Emerging Android malware leverages Gemini AI for real-time adaptation, but risks remain minimal for users
Published on: 2026-02-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Android malware is now using Googles own Gemini AI to adapt in real time
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
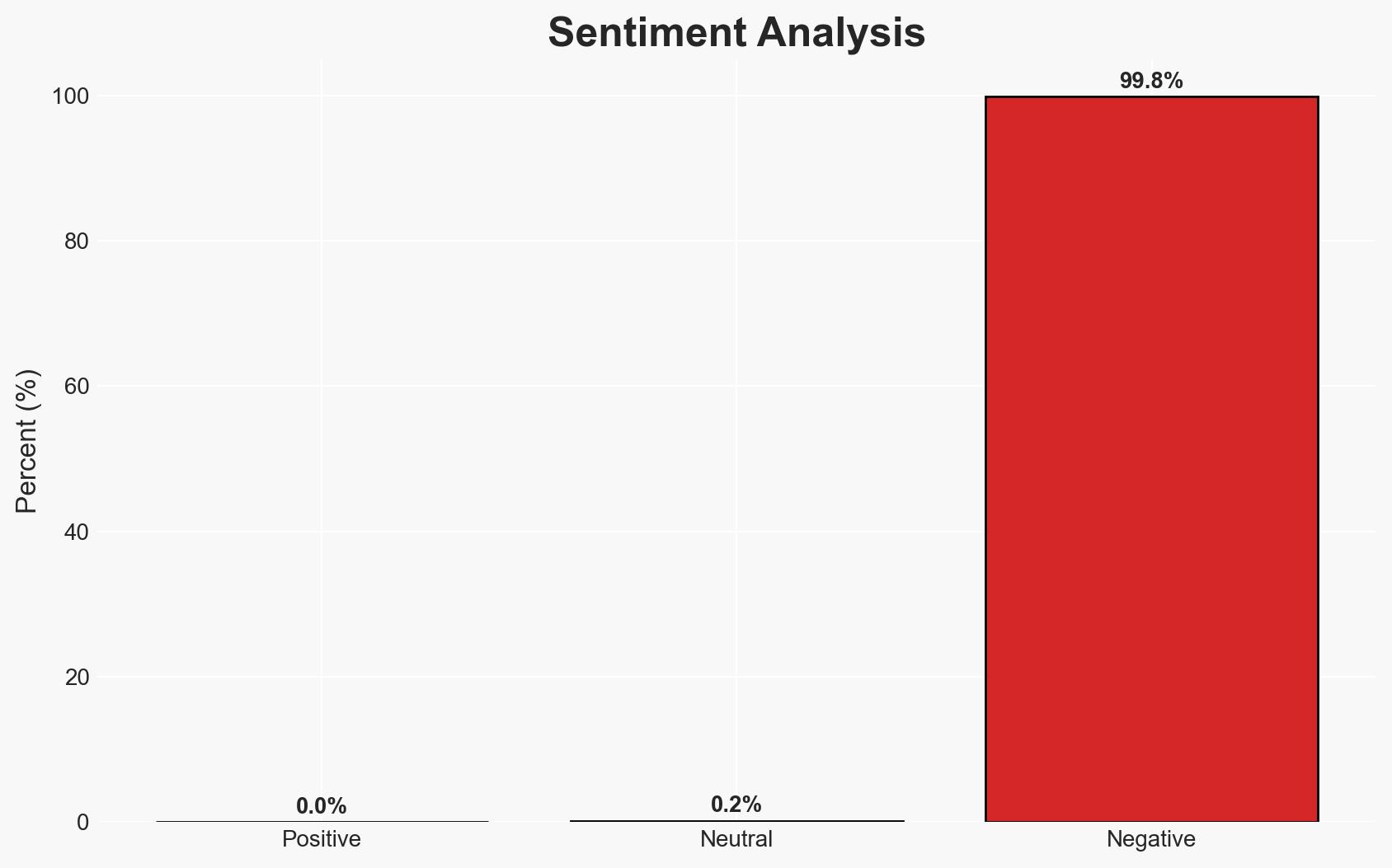
The emergence of Android malware leveraging Google’s Gemini AI represents a significant evolution in malware adaptability and sophistication. The most likely hypothesis is that this development is an early-stage proof-of-concept with limited current impact but high potential for future exploitation. While Google Play Protect currently mitigates risks, the adaptability of such malware poses a moderate confidence threat to Android users, particularly those downloading apps from non-official sources.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: PromptSpy is a proof-of-concept malware designed to test the integration of AI into malware execution. Supporting evidence includes the lack of widespread detection and the use of a dedicated domain for distribution, suggesting an experimental phase. However, the impersonation of a major bank indicates potential for real-world application.
- Hypothesis B: PromptSpy is an operational malware campaign with active targeting of Android users. This is supported by its advanced capabilities and the impersonation of a major bank, but contradicted by the absence of telemetry data indicating widespread distribution.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the lack of evidence for widespread deployment and the experimental nature of the AI integration. Indicators such as increased detection in telemetry or reports of successful breaches could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Google Play Protect effectively mitigates known threats; the malware’s AI component is currently limited in scope; ESET’s findings are comprehensive and accurate.
- Information Gaps: The full extent of PromptSpy’s distribution and the effectiveness of its AI component in diverse environments.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in relying on vendor reports; possibility of deceptive practices by threat actors to mask true capabilities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to more sophisticated malware that is harder to detect and mitigate, influencing the broader cybersecurity landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased tension between tech companies and governments over AI regulation and cybersecurity responsibilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat landscape requiring updated defensive strategies and tools.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for AI-driven malware to bypass traditional security measures, increasing the need for advanced detection methods.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact from increased cybersecurity costs and social unrest from privacy breaches.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of non-official app sources; increase public awareness about downloading from trusted sources.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop AI-based detection and mitigation strategies; strengthen partnerships with cybersecurity firms and tech companies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: PromptSpy remains a limited proof-of-concept with no significant impact.
- Worst: Widespread adoption of AI-driven malware leading to significant breaches.
- Most-Likely: Gradual increase in AI-driven malware sophistication, necessitating ongoing adaptation of security measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Google (technology provider)
- ESET (cybersecurity firm)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI integration, malware adaptation, Android security, threat intelligence, digital espionage, cybersecurity policy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us