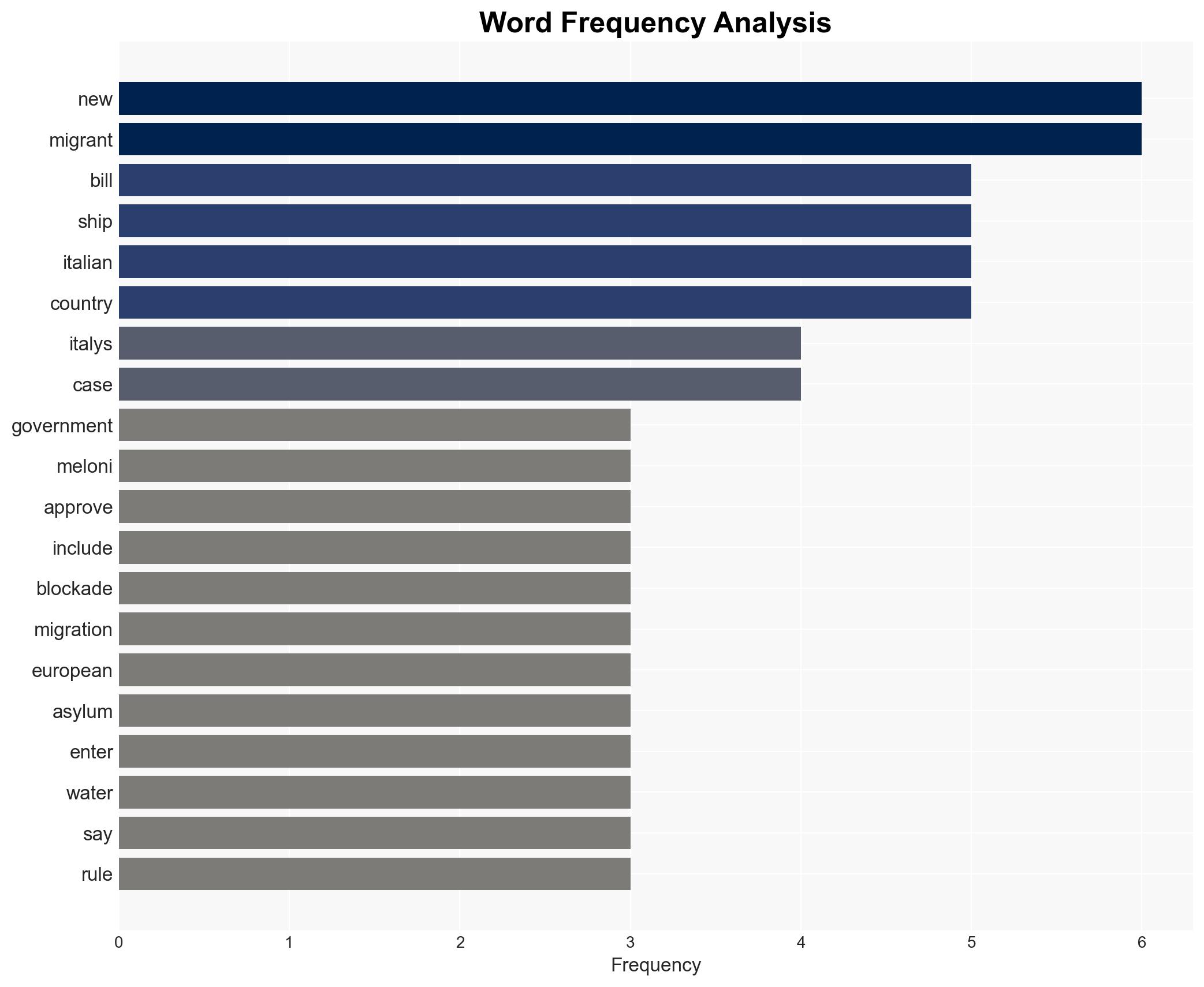
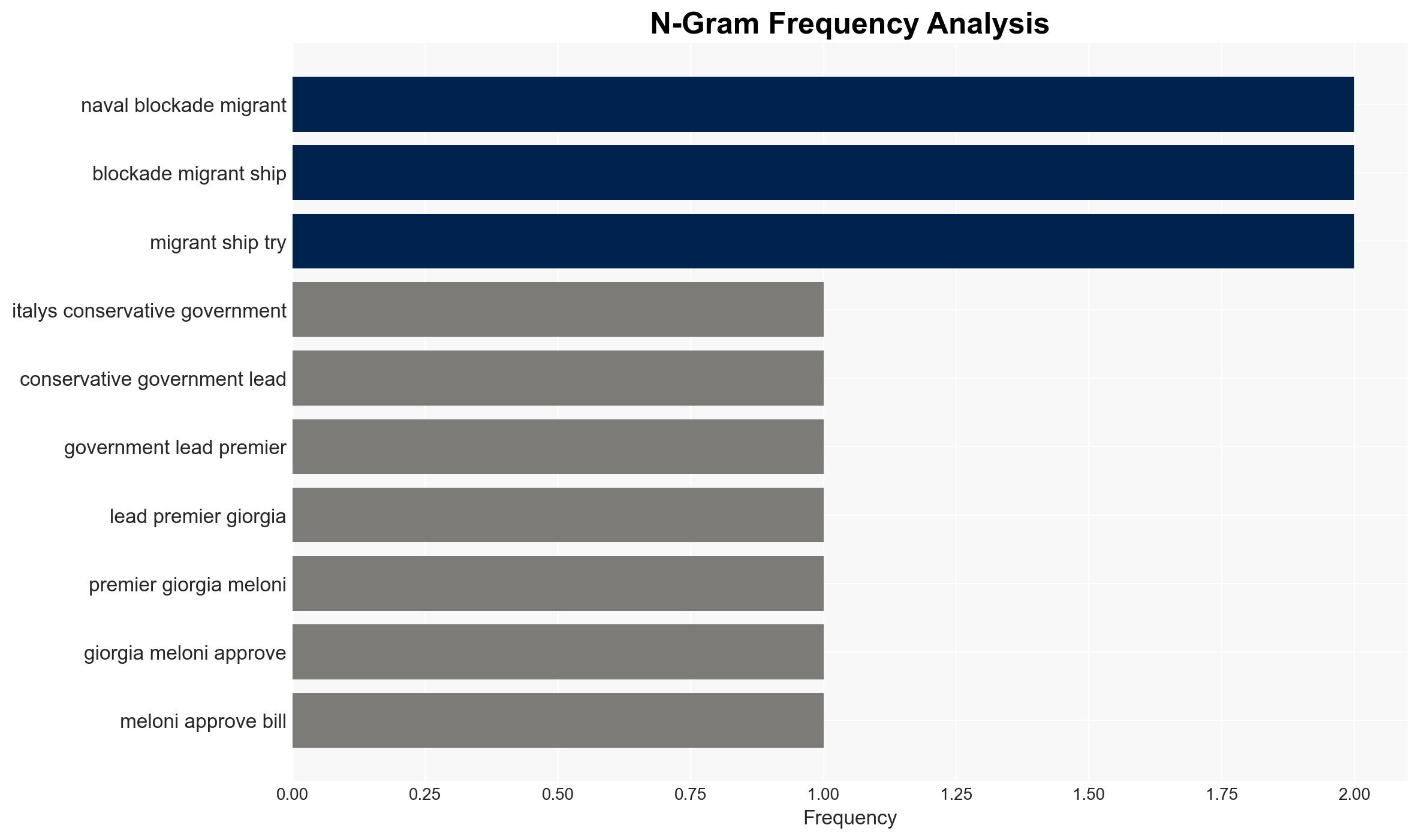
national security threats, immigration policy, national security, EU relations, humanitarian impact, naval operations, legal challenges, public opinion
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us