Exploitation Window Narrows 94% as N-Day Vulnerabilities Surge in Cyber Threat Landscape
Published on: 2026-02-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Time to Exploit Plummets as N-Day Flaws Dominate
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
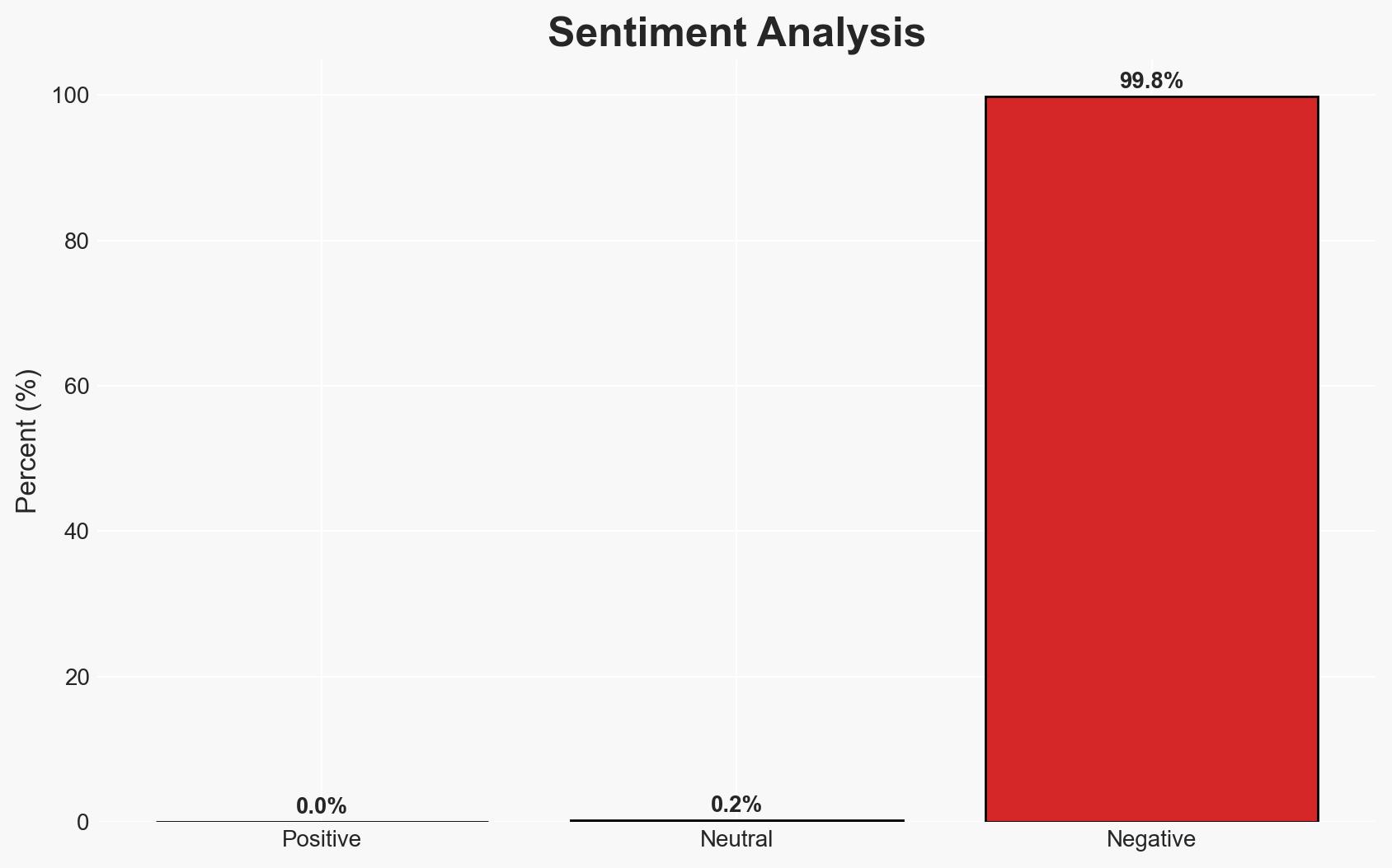
The rapid decrease in the time to exploit vulnerabilities, particularly n-day flaws, poses a significant threat to organizational cybersecurity. This trend is driven by the accessibility of proof-of-concept code and internet-wide scanning tools, affecting IT and security teams’ ability to respond effectively. The most likely hypothesis is that threat actors will increasingly leverage n-day vulnerabilities due to their lower cost and effort compared to zero-days. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The decrease in time to exploit is primarily due to the increased availability of n-day exploits and the use of automated tools by less sophisticated threat actors. Supporting evidence includes the high percentage of n-days in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities database and the use of scanning tools. Key uncertainties include the exact role of nation-state actors in this trend.
- Hypothesis B: The trend is driven by a strategic shift among advanced persistent threat (APT) groups to focus on n-day vulnerabilities as a more efficient means of attack. Supporting evidence includes recent nation-state exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities, but this is less directly linked to n-day trends.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the widespread availability and lower barriers to entry for exploiting n-day vulnerabilities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include increased evidence of coordinated nation-state campaigns focusing on n-days.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Organizations will continue to lag in patching vulnerabilities; threat actors will prioritize low-cost, high-impact exploits; the availability of PoC code will remain high.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of recent n-day exploit campaigns; comprehensive data on organizational patching timelines.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in vendor-reported data; risk of overestimating the role of unsophisticated actors due to lack of visibility into APT activities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The rapid exploitation of n-day vulnerabilities could lead to increased cyber incidents, impacting organizational and national security. Over time, this may force a reevaluation of vulnerability management practices.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if nation-states are implicated in exploiting n-day vulnerabilities against critical infrastructure.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks disrupting essential services or compromising sensitive data.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for improved vulnerability management tools and practices; potential rise in cyber insurance claims.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impacts from disrupted business operations; increased public concern over cybersecurity risks.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of known vulnerabilities; prioritize patching of n-day vulnerabilities; increase awareness and training for IT staff.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships for threat intelligence sharing; invest in automated patch management solutions; conduct regular security audits.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Organizations improve patching timelines, reducing n-day exploitation opportunities.
- Worst: A major cyber incident occurs due to unpatched n-day vulnerabilities, leading to significant economic and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Continued moderate increase in n-day exploitations, with gradual improvements in organizational responses.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, n-day vulnerabilities, threat intelligence, patch management, cyber threats, vulnerability exploitation
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us