SpyNote Malware Targets Android Users with Fake Google Play Pages – Infosecurity Magazine
Published on: 2025-04-10
Intelligence Report: SpyNote Malware Targets Android Users with Fake Google Play Pages – Infosecurity Magazine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
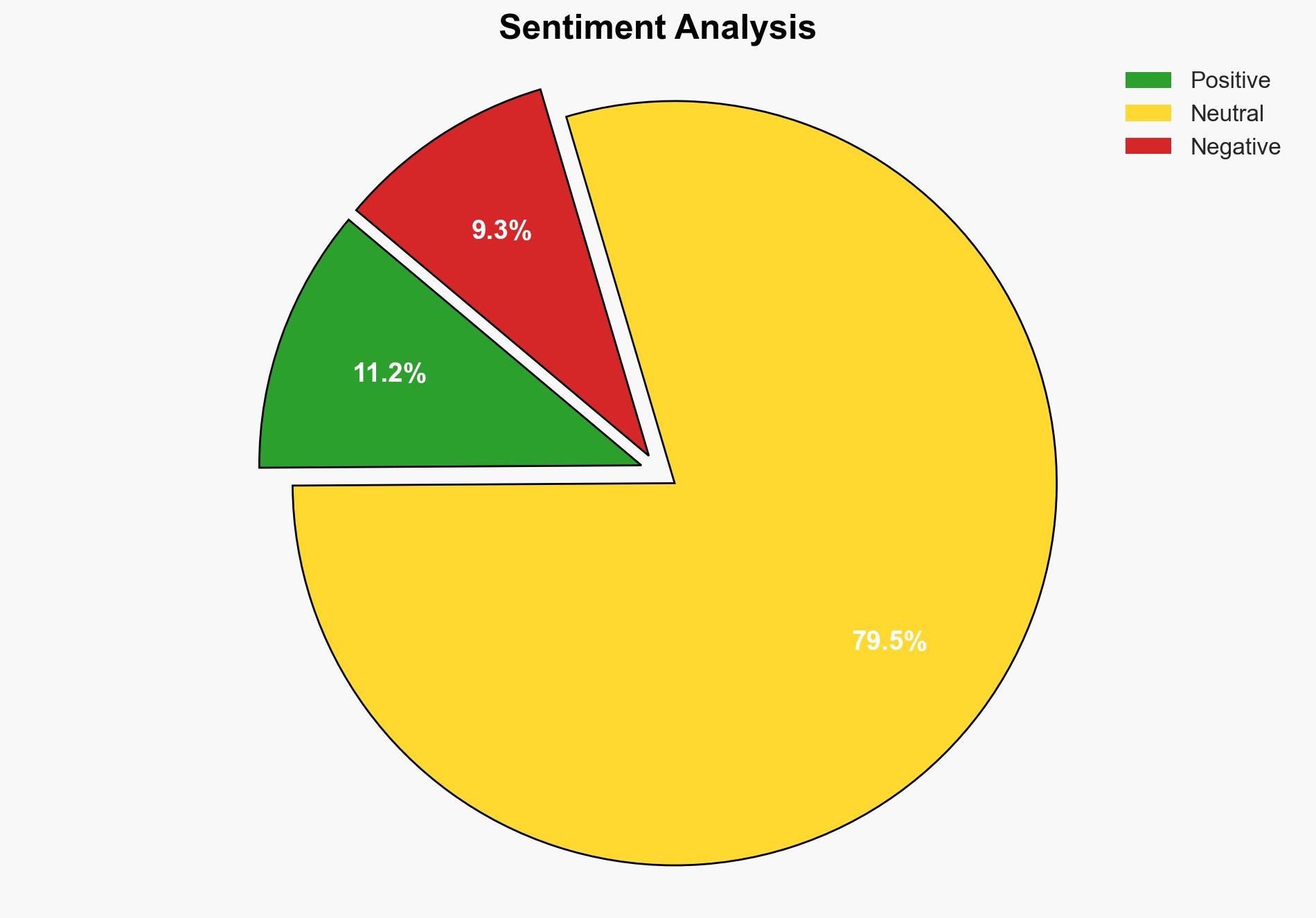
A sophisticated Android malware campaign has been identified, utilizing fake Google Play Store pages to distribute SpyNote, a remote access Trojan (RAT). The campaign employs newly registered domains to mimic legitimate app pages, deceiving users into downloading malicious APK files. SpyNote’s capabilities include intercepting communications, remote surveillance, and device control. Evidence suggests a potential China-based origin, with links to previous espionage campaigns targeting Indian defense personnel. Immediate action is recommended to mitigate risks to Android users and national security.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
The campaign leverages deceptive tactics by creating fake app pages that replicate the Google Play Store interface. These pages include elements such as image carousels and “Install” buttons, which, when clicked, execute scripts to download a malicious APK. The initial APK acts as a dropper, deploying a secondary payload containing SpyNote’s core functionalities. The malware communicates with command-and-control servers using embedded IP addresses and ports, allowing threat actors to execute a wide range of surveillance and control actions on infected devices.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The deployment of SpyNote poses significant risks to national security, particularly if leveraged for espionage against government personnel or critical infrastructure. The malware’s ability to intercept communications and access sensitive data could lead to breaches of confidential information. The potential China-based origin raises concerns about state-sponsored cyber activities targeting regional stability and economic interests. Additionally, the malware’s persistence and ability to evade detection complicate mitigation efforts.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Enhance cybersecurity awareness among Android users to recognize and avoid fake app pages.
- Implement stricter app vetting processes and domain registration monitoring to prevent similar campaigns.
- Encourage collaboration between government agencies and cybersecurity firms to share intelligence and develop countermeasures.
Outlook:
In the best-case scenario, increased awareness and improved security measures could significantly reduce the impact of such malware campaigns. In the worst-case scenario, failure to address the threat could lead to widespread data breaches and compromised national security. The most likely outcome involves ongoing efforts to mitigate risks while adapting to evolving tactics by threat actors.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report mentions DomainTools as the entity that discovered the new campaign. Additionally, the malware has been linked to advanced persistent threat groups such as OilRig and APT-C-37.