Why Claude’s Comment Paper Is a Poor Rebuttal – Victoramartinez.com
Published on: 2025-06-16
Intelligence Report: Why Claude’s Comment Paper Is a Poor Rebuttal – Victoramartinez.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
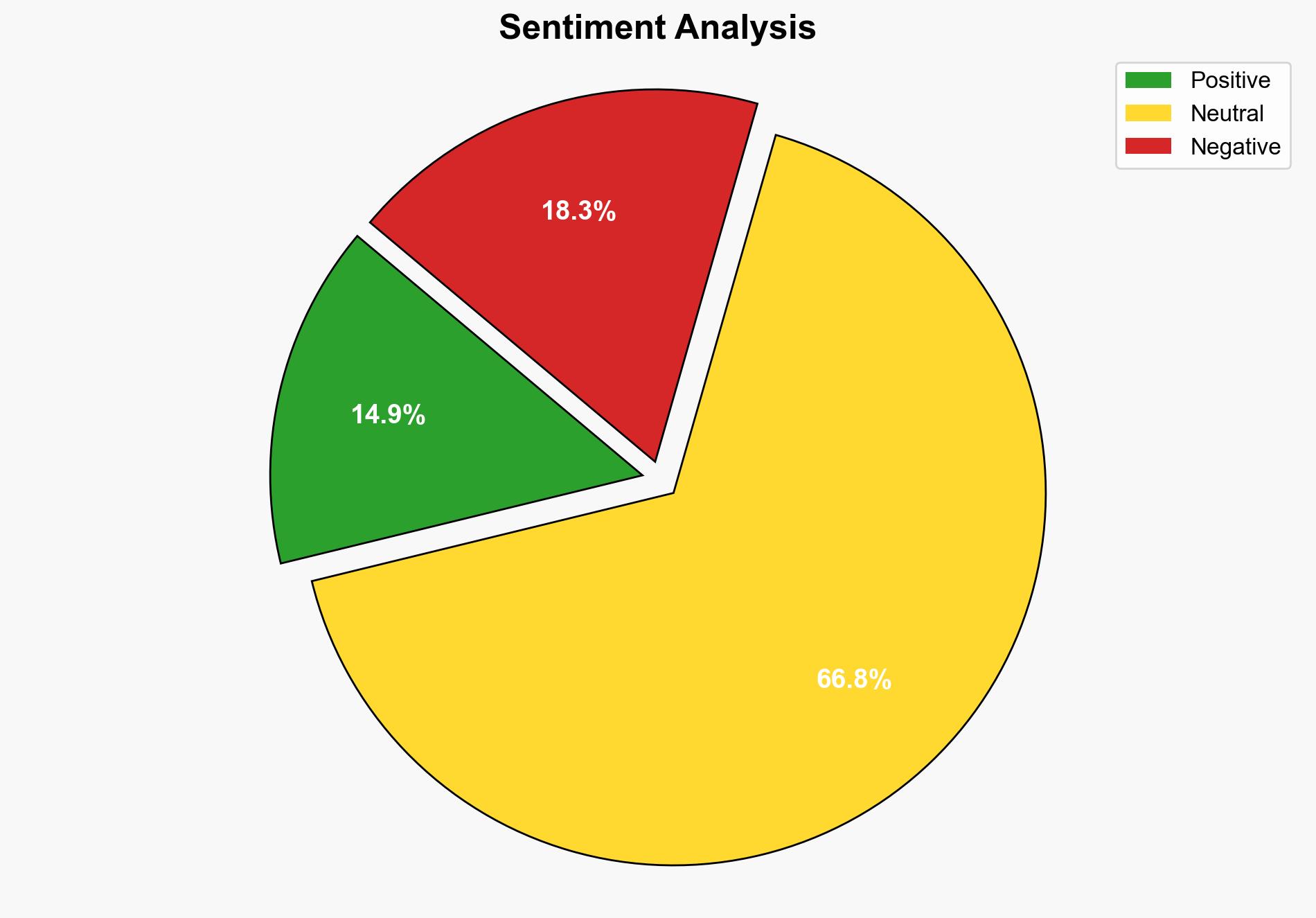
The rebuttal to Apple’s paper on Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) fails to address critical mathematical and conceptual points, undermining its credibility. The rebuttal overlooks key findings from Apple’s research, particularly regarding token growth and reasoning complexity. Recommendations include further investigation into the limitations of LRMs and refinement of methodologies to enhance model accuracy and efficiency.
2. Detailed Analysis
The following structured analytic techniques have been applied to ensure methodological consistency:
Adversarial Threat Simulation
The rebuttal’s failure to accurately simulate the computational demands of complex problems like the Tower of Hanoi highlights vulnerabilities in reasoning models. This oversight suggests potential weaknesses in adversarial modeling, which could be exploited in cybersecurity contexts.
Indicators Development
The rebuttal’s inability to recognize systematic reasoning patterns indicates a gap in detecting behavioral anomalies, crucial for early threat detection in AI systems.
Bayesian Scenario Modeling
The rebuttal’s paradoxical findings, where models reduce reasoning effort as problem complexity increases, suggest a need for improved probabilistic inference to predict model behavior accurately.
3. Implications and Strategic Risks
The rebuttal’s shortcomings highlight systemic vulnerabilities in AI reasoning models, which could have broader implications for AI deployment in critical sectors. The failure to address these issues may lead to cascading effects, such as compromised decision-making in automated systems and increased susceptibility to cyber threats.
4. Recommendations and Outlook
- Conduct comprehensive reviews of LRM methodologies to address identified mathematical errors and reasoning limitations.
- Develop enhanced models that accurately simulate complex problem-solving scenarios to improve AI resilience.
- Scenario-based projections suggest that without intervention, AI models may continue to underperform in high-stakes environments, posing significant risks.
5. Key Individuals and Entities
Subbaro Kambhampati, Yann LeCun, Andreas Kirsch, Shojaee
6. Thematic Tags
artificial intelligence, computational modeling, cybersecurity, reasoning models