Adam Back Bitcoin faces no quantum risk for next 2040 years – Cointelegraph
Published on: 2025-11-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
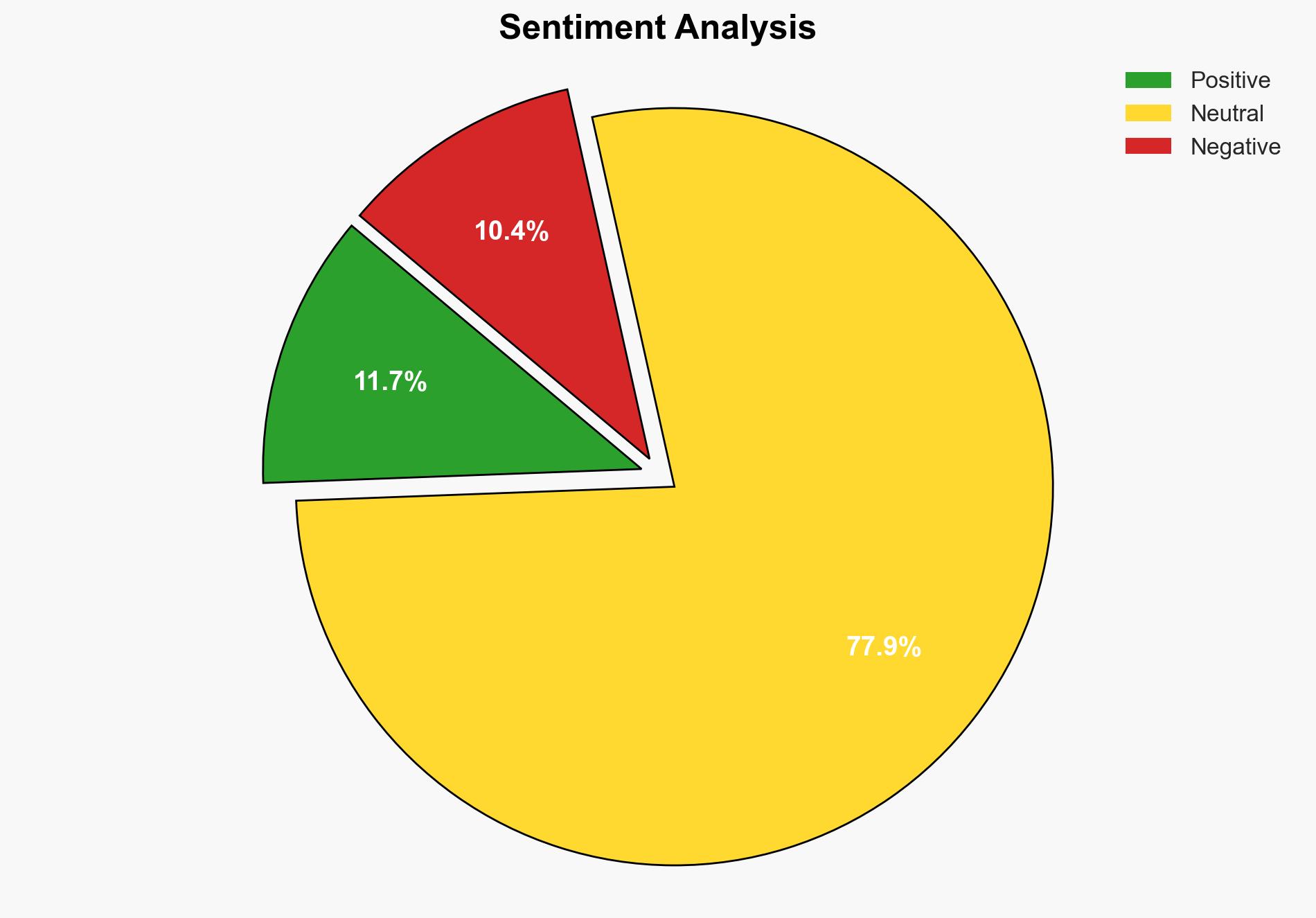
With a moderate confidence level, it is assessed that Bitcoin will not face a significant quantum computing threat in the next two decades. The most supported hypothesis is that quantum computing will not advance to a level capable of breaking Bitcoin’s cryptographic standards in the near future. Recommended action includes proactive investment in quantum-resistant cryptographic research and timely updates to Bitcoin’s security protocols.
2. Competing Hypotheses
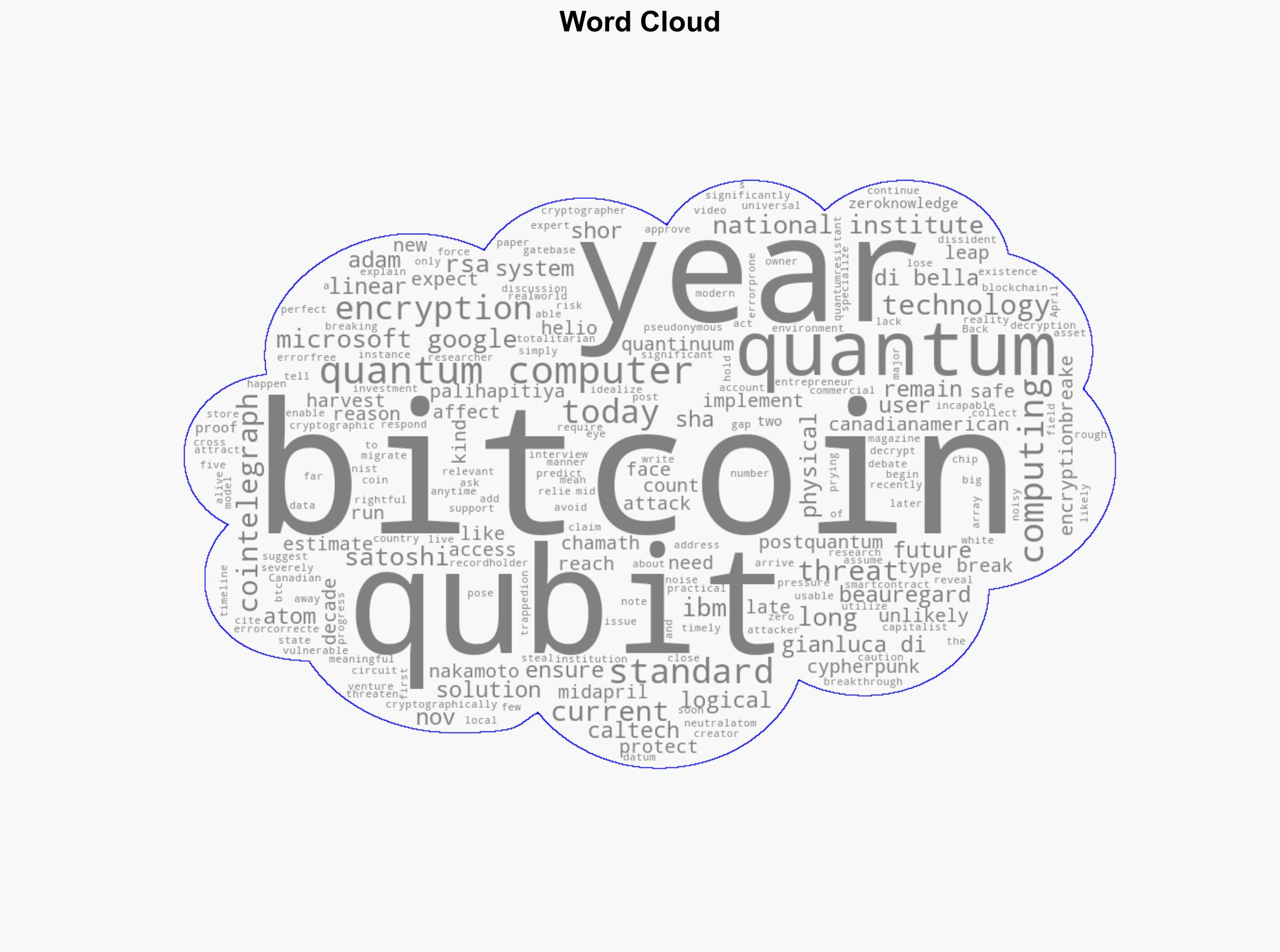
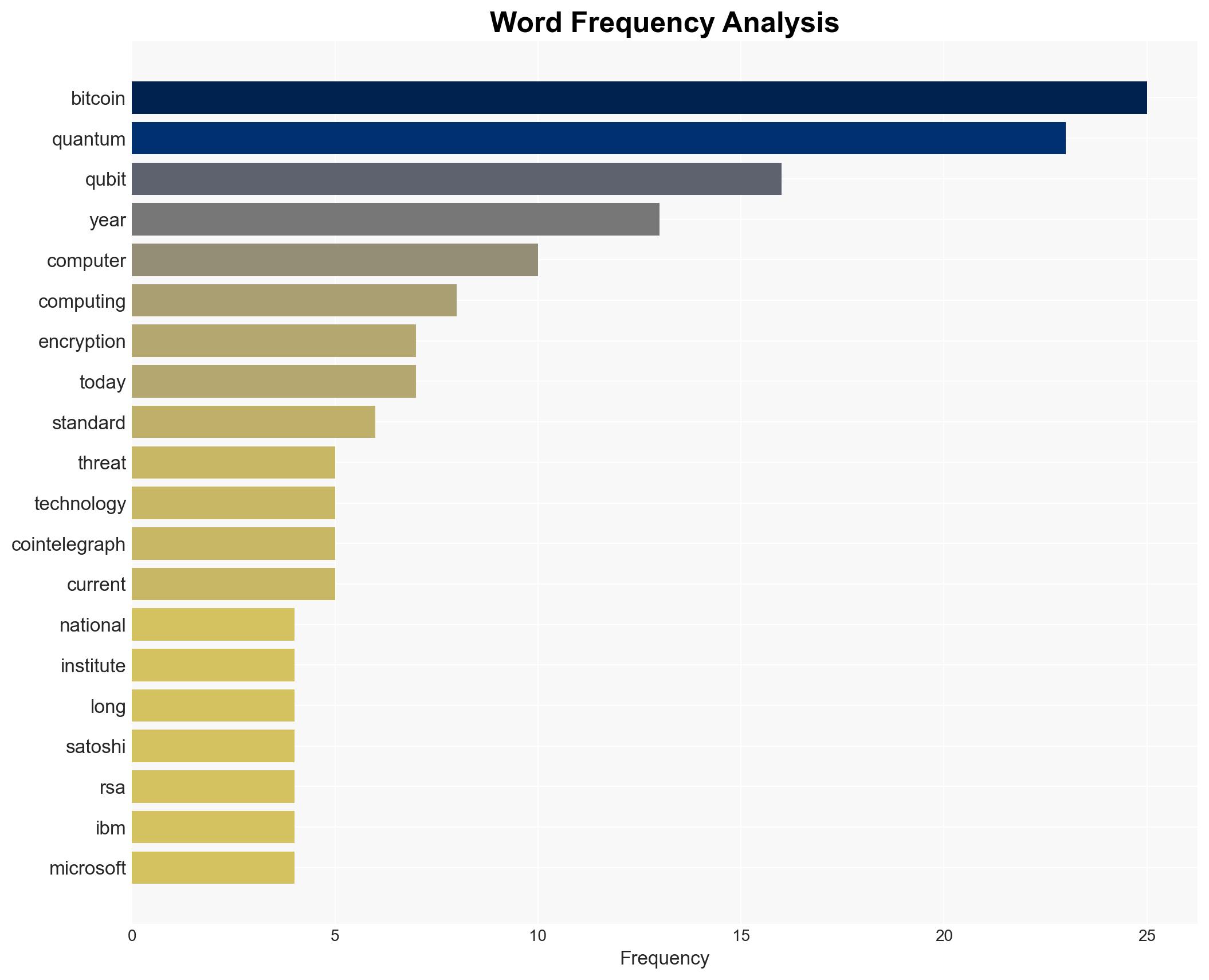
Hypothesis 1: Quantum computing will not pose a significant threat to Bitcoin within the next 20-40 years. This is supported by the current state of quantum computing, which is far from achieving the necessary qubit count to break Bitcoin’s cryptographic standards.
Hypothesis 2: Quantum computing will advance rapidly, posing a threat to Bitcoin’s security within the next 5-10 years. This is based on predictions by some experts and the significant investment in quantum research by major tech companies.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the current technological limitations and expert consensus on the timeline for quantum advancements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The assumption that quantum computing will progress linearly and not experience sudden breakthroughs is critical. Additionally, the belief that Bitcoin will implement quantum-resistant measures in a timely manner is assumed.
Red Flags: Over-reliance on current technological assessments without accounting for potential breakthroughs. Potential bias from stakeholders invested in Bitcoin’s stability.
Deception Indicators: Overly optimistic predictions about quantum computing capabilities from parties with vested interests in promoting fear or uncertainty in cryptocurrency markets.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Should quantum computing advance unexpectedly, there could be significant cyber and economic risks, including the potential for large-scale theft of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. This could lead to a loss of confidence in digital currencies and broader financial instability. Conversely, if Bitcoin successfully implements quantum-resistant measures, it could strengthen its position as a secure digital asset.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor advancements in quantum computing closely and establish partnerships with leading quantum research institutions.
- Invest in developing and testing quantum-resistant cryptographic protocols.
- Best-case scenario: Bitcoin implements quantum-resistant measures well before quantum computing becomes a threat, maintaining its security and market confidence.
- Worst-case scenario: Quantum computing advances rapidly, and Bitcoin fails to adapt in time, leading to significant security breaches and loss of value.
- Most-likely scenario: Gradual advancements in quantum computing with Bitcoin adapting its security protocols in a timely manner to mitigate risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
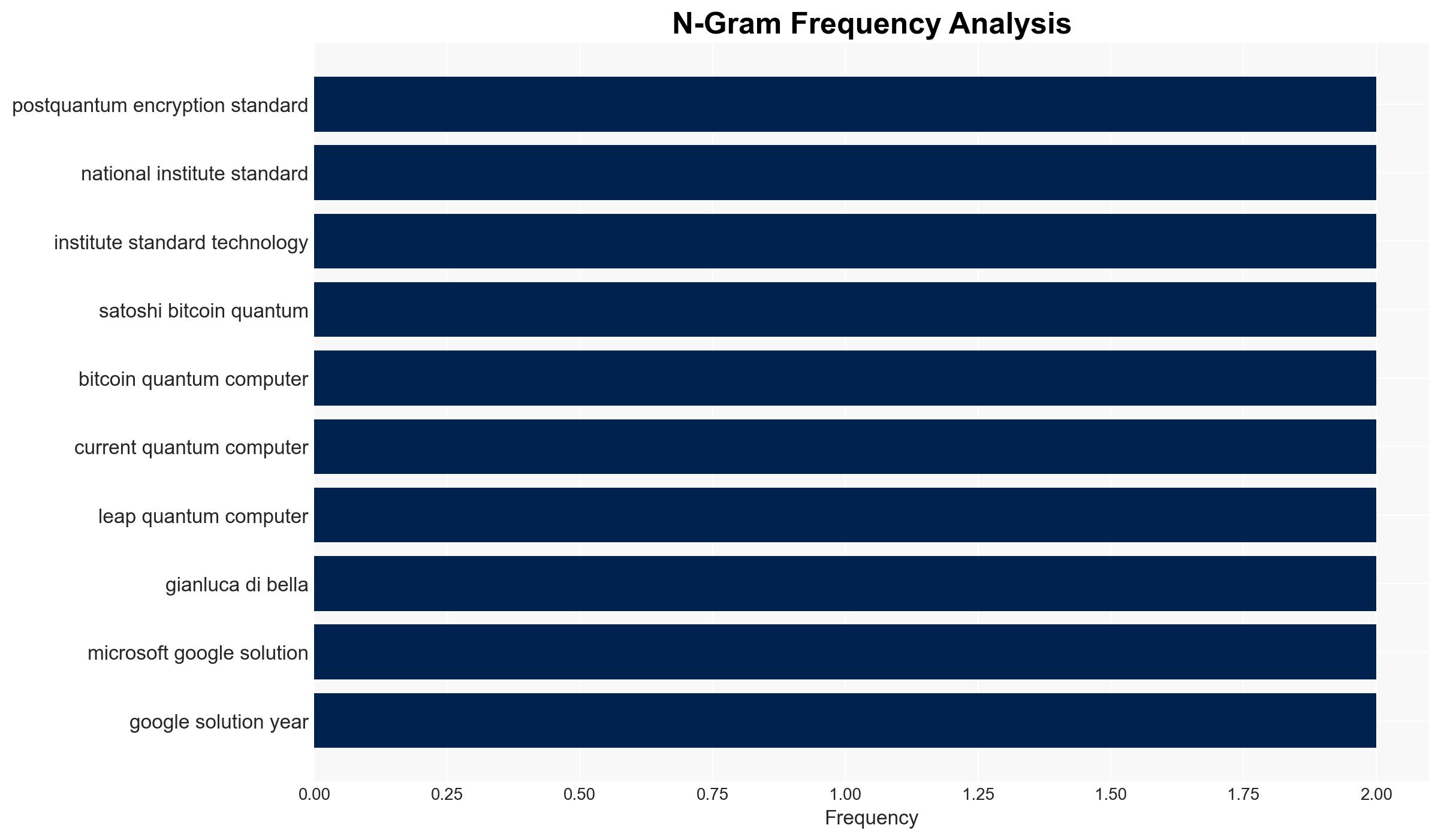
Adam Back, Chamath Palihapitiya, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), IBM, Microsoft, Google.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·