India’s Rapid Data Centre Expansion Raises Alarms Over Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
Published on: 2026-02-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Cyber risks lurking beneath India’s data centre ops build out
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
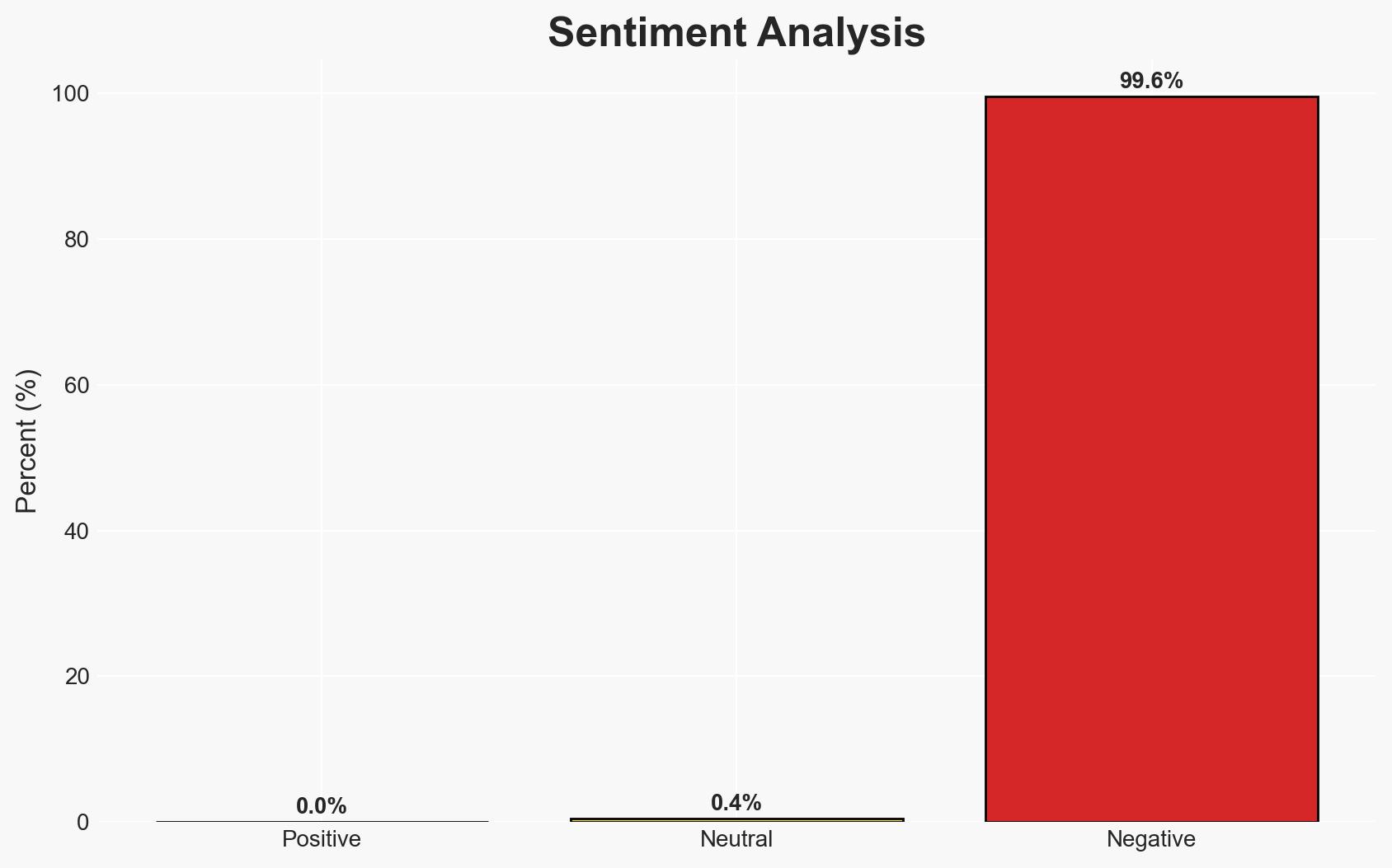
India’s rapid expansion of its data center infrastructure, driven by significant tax incentives, is outpacing its cybersecurity capabilities, creating vulnerabilities to state-backed cyber threats. The most likely hypothesis is that these data centers will become prime targets for nation-state actors, particularly from China, seeking strategic data and AI models. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to existing evidence of increased cyber incidents targeting cloud systems.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: India’s data centers will become high-value targets for state-backed cyber actors due to inadequate cybersecurity measures. Supporting evidence includes the rapid growth of infrastructure without corresponding security upgrades and reports of Chinese-linked groups targeting cloud credentials. Key uncertainties include the exact scope of state-backed activities and potential improvements in India’s cybersecurity posture.
- Hypothesis B: India will successfully mitigate cyber threats through international collaboration and domestic policy updates. This is supported by potential for policy evolution and global cybersecurity partnerships. However, current evidence of outdated policies and ongoing attacks contradicts this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in cyber incidents and the strategic interest of nation-states in India’s burgeoning AI infrastructure. Indicators such as policy updates or international cybersecurity agreements could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The pace of data center growth will continue; India’s cybersecurity policy will not significantly change in the short term; state-backed actors have the capability and intent to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into India’s current cybersecurity capabilities and specific measures being implemented to protect new infrastructure.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from cybersecurity firms with vested interests in highlighting threats; risk of underestimating India’s capacity to adapt and respond.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of India’s data center infrastructure could lead to increased geopolitical tensions, especially with China, and elevate the cyber threat landscape. The economic benefits might be undermined by security vulnerabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tension with China and other state actors targeting Indian infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment with increased cyber espionage and potential for infrastructure disruption.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater focus on cybersecurity resilience and potential for increased cyber defense collaboration.
- Economic / Social: Economic growth from data center investments could be impacted by security breaches, affecting investor confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive cybersecurity audit of existing and planned data centers; enhance monitoring for state-backed cyber activities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with international cybersecurity firms; update national cybersecurity policies to address current threats.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: India strengthens its cybersecurity framework, reducing vulnerabilities (trigger: policy updates).
- Worst: Major data breach occurs, leading to economic and reputational damage (trigger: significant cyber incident).
- Most-Likely: Continued targeting by state actors with intermittent successful breaches (trigger: ongoing cyber incidents).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
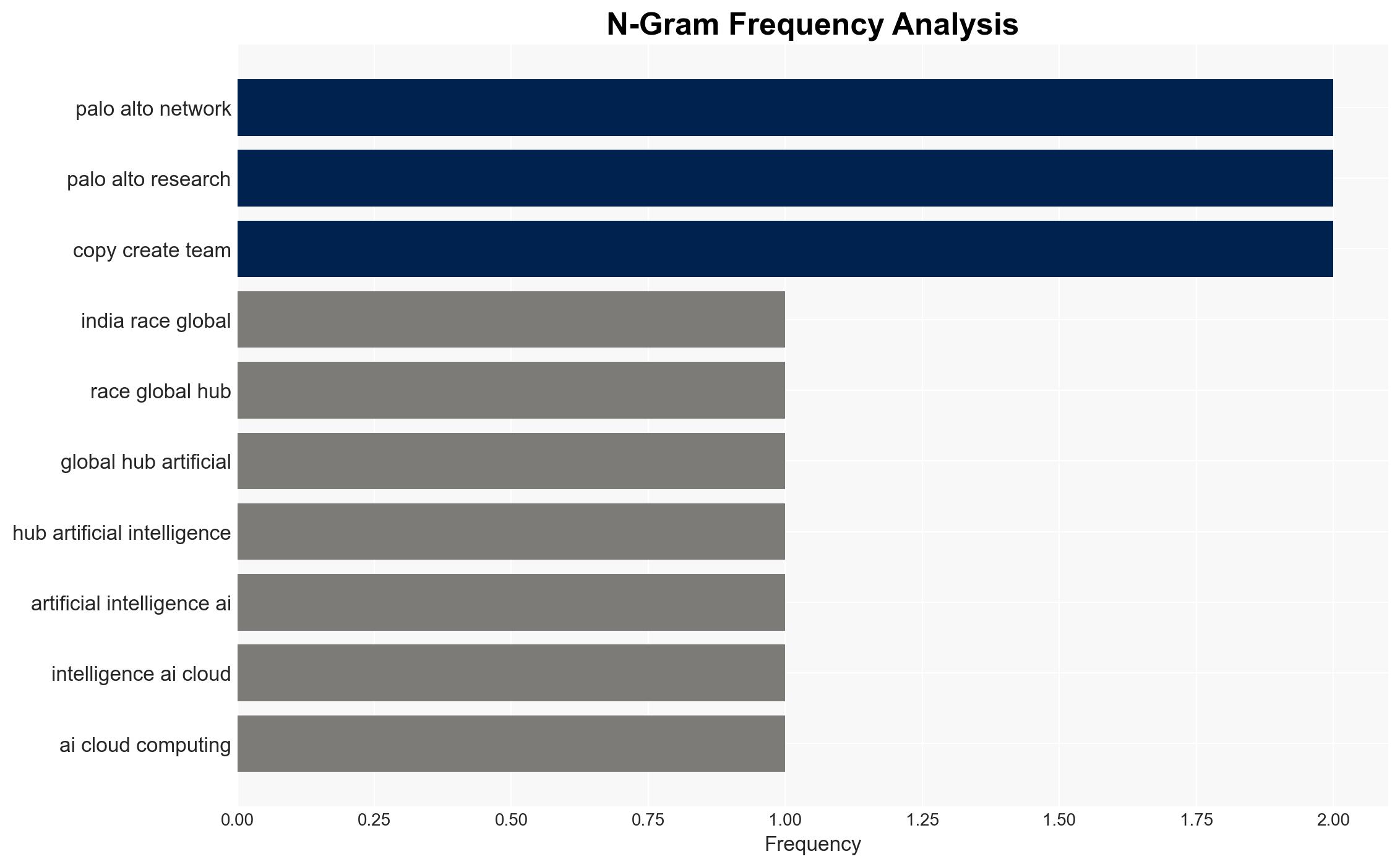
- Huzefa Motiwala, Senior Director, India and SAARC, Palo Alto Networks
- Apeksha Kaushik, Principal Analyst, Gartner
- Jaydeep Singh, General Manager, India, Kaspersky
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
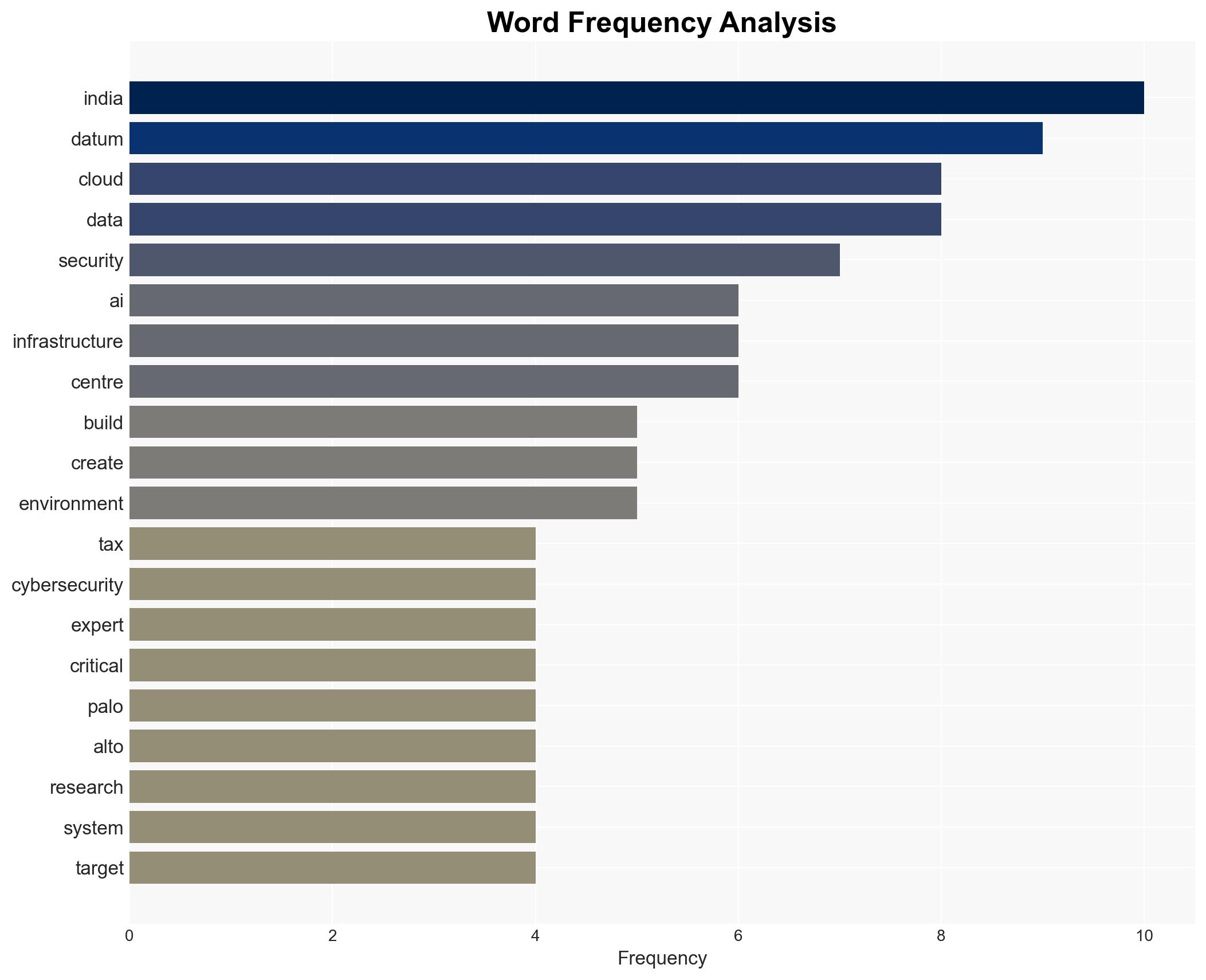
cybersecurity, data centers, nation-state actors, cloud computing, AI infrastructure, economic growth, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us