A businesss cyber insurance policy included ransom coverage but when they needed it the insurer refused to pay Why – Databreaches.net
Published on: 2025-10-19
Intelligence Report: A business’s cyber insurance policy included ransom coverage but when they needed it the insurer refused to pay – Databreaches.net
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
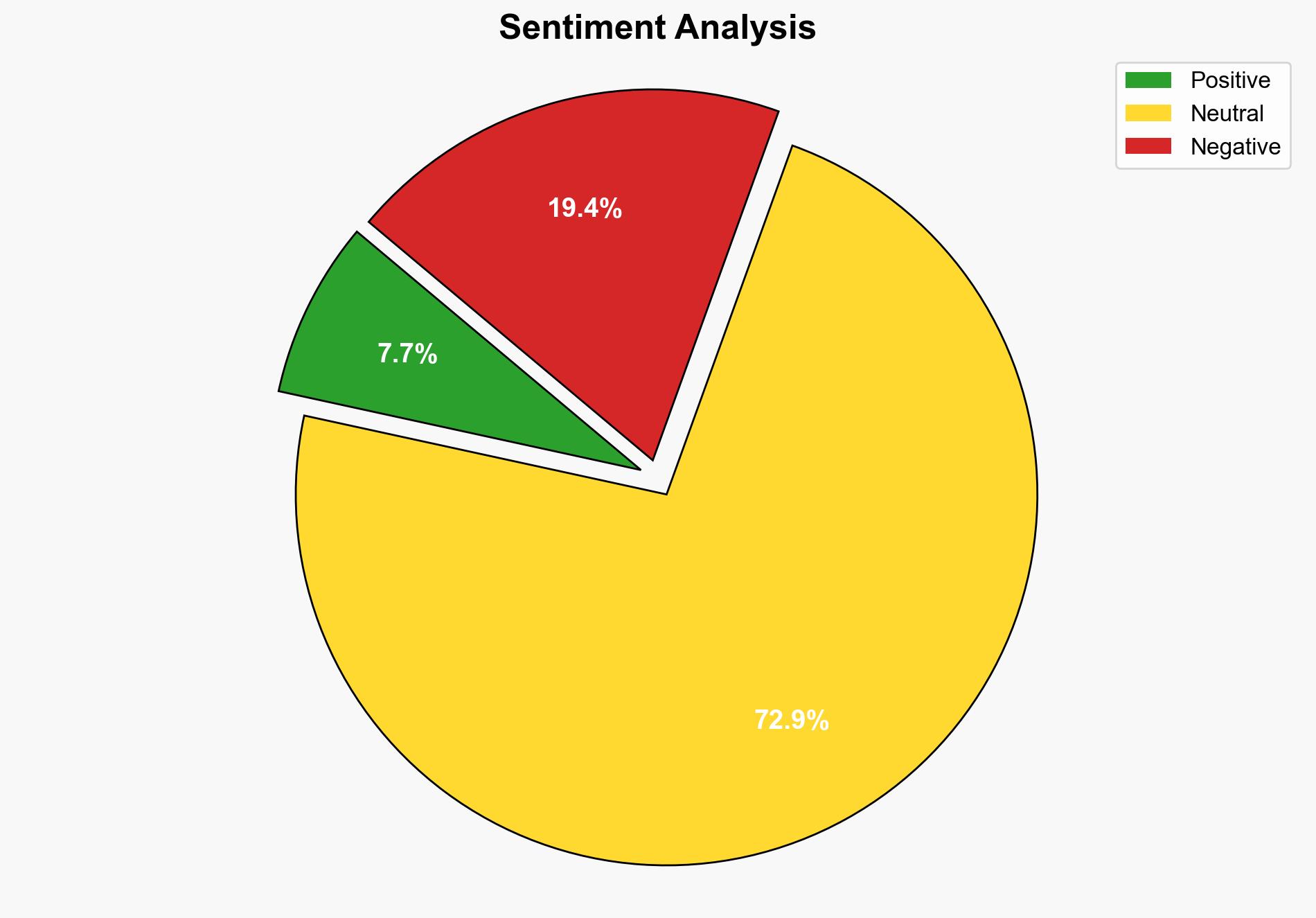
The most supported hypothesis is that the insurer refused to pay due to a breach of the policy’s cooperation clause by the insured business. Confidence level: Moderate. It is recommended that businesses enhance their understanding of policy requirements and ensure compliance to avoid similar issues.
2. Competing Hypotheses
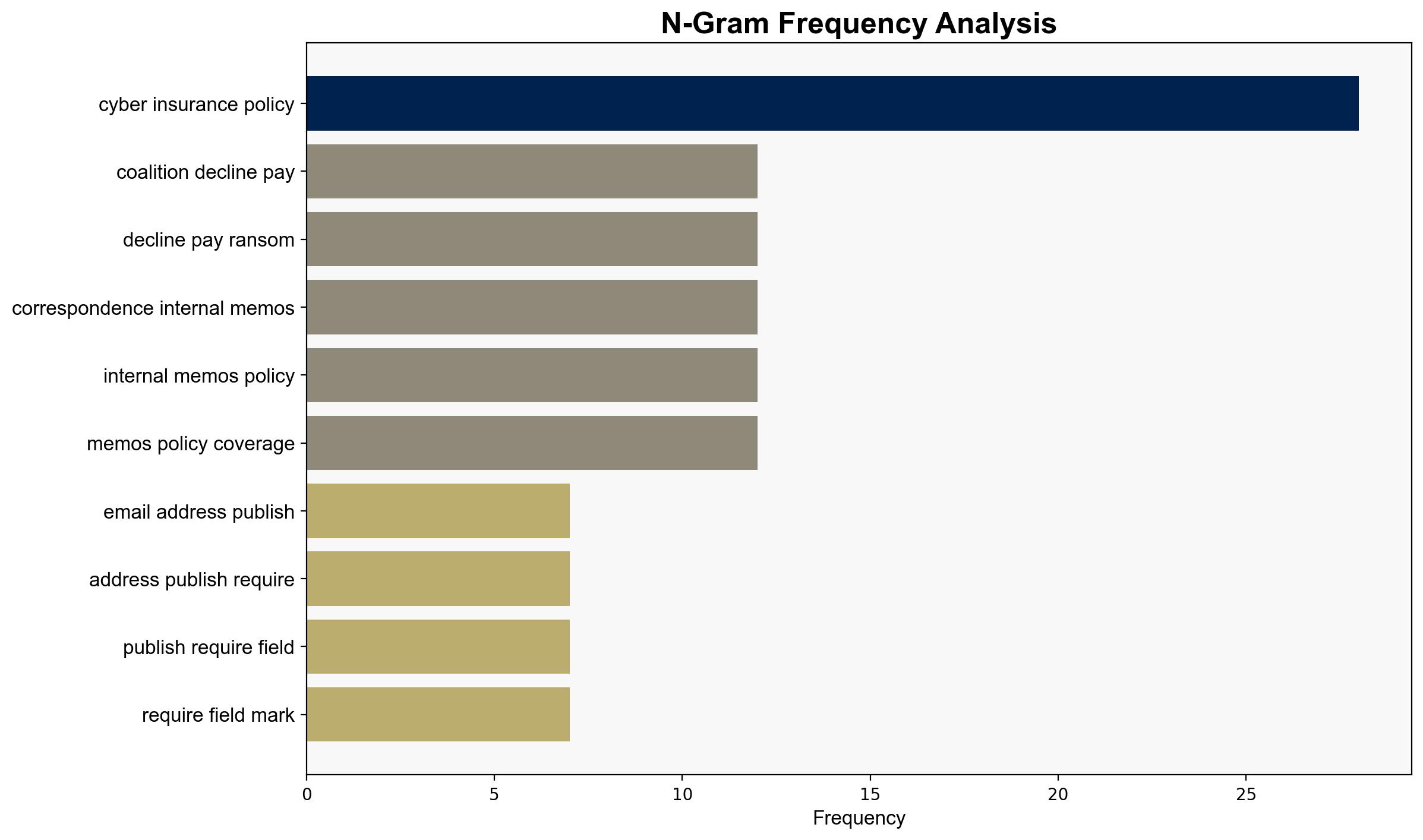
1. **Hypothesis A**: The insurer refused to pay because the business violated the cooperation clause by not disclosing the existence of the insurance policy to the ransomware attackers, which is a critical requirement for coverage activation.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The insurer’s refusal was a strategic decision to avoid setting a precedent of paying ransoms, which could encourage further cybercriminal activity.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the evidence that the business did not fully comply with the policy’s cooperation requirements, as indicated by the failure to disclose the insurance policy to the attackers and the insurer’s emphasis on cooperation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the insurer’s decision was solely based on policy compliance issues. Another assumption is that the business was aware of all policy requirements.
– **Red Flags**: The lack of clarity on whether the ransom demand was paid and the insurer’s specific reasons for refusal remain unclear. The possibility of strategic non-payment by the insurer to deter future claims is not fully explored.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic Risks**: Non-payment of ransom could lead to significant financial losses for the business, impacting its operations and market position.
– **Cyber Risks**: This incident could embolden ransomware groups to target businesses with known insurance policies, expecting non-compliance with policy terms.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Increased ransomware activity could strain international relations if attacks are traced back to state-sponsored actors.
– **Psychological Risks**: Businesses may lose confidence in cyber insurance as a risk mitigation tool, potentially leading to reduced uptake of such policies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Businesses should conduct regular reviews of their cyber insurance policies to ensure compliance with all terms and conditions.
- Insurers should provide clearer guidance and training to policyholders on compliance requirements.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Improved compliance leads to successful claims and reduced financial impact from cyberattacks.
- **Worst Case**: Continued non-compliance results in widespread non-payment of claims, undermining the cyber insurance market.
- **Most Likely**: Incremental improvements in compliance and insurer transparency lead to a gradual stabilization of the market.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
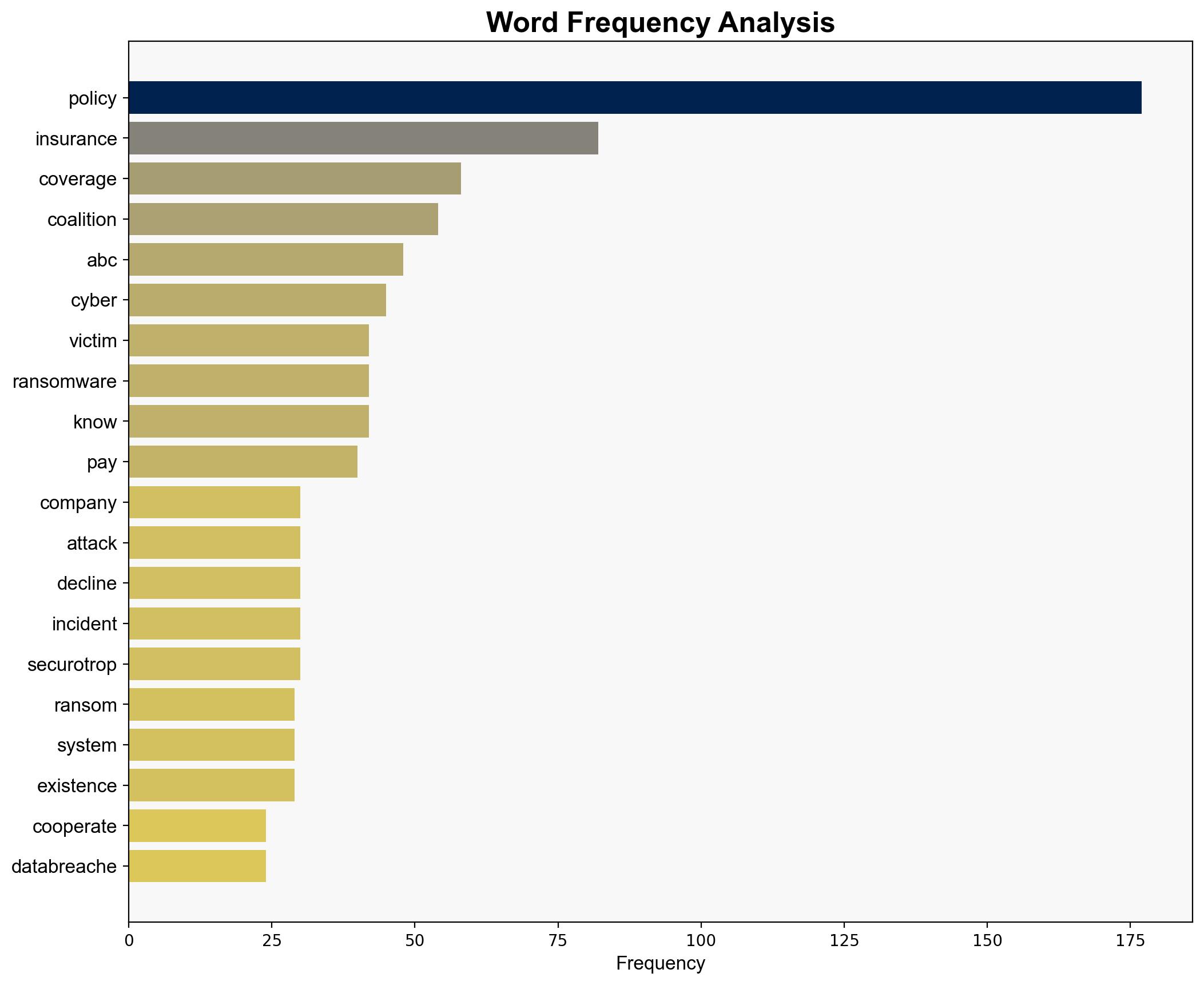
– Allardyce Bower Consulting (ABC)
– Coalition (Insurance Provider)
– Securotrop (Ransomware Group)
– Marco De Felice (Author)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, insurance compliance, ransomware, risk management