A National Consensus for Nepals Strategic Stability – Khabarhub.com
Published on: 2025-11-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
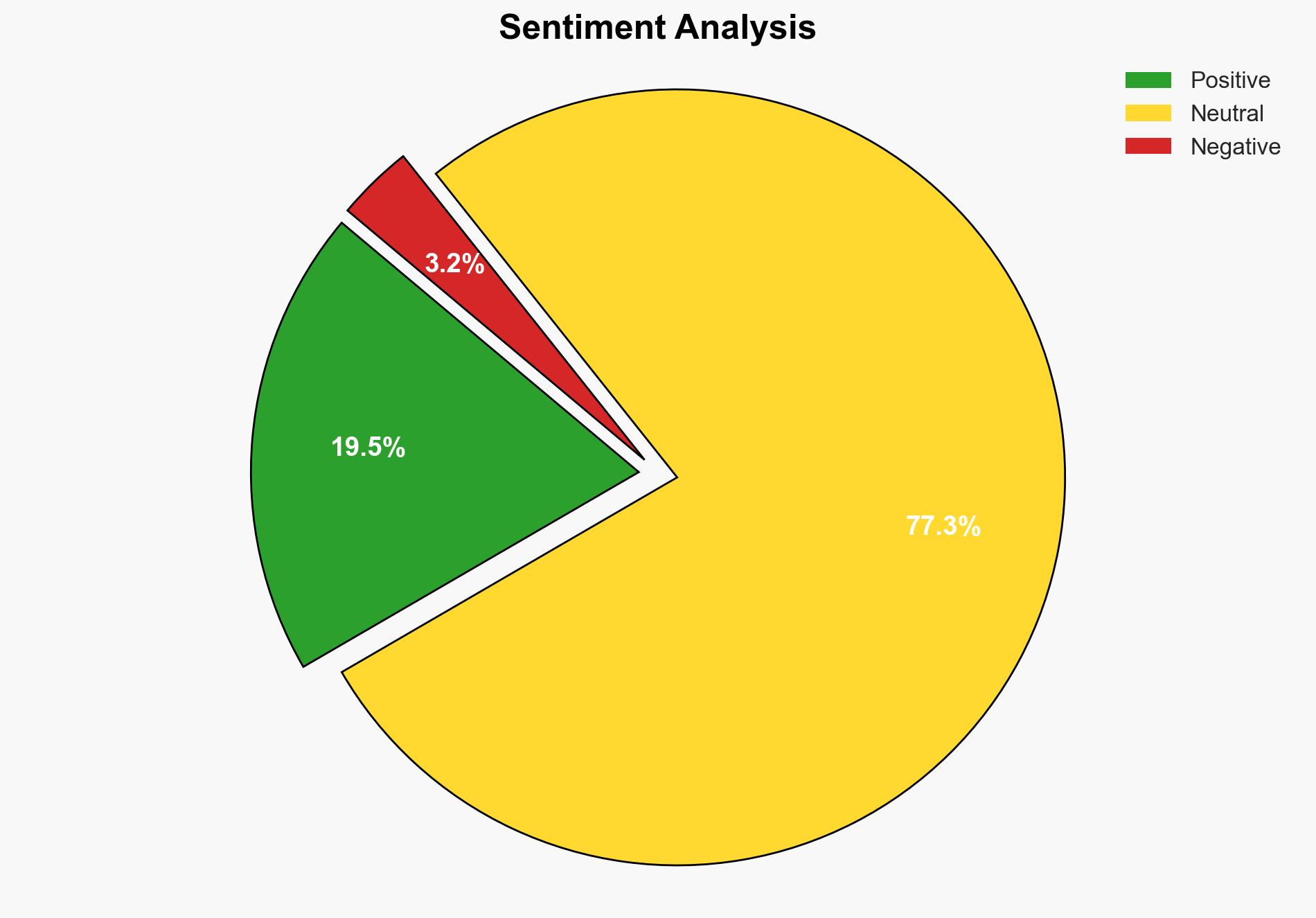
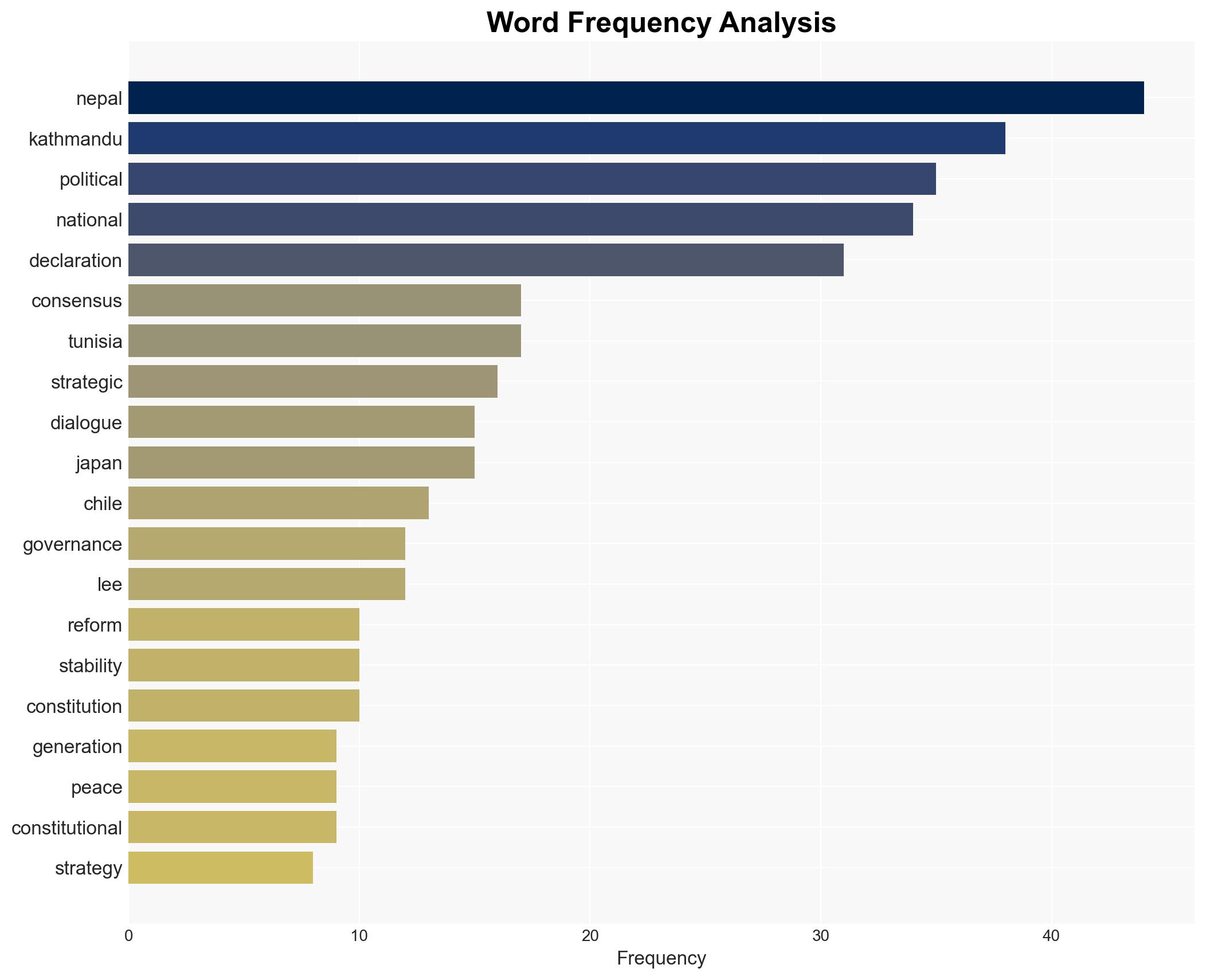
With a moderate confidence level, the most supported hypothesis is that Nepal’s current political landscape is at a critical juncture where strategic stability can be achieved through a national consensus that incorporates youth movements, civil society, and political elites. Recommended actions include fostering inclusive dialogue and revisiting governance models to ensure long-term stability and regional influence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Nepal will achieve strategic stability through a national consensus that integrates diverse political and social stakeholders, leading to effective governance reforms.
Hypothesis 2: Nepal will continue to experience political stagnation and instability due to entrenched corruption, generational inequality, and ineffective governance reforms, resulting in further social unrest.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to recent initiatives such as the interim government’s formation and trilateral dialogues, which indicate a willingness to address systemic issues. However, the success of these efforts depends on overcoming entrenched political interests and ensuring genuine inclusivity.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that political elites are genuinely committed to reform and that youth movements will remain peaceful and constructive.
Red Flags: Potential red flags include the risk of political elites co-opting reform efforts for personal gain and the possibility of youth movements becoming radicalized if reforms are perceived as insufficient.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
If Nepal successfully achieves a national consensus, it could stabilize its political environment and enhance its regional influence. However, failure to address governance gaps could lead to increased political fragmentation, economic instability, and potential exploitation by external geopolitical actors. Cyber and informational threats could also escalate if political divisions deepen.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Facilitate inclusive dialogues among political parties, youth representatives, and civil society to build a shared vision for governance reform.
- Implement transparent mechanisms to monitor and evaluate reform initiatives to prevent co-optation by political elites.
- Best-case scenario: Successful national consensus leads to effective governance reforms and regional stability.
- Worst-case scenario: Continued political stagnation results in increased social unrest and regional instability.
- Most-likely scenario: Incremental progress towards consensus with periodic setbacks due to entrenched political interests.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Key individuals include leaders of major political parties, youth movement representatives, and civil society leaders. Their roles are crucial in shaping the dialogue and reform process.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us