Adapting to New Threats: Strategies for SMBs to Enhance Cybersecurity in 2026
Published on: 2025-12-24
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Attacks are Evolving 3 Ways to Protect Your Business in 2026
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
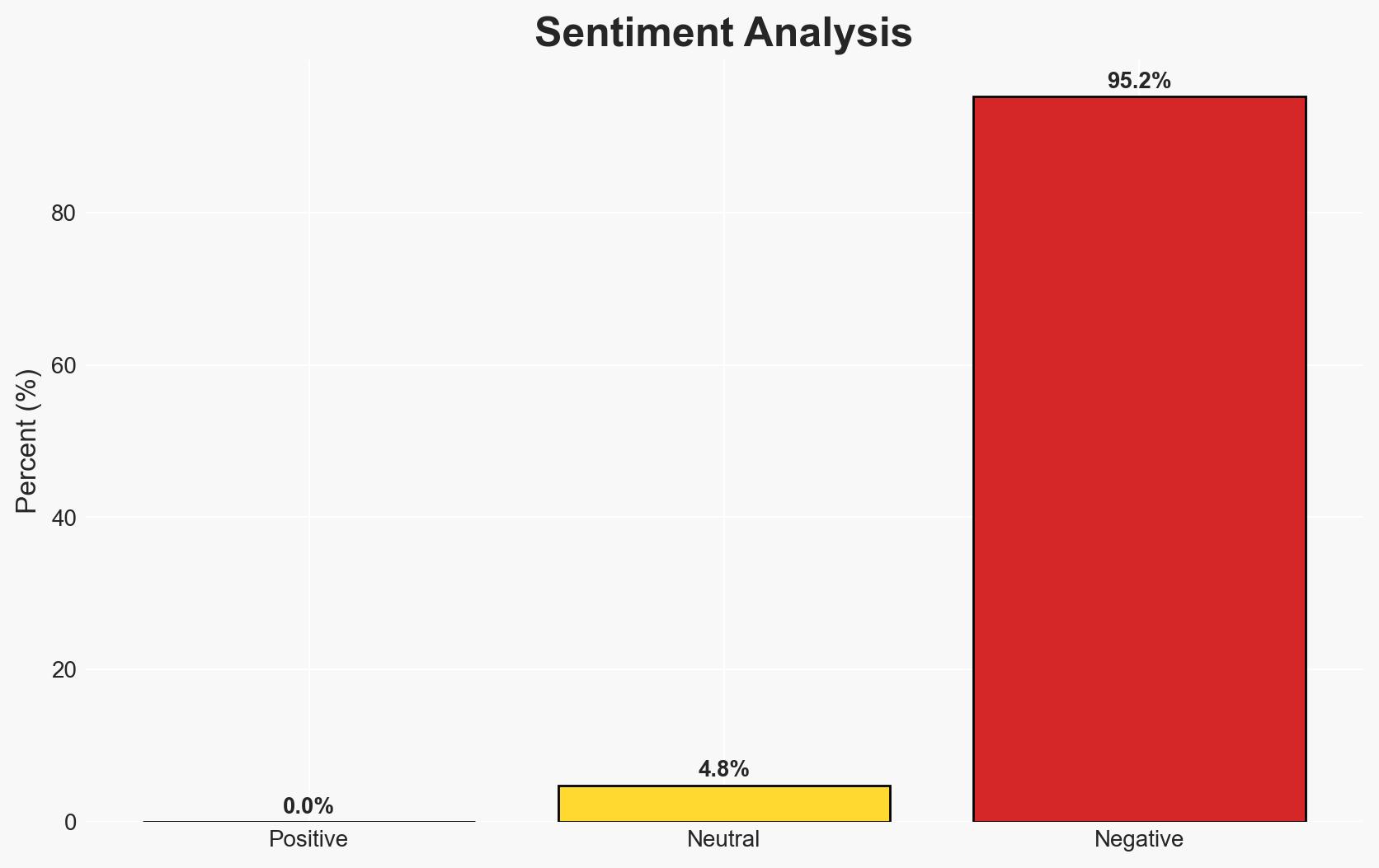
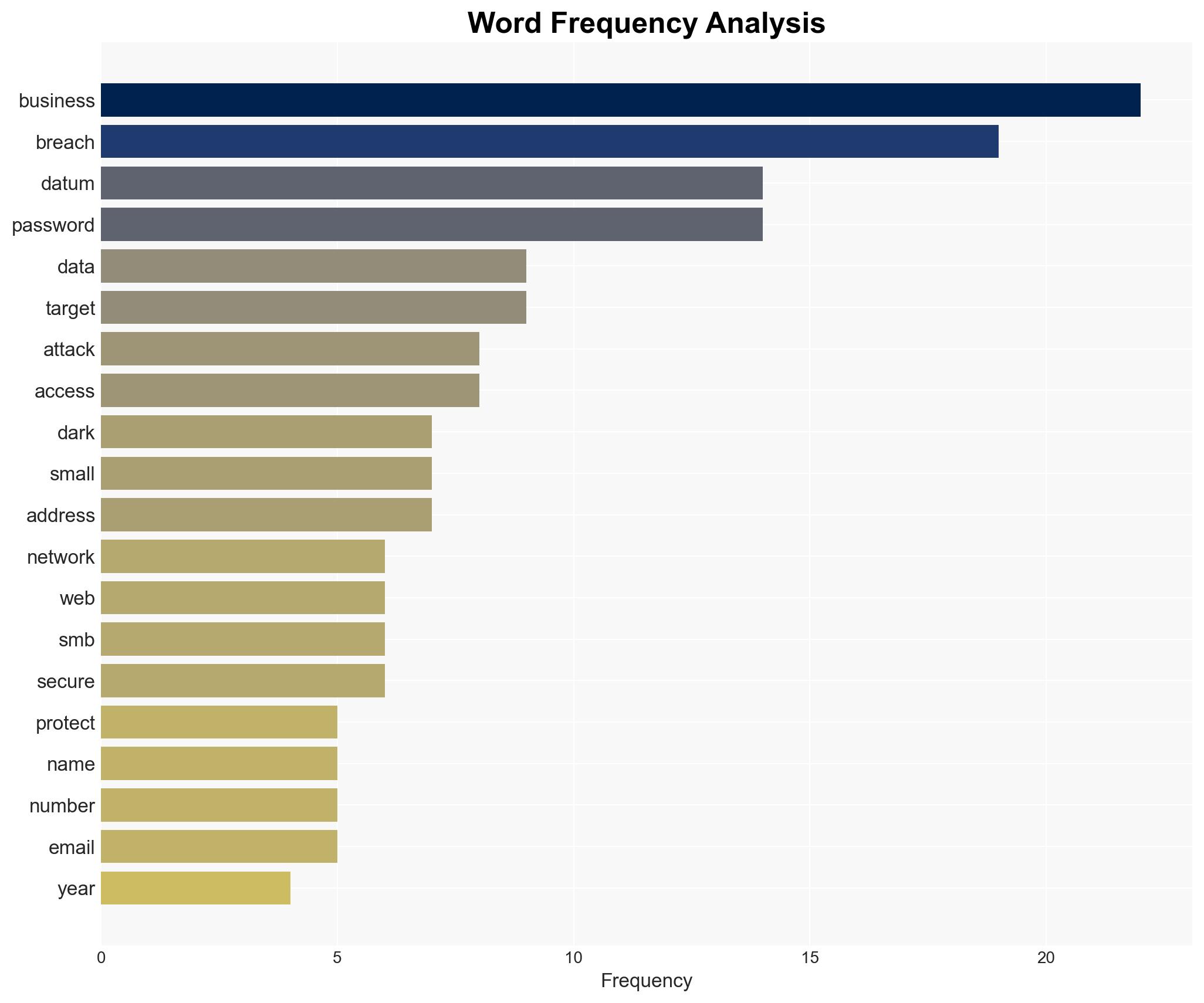
In 2025, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) became the primary targets for cybercriminals, accounting for 70.5% of data breaches. This shift is attributed to increased cybersecurity measures by larger businesses and their refusal to pay ransoms. The trend is likely to continue into 2026, with SMBs remaining vulnerable due to limited resources. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
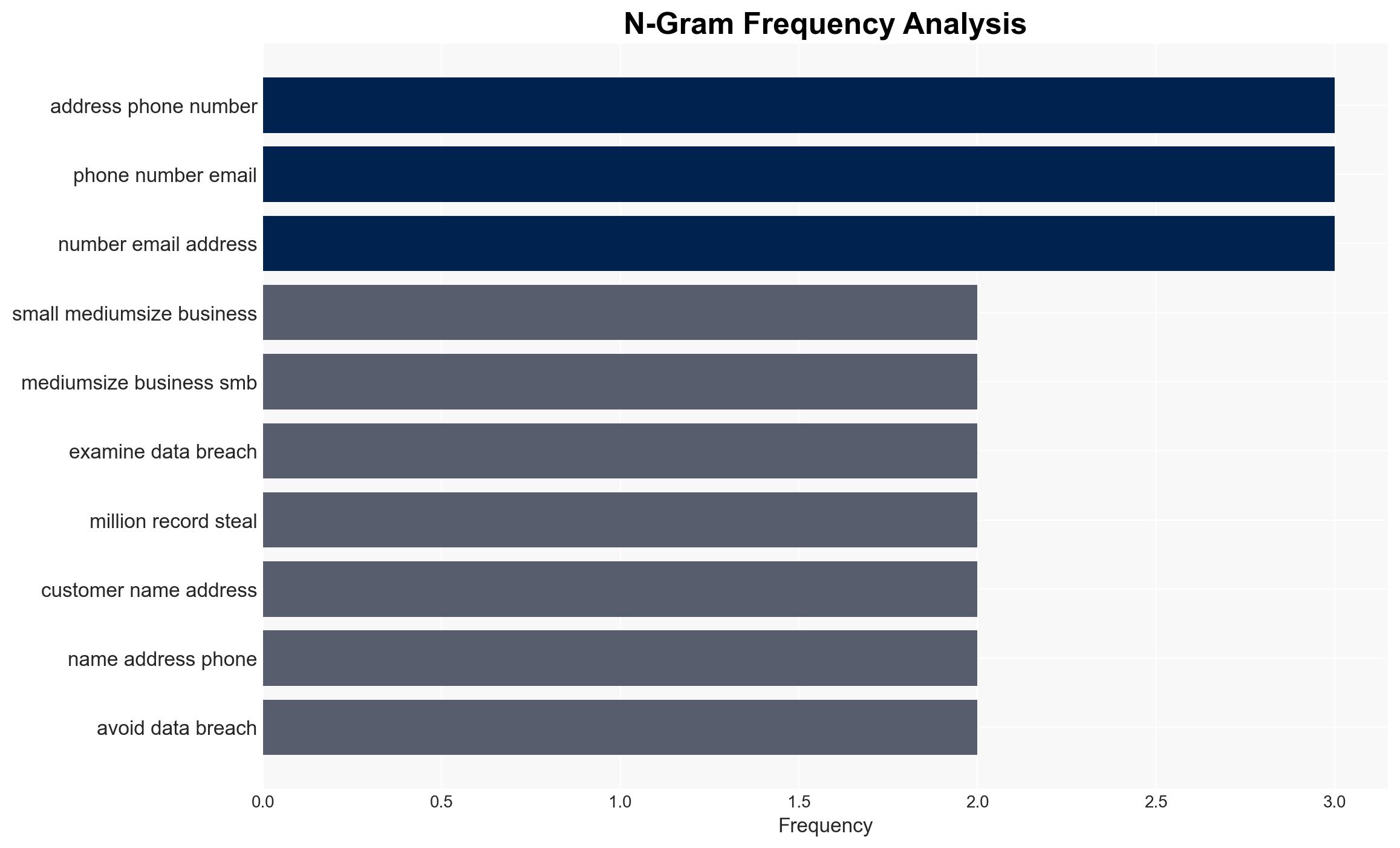
- Hypothesis A: Cybercriminals are targeting SMBs because they are easier to breach and offer a higher success rate for data theft. This is supported by the high percentage of SMB breaches in 2025 and the detailed examples of successful attacks.
- Hypothesis B: The focus on SMBs is a temporary shift, and cybercriminals will return to targeting larger businesses as new vulnerabilities are discovered. This hypothesis lacks strong supporting evidence given the current trend of increased security investments by larger companies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the consistent pattern of SMB breaches and the strategic shift by cybercriminals to target less protected entities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include significant security failures in large enterprises or new, exploitable vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: SMBs will not significantly increase their cybersecurity investments; large businesses will maintain or increase their current security posture; cybercriminals will continue to seek the path of least resistance.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on SMB cybersecurity practices and investments; specific motivations and strategies of cybercriminal groups targeting SMBs.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in data from the Data Breach Observatory due to reporting discrepancies; risk of underestimating cybercriminal adaptability and innovation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued targeting of SMBs by cybercriminals could lead to increased economic instability and loss of consumer trust in these businesses. This development may also encourage SMBs to invest more in cybersecurity, potentially altering the threat landscape.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased cyber threats to SMBs could lead to calls for more stringent cybersecurity regulations and international cooperation.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: The shift in targets may require law enforcement and intelligence agencies to adjust their focus and resources towards protecting SMBs.
- Cyber / Information Space: The trend may drive innovation in cybersecurity solutions tailored for SMBs, potentially altering the market dynamics.
- Economic / Social: Persistent breaches could undermine consumer confidence and lead to economic disruptions, particularly in sectors heavily reliant on SMBs.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of SMB cyber activity; provide guidance and resources for SMBs to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships between government and private sector to support SMB cybersecurity; invest in awareness campaigns and training for SMBs.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: SMBs significantly improve cybersecurity, reducing breach incidents.
- Worst: Continued breaches lead to widespread economic impact and loss of trust.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in SMB cybersecurity with ongoing, albeit reduced, breach incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Tracelo
- PhoneMondo
- SkilloVilla
- Data Breach Observatory
- Satanic (hacker)
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, SMBs, data breaches, cybercrime, economic impact, cybersecurity investment, cyber resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us