Google alerts on integration of AI in live cyberattacks, revealing advanced tactics by threat actors.
Published on: 2026-02-13
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Google warns attackers are wiring AI directly into live cyberattacks
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
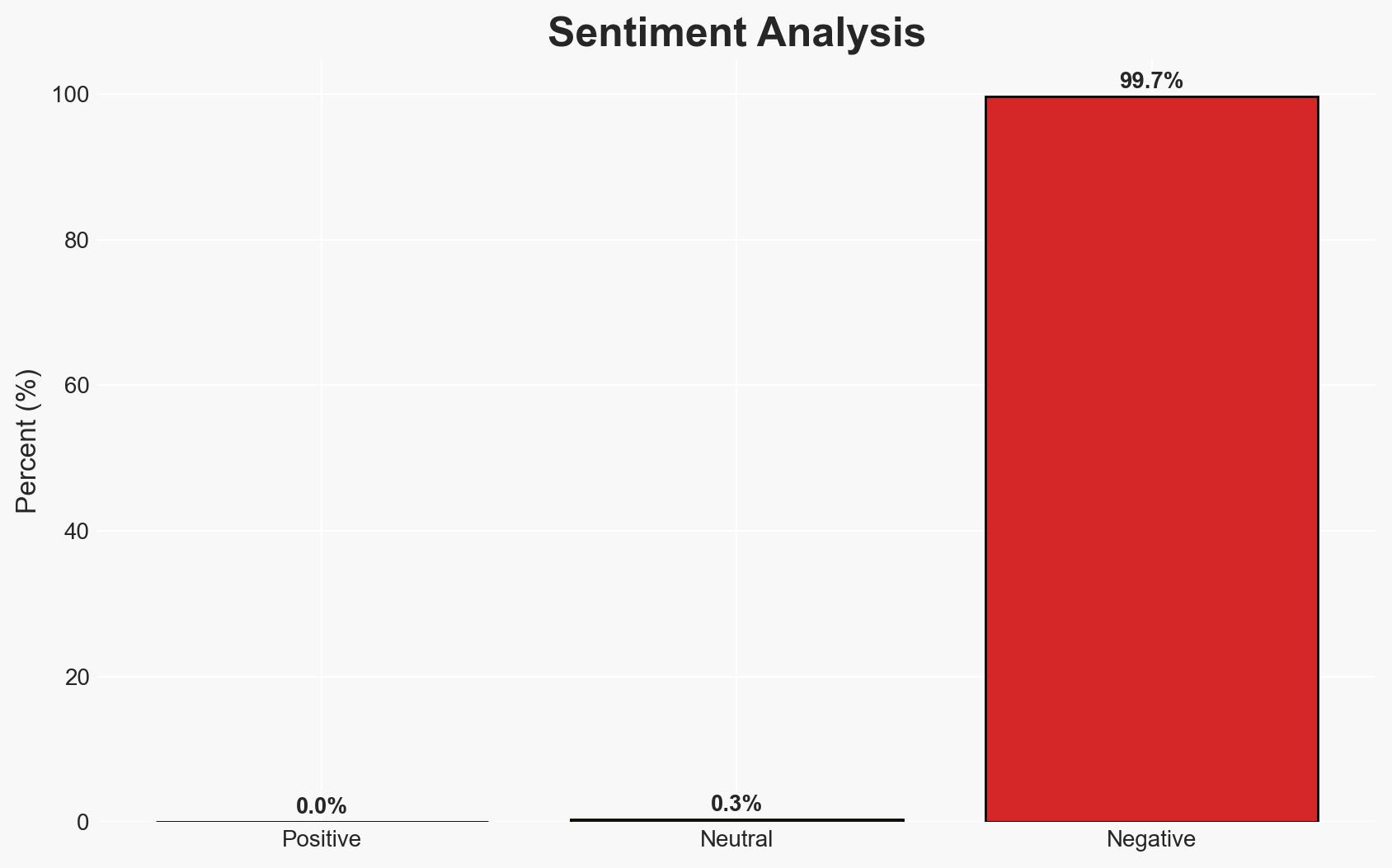
Threat actors are increasingly integrating AI into cyberattack workflows, enhancing their capabilities and complicating detection efforts. This development primarily affects cybersecurity defenses and could have broader implications for national security. The most likely hypothesis is that AI is being used to augment existing attack strategies rather than replace human operators. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Threat actors are using AI to augment existing cyberattack strategies, enhancing efficiency and effectiveness without replacing human operators. This is supported by evidence of AI being used for specific tasks such as code generation and reconnaissance, but not for autonomous decision-making.
- Hypothesis B: Threat actors are moving towards fully autonomous AI-driven cyberattacks, aiming to replace human operators entirely. This hypothesis is less supported as there is currently no evidence of widespread deployment of autonomous AI in attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the observed use of AI as an augmentation tool rather than a replacement. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of autonomous AI deployment in cyberattacks.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI integration in cyberattacks will continue to evolve; AI will primarily serve as an augmentation tool in the near term; adversaries will prioritize cost-effective strategies.
- Information Gaps: The extent of AI integration across different threat actor groups; specific capabilities of AI models being exploited.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in Google’s reporting due to vested interests; possibility of threat actors using misinformation to exaggerate AI capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI into cyberattacks could significantly alter the threat landscape, necessitating adaptive defense strategies. Over time, this could lead to more sophisticated and harder-to-detect attacks.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between nations over cyber capabilities and AI development.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment requiring updated countermeasures and intelligence strategies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for more dynamic and adaptive cyber threats, challenging existing cybersecurity frameworks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from increased cybercrime and the need for investment in cybersecurity infrastructure.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI-related cyber activities; enhance detection capabilities for AI-augmented attacks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies for AI threat intelligence sharing; invest in AI research for defensive applications.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: AI integration remains limited to augmentation, allowing defenses to adapt effectively.
- Worst: Rapid development of autonomous AI cyber capabilities leads to a surge in sophisticated attacks.
- Most-Likely: Continued use of AI for augmentation with gradual evolution towards more autonomous capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Google Threat Intelligence Group
- Dr. Ilia Kolochenko, Chief Executive at ImmuniWeb SA
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for specific threat actors
7. Thematic Tags
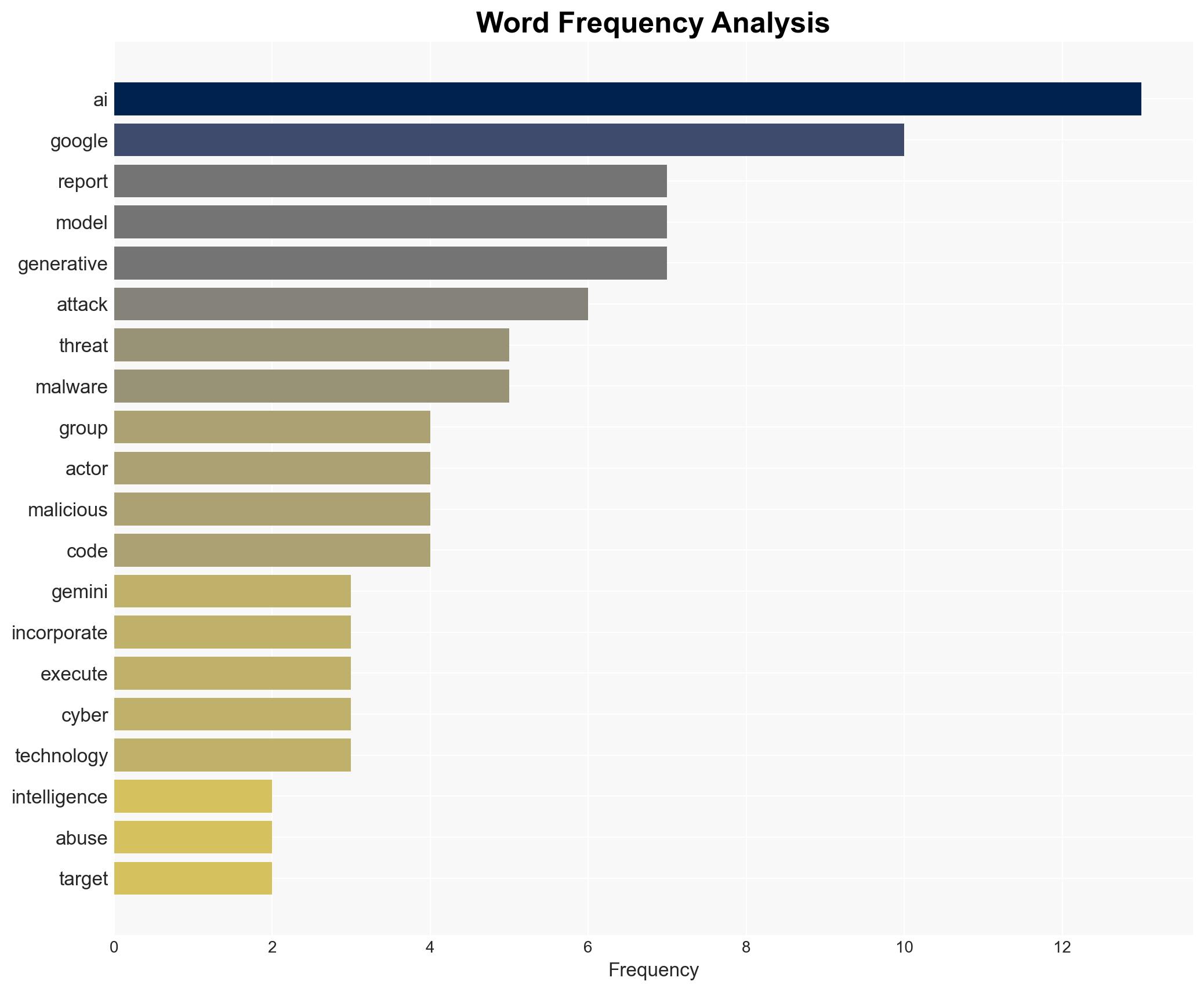
cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, cyberattacks, threat intelligence, AI augmentation, malware, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us