Strait of Hormuz: A Critical Chokepoint Threatening Global Oil and Gas Supply Chains
Published on: 2026-02-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The 21-Mile Trigger How a Narrow Strait Holds the Global Economy Hostage
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
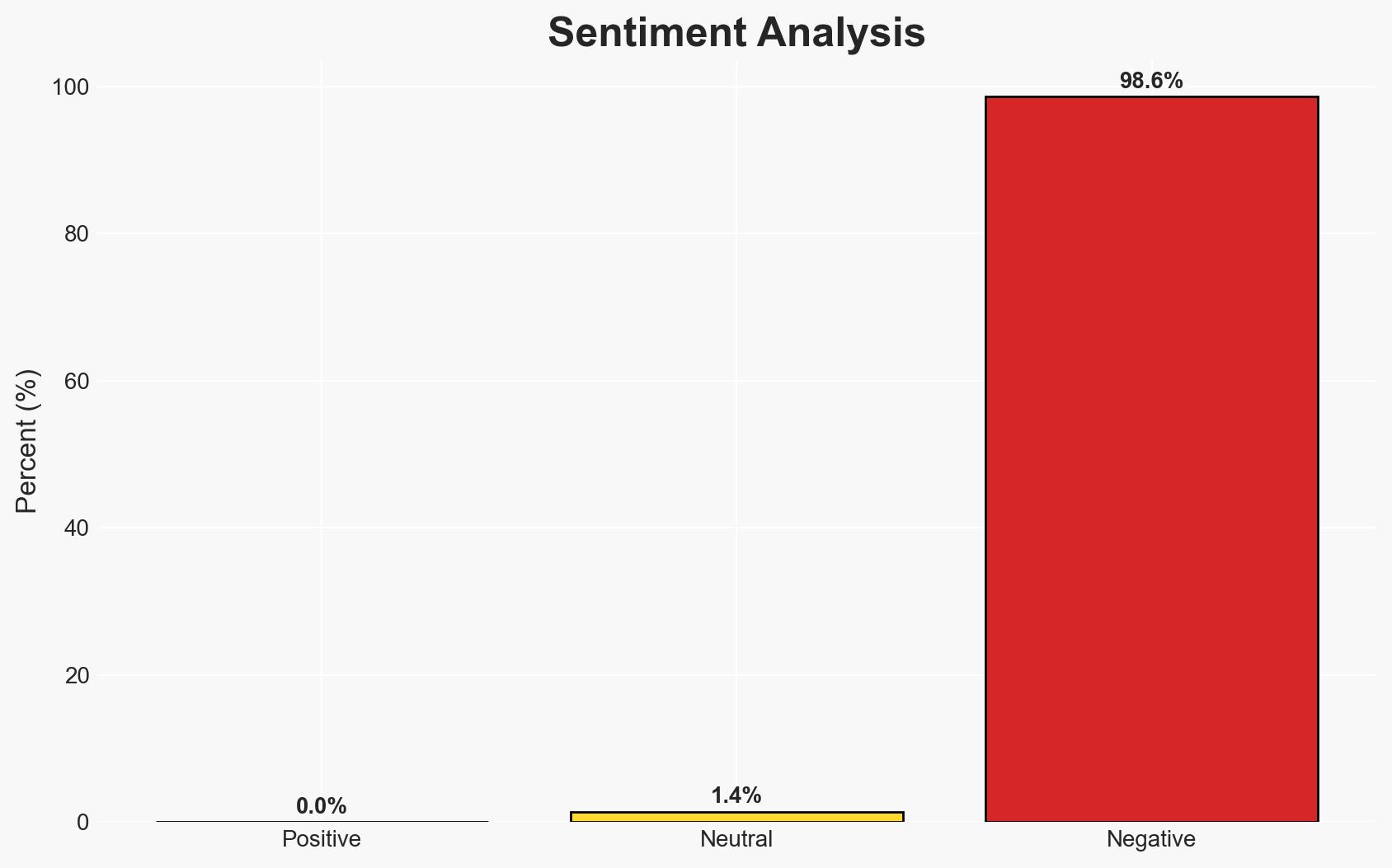
The Strait of Hormuz remains a critical chokepoint for global energy supplies, with geopolitical tensions in the region posing significant risks to global economic stability. The most likely hypothesis is that any closure or disruption of the Strait would lead to severe economic and security repercussions worldwide. Confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the potential for rapid escalation and the complexity of regional dynamics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Strait of Hormuz will remain open despite regional tensions, as stakeholders recognize the catastrophic global economic impact of its closure. This hypothesis is supported by historical precedence where threats to close the Strait have not been actualized. However, uncertainties include the unpredictable nature of regional actors and potential miscalculations.
- Hypothesis B: The Strait of Hormuz could be closed temporarily due to escalating military conflicts or strategic decisions by Iran, leading to immediate global economic disruptions. This is supported by recent tensions and Iran’s parliamentary vote to close the Strait. Contradicting evidence includes the lack of final approval from Iran’s Supreme National Security Council.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the historical reluctance of regional powers to engage in actions that would severely disrupt global oil markets. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in Iran’s political stance or significant military escalations in the region.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The global economy’s reliance on the Strait of Hormuz remains unchanged; regional actors will act rationally to avoid economic self-harm; current geopolitical alliances will hold.
- Information Gaps: Detailed intelligence on Iran’s internal decision-making processes and the readiness of regional military forces.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on historical patterns; underestimation of regional actors’ willingness to escalate; possible misinformation from state actors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The situation in the Strait of Hormuz could lead to significant global economic disruptions and increased geopolitical tensions. Over time, this could affect energy prices, global trade routes, and international relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tensions between Iran and Western powers; potential for new alliances or shifts in regional power dynamics.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened military readiness and potential for asymmetric warfare tactics by regional actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure and information warfare to influence public perception.
- Economic / Social: Volatility in global oil prices; potential for economic recession in oil-dependent economies; social unrest due to economic instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of regional military movements; engage in diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions; prepare contingency plans for energy supply disruptions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen alliances with key regional partners; invest in alternative energy routes and sources; develop resilience measures for critical infrastructure.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Diplomatic resolution reduces tensions, maintaining open Strait access.
- Worst Case: Military conflict leads to prolonged closure, severe global economic impact.
- Most Likely: Periodic tensions without closure, causing temporary market volatility.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
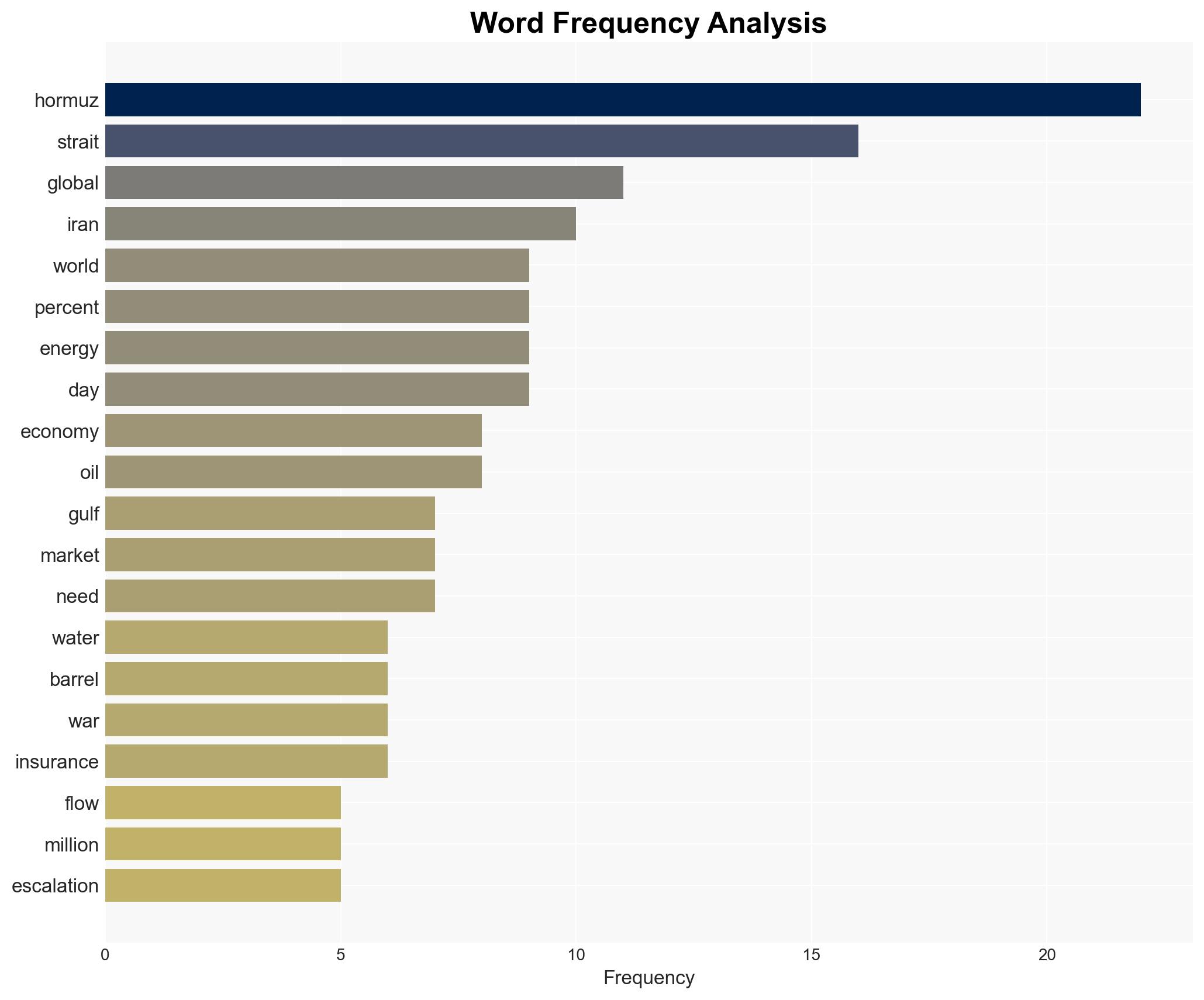
national security threats, global economy, energy security, geopolitical tensions, Strait of Hormuz, oil markets, regional stability, military conflict
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us