Vast online database leak reveals millions of Social Security numbers, emails, and passwords, posing ongoing…
Published on: 2026-02-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Massive data leak exposes millions of social security numbers emails and passwords experts warn of ongoing risk
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
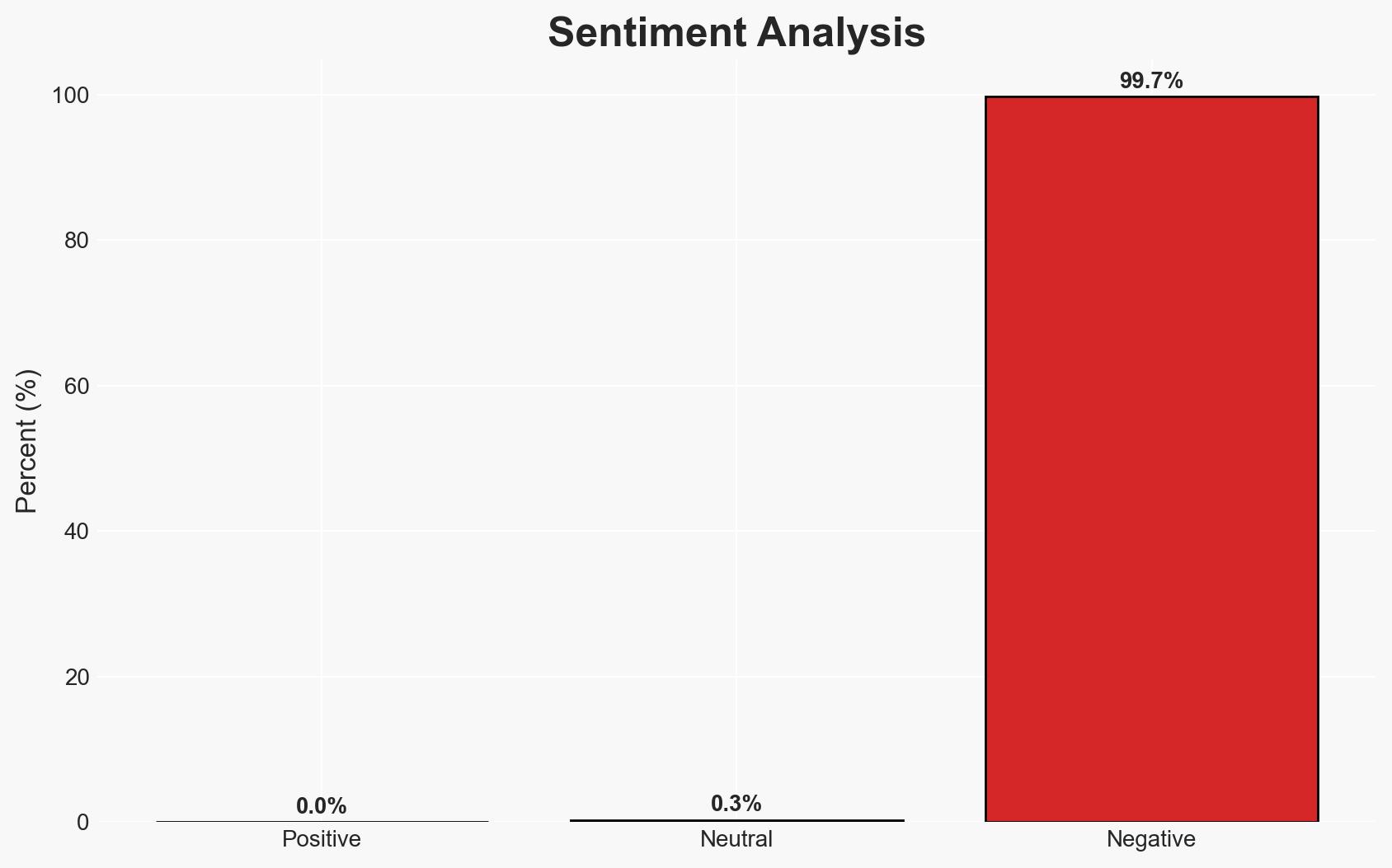
A massive unsecured database containing billions of records, including Social Security numbers, emails, and passwords, poses a significant ongoing risk. The data, likely aggregated from multiple breaches over a decade, affects tens to hundreds of millions of individuals. The most supported hypothesis is that the data has not yet been fully exploited by malicious actors, creating a latent threat. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The data was collected from multiple breaches over a decade and remains largely unused by malicious actors. This is supported by the age of the data and the lack of widespread reports of misuse. However, the possibility of undetected exploitation remains a key uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: The data has been actively used by cybercriminals, but the impact has been underreported or misattributed. This hypothesis is less supported due to the lack of evidence of widespread misuse and the age of the data.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the evidence of the data’s age and the lack of significant reports of misuse. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a surge in identity theft cases or new information on data exploitation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The data is primarily from historical breaches; the majority of Social Security numbers are accurate; the data has not been widely exploited yet.
- Information Gaps: The exact sources of the data breaches; the current status of data exploitation by threat actors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data interpretation due to reliance on a single cybersecurity firm’s analysis; risk of underestimating the threat due to lack of immediate consequences.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased identity theft and fraud if the data is exploited. The exposure of Social Security numbers poses a long-term risk to affected individuals.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential strain on international relations if data misuse affects foreign nationals.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of identity theft could facilitate criminal and terrorist activities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Highlights vulnerabilities in data protection and the need for improved cybersecurity measures.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from fraud and identity theft; erosion of public trust in data security.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring for signs of data misuse; inform potentially affected individuals; promote use of password managers and strong passwords.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Strengthen data breach response protocols; develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Data remains unused, and security measures improve. Worst: Data is exploited, leading to widespread identity theft. Most-Likely: Limited exploitation occurs, prompting gradual improvements in cybersecurity practices.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- UpGuard (cybersecurity company)
- 9to5Mac (source of reported information)
- Pollock (expert cited in the snippet)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, data breach, identity theft, information security, cyber risk, personal data protection
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us