University of Mississippi Medical Center Shuts Down Clinics Statewide Following Ransomware Incident
Published on: 2026-02-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Mississippi medical center closes all clinics after ransomware attack
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
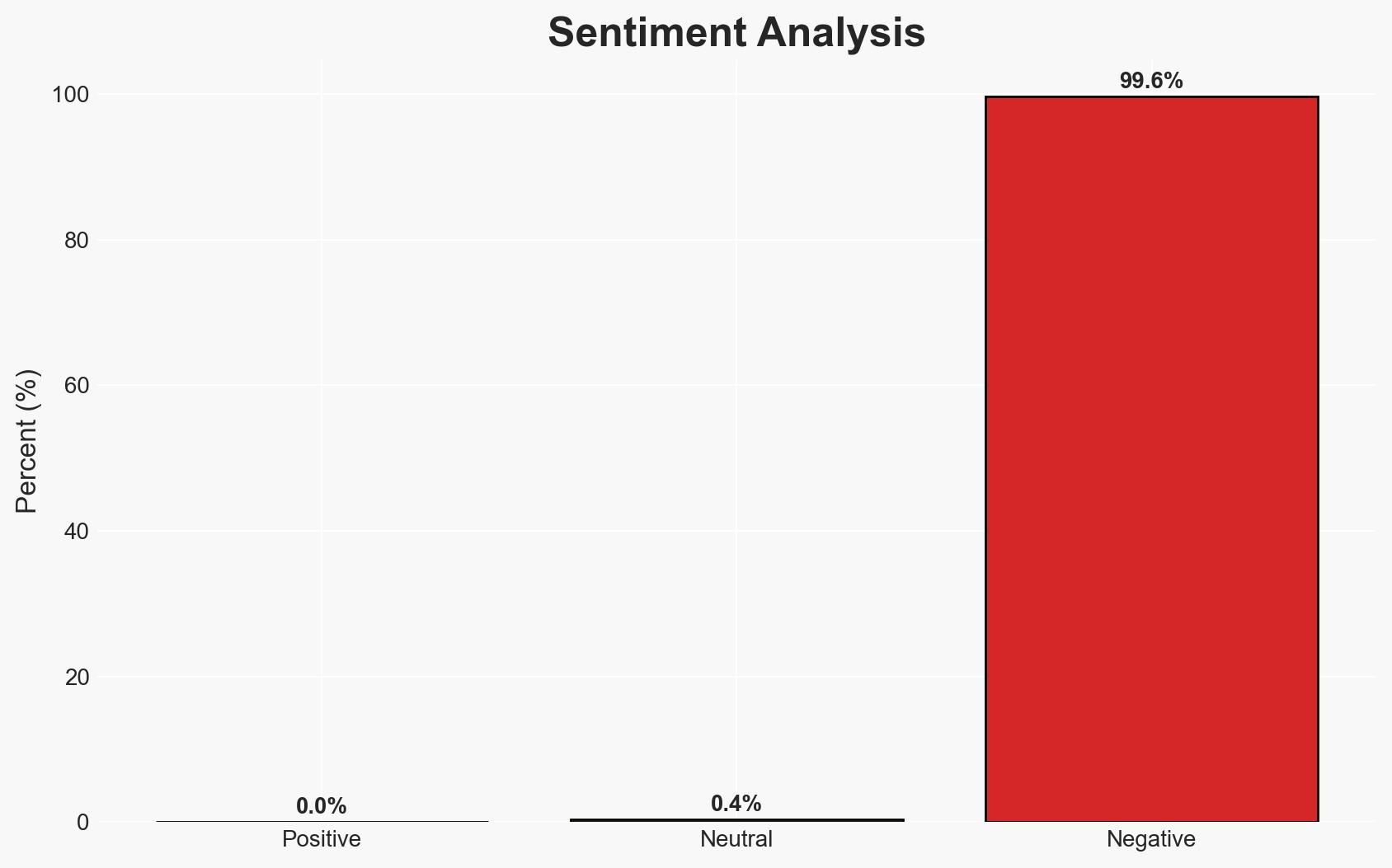
The University of Mississippi Medical Center (UMMC) has closed all clinics statewide following a ransomware attack, severely impacting its operations. The attack has disrupted IT systems, including electronic medical records, but hospital services continue under emergency procedures. The incident highlights vulnerabilities in critical healthcare infrastructure. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to ongoing investigations and incomplete information about the attackers’ identity and motives.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The ransomware attack is financially motivated, aiming to extort UMMC for a ransom payment. This is supported by the communication between UMMC and the attackers, typical of ransomware operations. However, the lack of a public claim by a known ransomware group leaves uncertainty about the attackers’ identity.
- Hypothesis B: The attack may be part of a broader strategy to disrupt critical infrastructure, possibly by state-sponsored actors. The strategic importance of UMMC’s facilities supports this, but there is no direct evidence linking the attack to geopolitical motives.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the typical ransomware communication pattern and lack of geopolitical indicators. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the emergence of a claim by a known ransomware group or evidence of state-sponsored involvement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The attackers are primarily financially motivated; UMMC’s emergency procedures can sustain operations; the attack is isolated to UMMC.
- Information Gaps: Identity and motives of the attackers; extent of data compromised; potential for further attacks on related infrastructure.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias towards financial motives; potential misinformation from attackers to manipulate negotiations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This ransomware attack could set a precedent for targeting critical healthcare infrastructure, increasing risks of future attacks. It may also prompt regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cybersecurity measures in the healthcare sector.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory actions and international cooperation on cybersecurity.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alert for similar attacks on critical infrastructure, necessitating improved threat detection and response capabilities.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing health IT systems and potential for information operations exploiting the incident.
- Economic / Social: Disruption to healthcare services could impact public trust and economic stability, particularly in regions heavily reliant on UMMC.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of healthcare IT systems, engage with cybersecurity experts, and communicate transparently with stakeholders.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures, including backup systems and staff training, and strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity agencies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Attack resolved with minimal data loss and improved cybersecurity measures.
- Worst Case: Prolonged disruption and significant data breach, leading to regulatory penalties and loss of public trust.
- Most Likely: Resolution through negotiation with attackers, followed by increased cybersecurity investments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- LouAnn Woodward, Dean of the School of Medicine at UMMC
- Dr. Alan Jones, Associate Vice Chancellor for Health Affairs at UMMC
- U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, ransomware, healthcare cybersecurity, critical infrastructure, UMMC, cyberattack response, emergency operations, data protection
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us