Why remote work is a security minefield and what you can do about it – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-04-11
Intelligence Report: Why remote work is a security minefield and what you can do about it – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
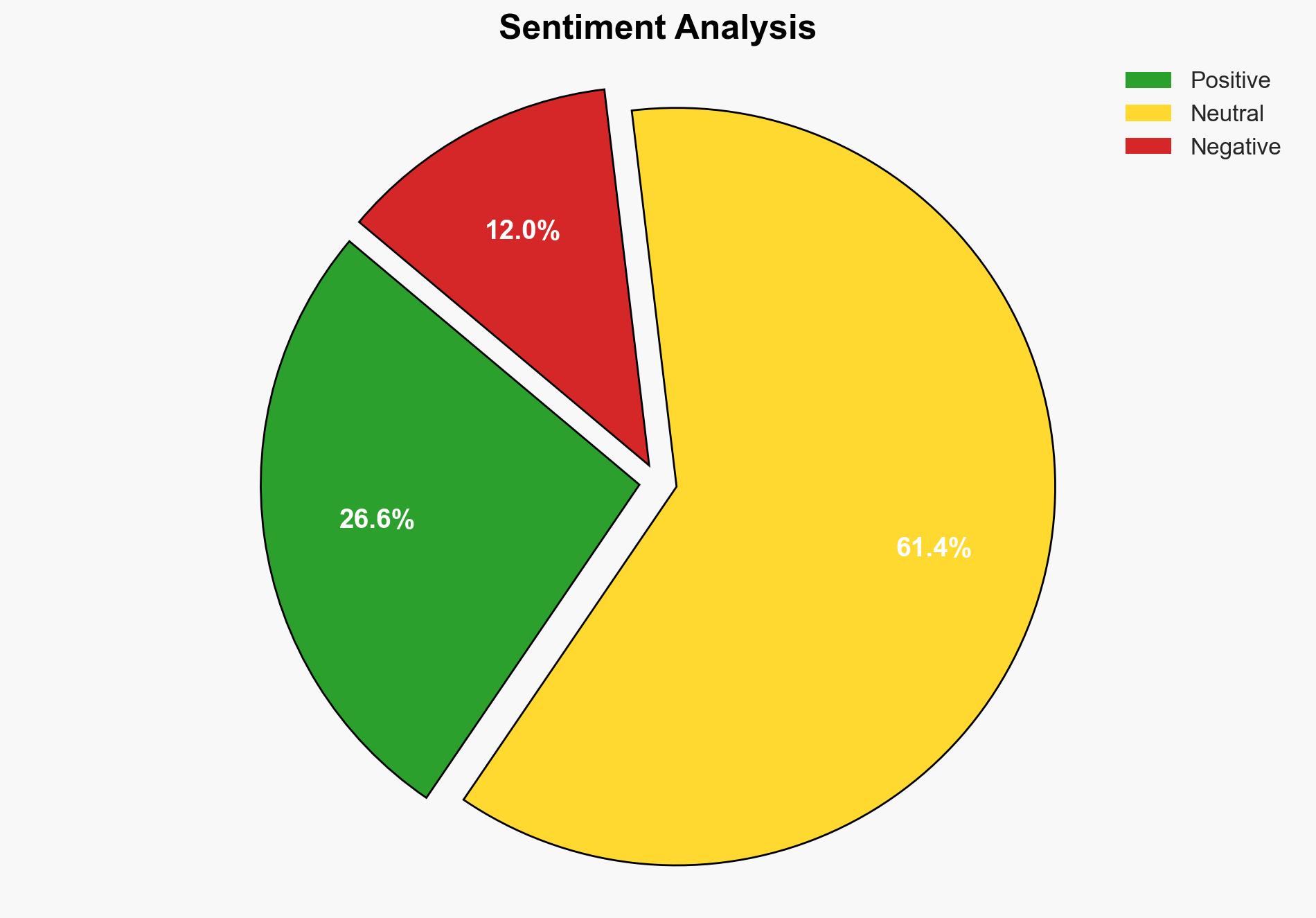
Remote work, while beneficial for operational flexibility, presents significant cybersecurity challenges. Key vulnerabilities include unsecured networks, the use of personal devices, and increased susceptibility to phishing and social engineering attacks. To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement comprehensive security policies, enhance network and device security, and foster a security-first culture. Immediate action is required to protect sensitive data and maintain operational integrity.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied for this analysis:
General Analysis
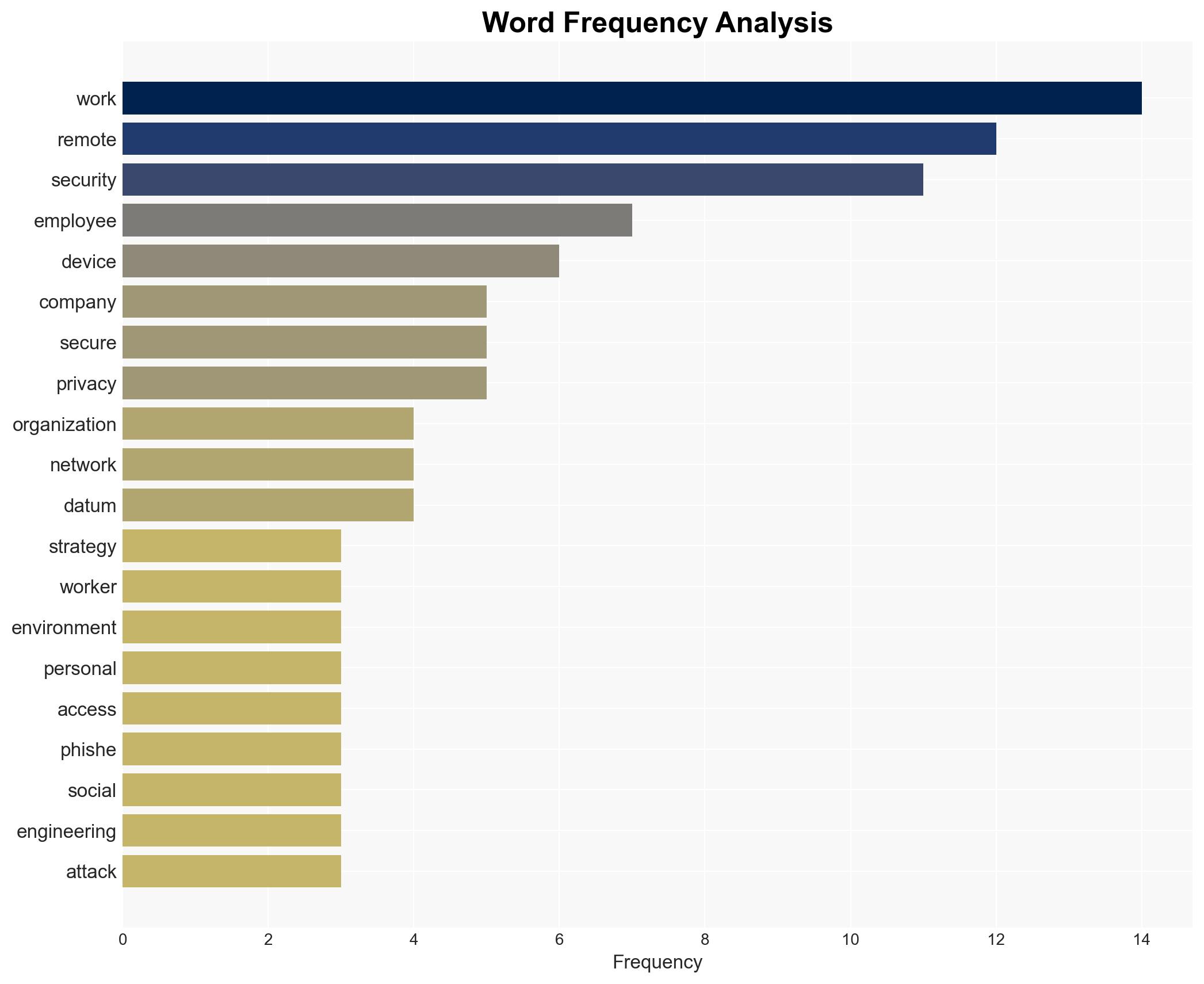
Remote work environments expose organizations to heightened cybersecurity risks. Unsecured home and public Wi-Fi networks lack robust security features, making data transmission vulnerable to interception. The prevalent use of personal devices, which often lack necessary security updates and antivirus protection, further exacerbates these vulnerabilities. Additionally, remote workers are more prone to phishing and social engineering attacks due to isolation and reduced direct verification capabilities. Cybercriminals exploit these conditions by impersonating IT staff or colleagues, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift to remote work poses significant risks to national security and economic interests. Unsecured networks and devices can lead to data breaches, compromising sensitive information and intellectual property. The increased likelihood of phishing attacks can result in financial losses and reputational damage. Furthermore, the lack of direct oversight in remote work environments can lead to compliance issues and regulatory breaches, affecting organizational stability and trust.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
Recommendations:
- Develop and enforce comprehensive security policies, including secure password practices, multi-factor authentication, and data encryption.
- Mandate the use of VPNs and encrypted Wi-Fi connections for remote work to secure data transmission.
- Implement regular security training for employees to recognize phishing attempts and secure device usage.
- Adopt a zero trust model to verify every access request, enhancing security across the organization.
- Establish incident response plans to address data breaches promptly and effectively.
Outlook:
In a best-case scenario, organizations adopting robust security measures will experience reduced cybersecurity incidents and maintain operational integrity. In a worst-case scenario, failure to address remote work vulnerabilities could lead to significant data breaches and financial losses. The most likely outcome is a gradual improvement in security posture as organizations adapt to the evolving threat landscape and implement recommended strategies.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
The report does not mention specific individuals or organizations by name. However, it emphasizes the importance of collaboration among all stakeholders, including executives and remote workers, to foster a security-first culture and enhance cybersecurity resilience.