Assessing the Growing Nuclear Capabilities of Russia and China: Implications for U.S. Security
Published on: 2026-02-15
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Do nuclear numbers matter
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
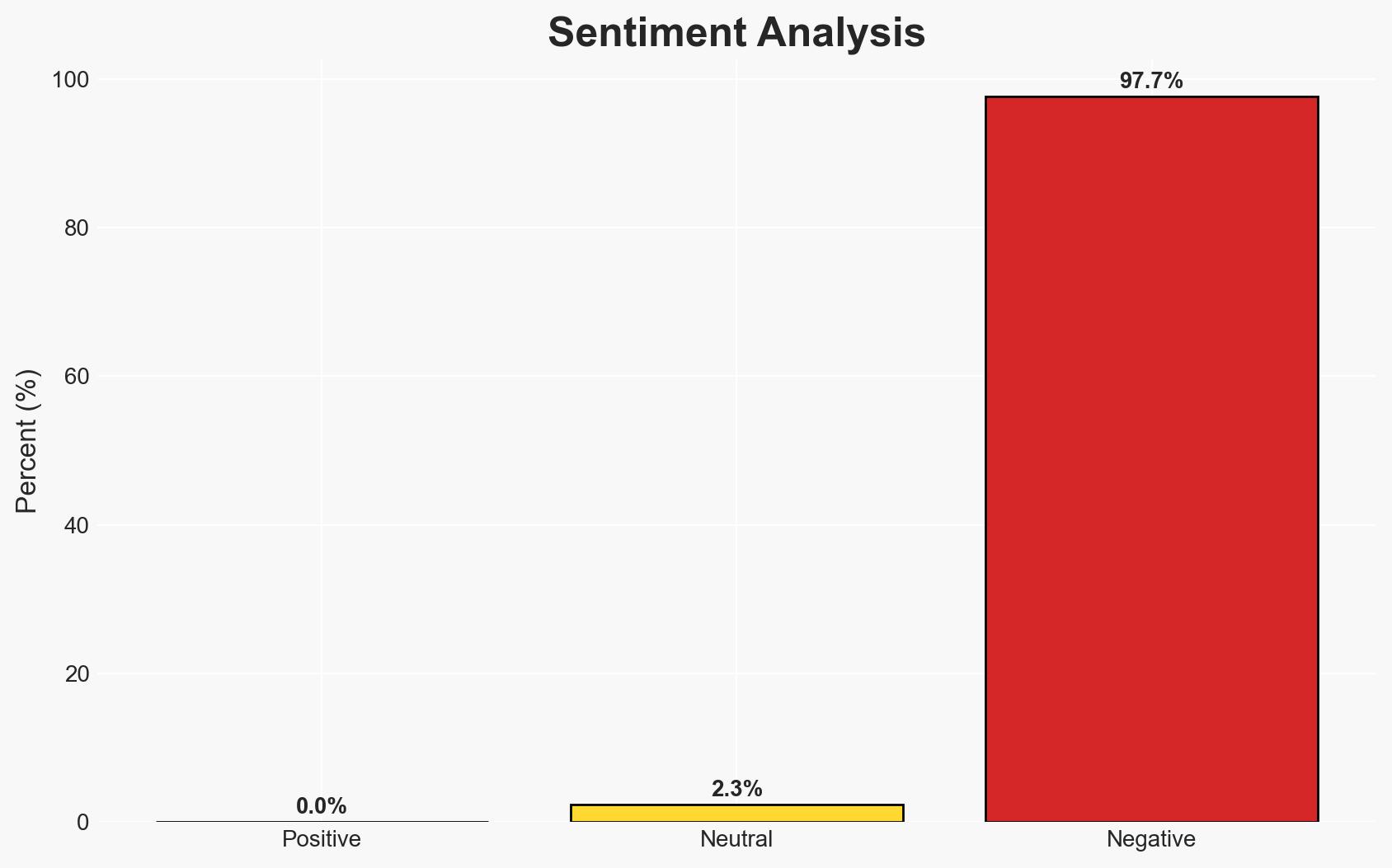
The increasing nuclear arsenals of Russia and China pose a significant strategic challenge to the United States, potentially surpassing U.S. capabilities and complicating deterrence strategies. The potential for collaboration between these adversaries further heightens the threat. This assessment carries a moderate confidence level due to existing information gaps and potential deception by China.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Russia and China are independently expanding their nuclear capabilities primarily for national defense and deterrence. Supporting evidence includes the detailed projections of their nuclear arsenals. However, uncertainties remain about the strategic intent behind these expansions and the potential for collaboration.
- Hypothesis B: Russia and China are expanding their nuclear arsenals as part of a coordinated strategy to challenge U.S. global influence and deterrence capabilities. This hypothesis is supported by the simultaneous growth in both countries’ arsenals and the potential for strategic deception. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of explicit public declarations of collaboration.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the synchronized nature of the nuclear expansions and historical patterns of strategic alignment between Russia and China. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of formal military collaboration or joint strategic exercises.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Russia and China will continue to prioritize nuclear expansion; U.S. intelligence assessments are accurate; strategic deception by China is ongoing; nuclear capabilities are primarily for deterrence.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on the strategic intentions behind Russia and China’s nuclear expansions; verification of the actual number of deployed warheads.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential underestimation of Chinese capabilities due to historical biases; reliance on open-source data that may be subject to manipulation by state actors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The expansion of Russian and Chinese nuclear capabilities could lead to a destabilized global nuclear balance, prompting an arms race and increased geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation of tensions between nuclear powers, increased pressure on U.S. alliances, and challenges to non-proliferation efforts.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of nuclear proliferation and increased focus on missile defense systems.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for increased cyber operations targeting nuclear command and control systems.
- Economic / Social: Increased defense spending could strain national budgets and impact economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence collection on Russian and Chinese nuclear activities; strengthen missile defense systems; engage in diplomatic efforts to address nuclear proliferation concerns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures and strategic partnerships with allies; invest in advanced deterrence capabilities and cybersecurity defenses.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic engagements lead to renewed arms control agreements.
- Worst: An arms race ensues, destabilizing global security.
- Most-Likely: Continued strategic competition with periodic diplomatic engagements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
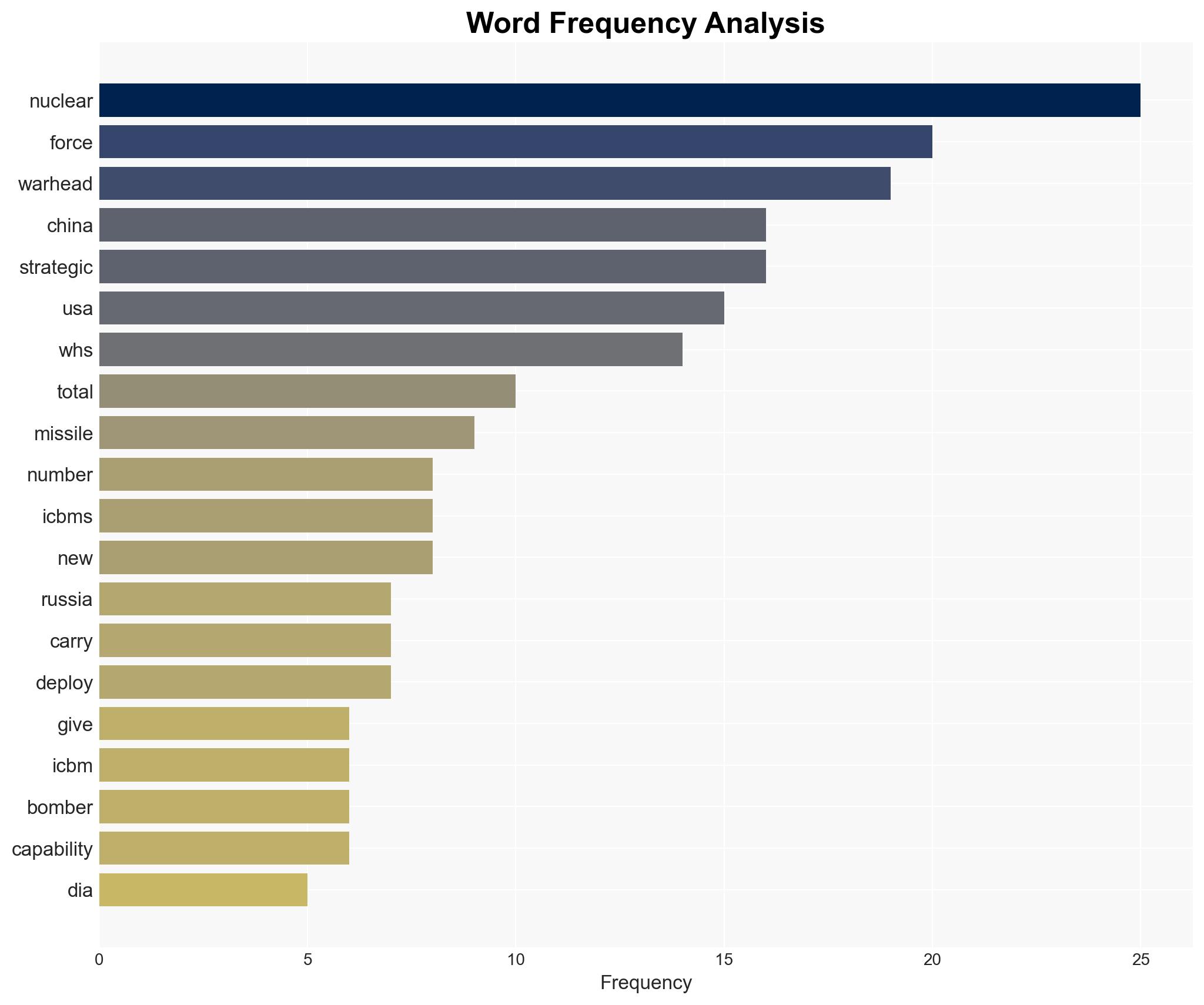
national security threats, nuclear deterrence, strategic competition, arms race, geopolitical tensions, missile defense, intelligence assessment, strategic deception
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us