Google is making sending end-to-end encrypted emails easy – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-04-02
Intelligence Report: Google is making sending end-to-end encrypted emails easy – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
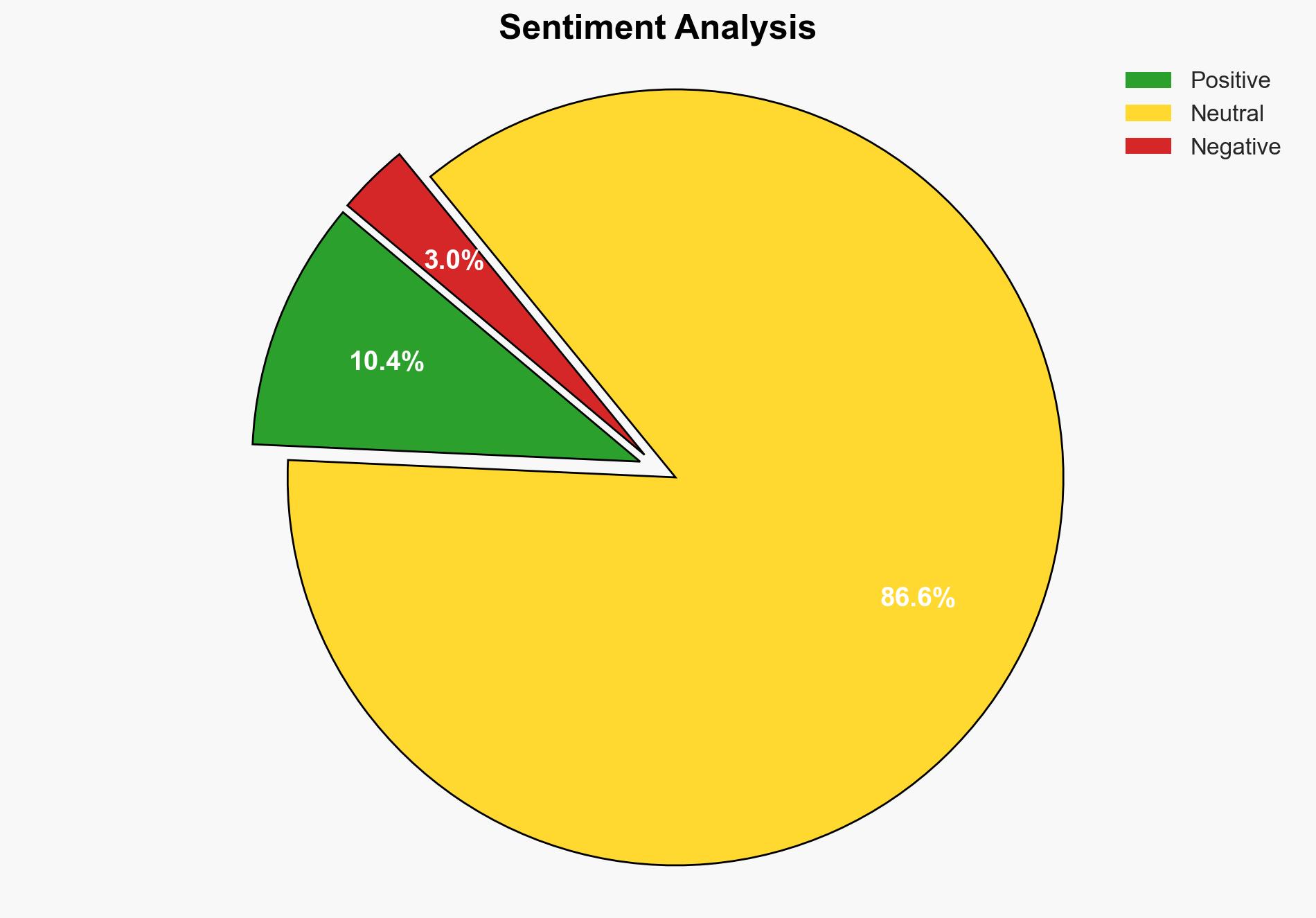
Google has announced enhancements to its Gmail service, making end-to-end encrypted email (EEE) more accessible to enterprise users. This development simplifies the encryption process, potentially increasing the adoption of secure communication practices across organizations. The move is expected to enhance data protection and privacy for Gmail users, both within and outside enterprise environments.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
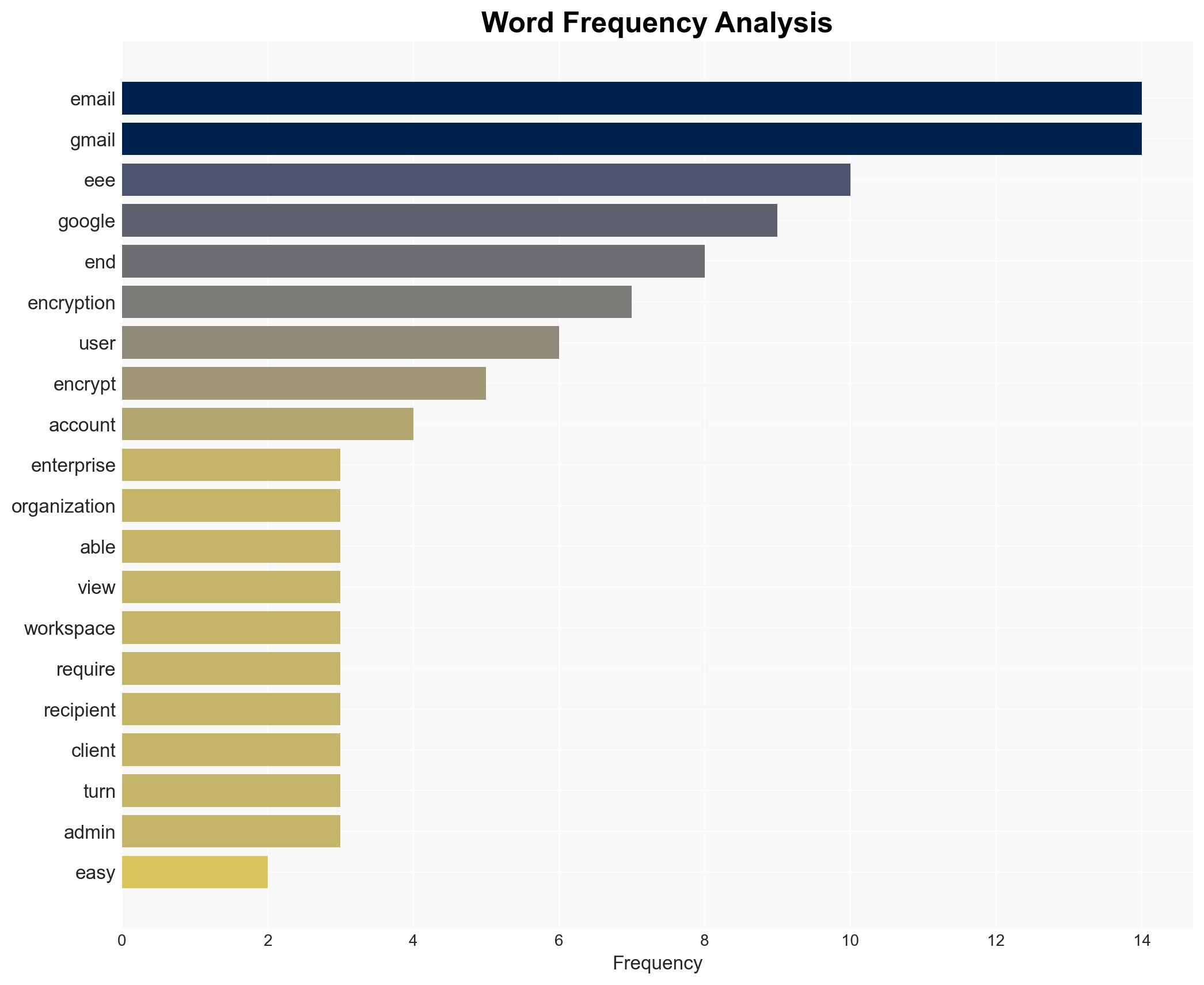
Google is introducing a simplified method for sending end-to-end encrypted emails through its Gmail service, specifically targeting enterprise accounts. The new feature allows users to encrypt emails with minimal effort, requiring only a few clicks. This advancement is significant as it democratizes access to encryption technology, previously reserved for organizations with substantial resources. The process involves a client-side encryption mechanism, ensuring that email content is protected from unauthorized access.
Recipients with Gmail accounts will automatically decrypt the emails, while non-Gmail users will receive an invitation to view and reply to encrypted messages. This approach enhances security while maintaining user convenience. The introduction of client-side encryption as a default mode for Gmail administrators further underscores Google’s commitment to data privacy.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The widespread adoption of end-to-end encryption in Gmail could have several implications:
- Increased data security for enterprises, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Potential challenges for law enforcement and intelligence agencies in accessing communications for investigative purposes.
- Encouragement for other email service providers to enhance their encryption offerings, potentially leading to industry-wide improvements in data security.
While the move enhances user privacy, it may also complicate efforts to monitor and intercept communications for national security purposes. This could lead to regulatory scrutiny and calls for backdoor access to encrypted communications.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Government agencies should engage with technology companies to balance privacy and security needs, potentially exploring frameworks for lawful access to encrypted communications.
- Organizations should update their data protection policies to incorporate the use of end-to-end encryption, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Consider investing in training programs to educate employees on the importance and use of encryption technologies.
Outlook:
Best-case scenario: Widespread adoption of encryption leads to enhanced data security across sectors without significant regulatory pushback.
Worst-case scenario: Increased encryption usage hampers law enforcement efforts, leading to stringent regulations and potential conflicts between technology companies and governments.
Most likely outcome: A gradual increase in encryption adoption with ongoing dialogues between stakeholders to address privacy and security concerns.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report mentions Johney Burke and Julien Duplant as significant individuals involved in the development and explanation of the new encryption features. The primary entity involved is Google, specifically its Gmail and Google Workspace services.