Afghanistan earthquake What we know – and what we don’t – BBC News
Published on: 2025-09-01
Intelligence Report: Afghanistan earthquake What we know – and what we don’t – BBC News
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that the earthquake’s impact is exacerbated by Afghanistan’s current socio-political and economic instability, leading to a severe humanitarian crisis. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: International humanitarian organizations should prioritize establishing secure corridors for aid delivery and negotiate with local authorities for access.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The earthquake’s impact is primarily a natural disaster issue, with the main challenges being logistical due to the terrain and aftershocks.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The earthquake’s impact is significantly worsened by Afghanistan’s political and economic instability, including the Taliban’s governance, which hampers effective disaster response and international aid delivery.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis B is better supported due to evidence of blocked roads, limited communication, and the Taliban’s governance issues, which complicate relief efforts.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Hypothesis A assumes that natural factors are the primary obstacles, ignoring socio-political influences. Hypothesis B assumes political instability is a significant barrier to aid.
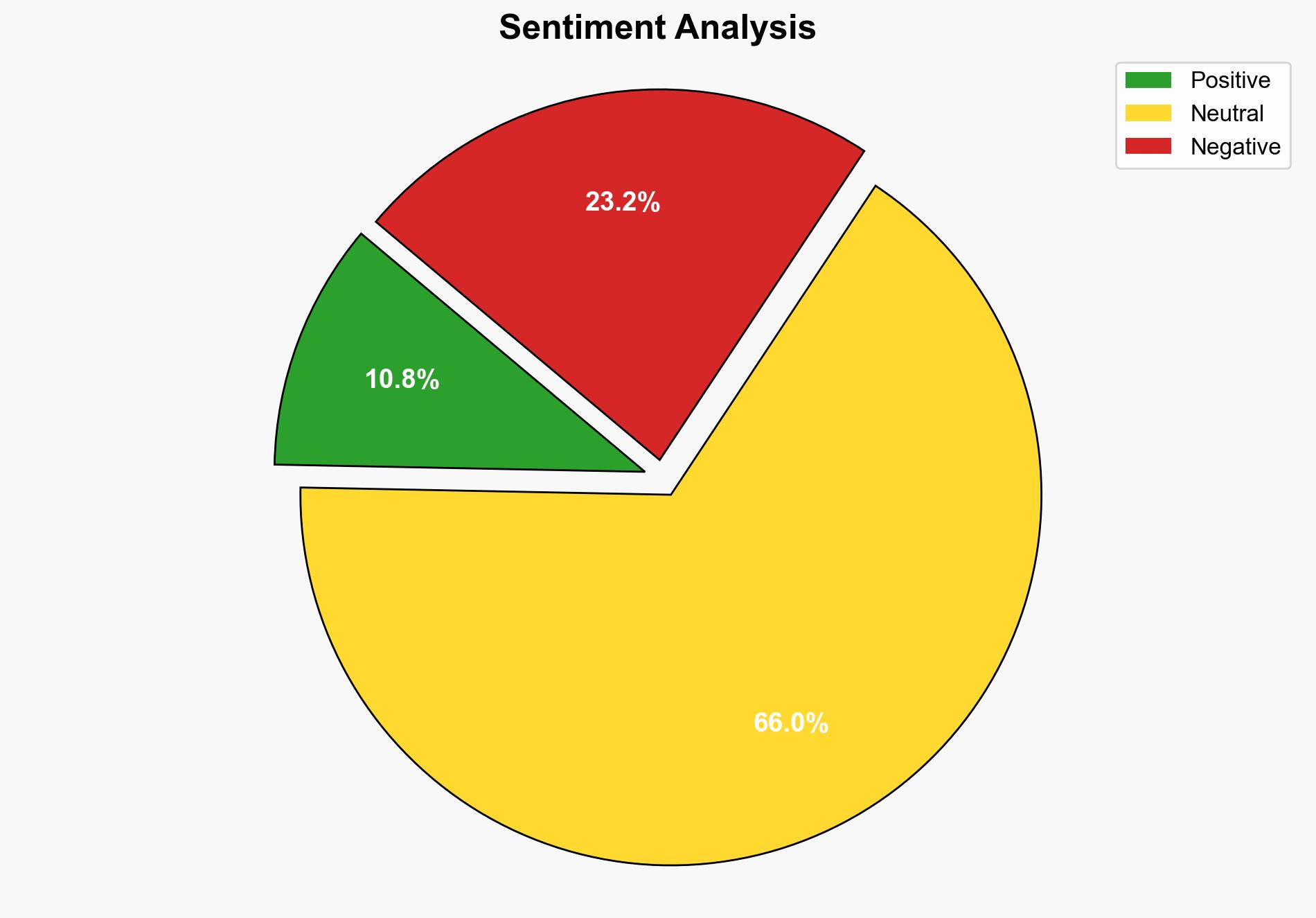
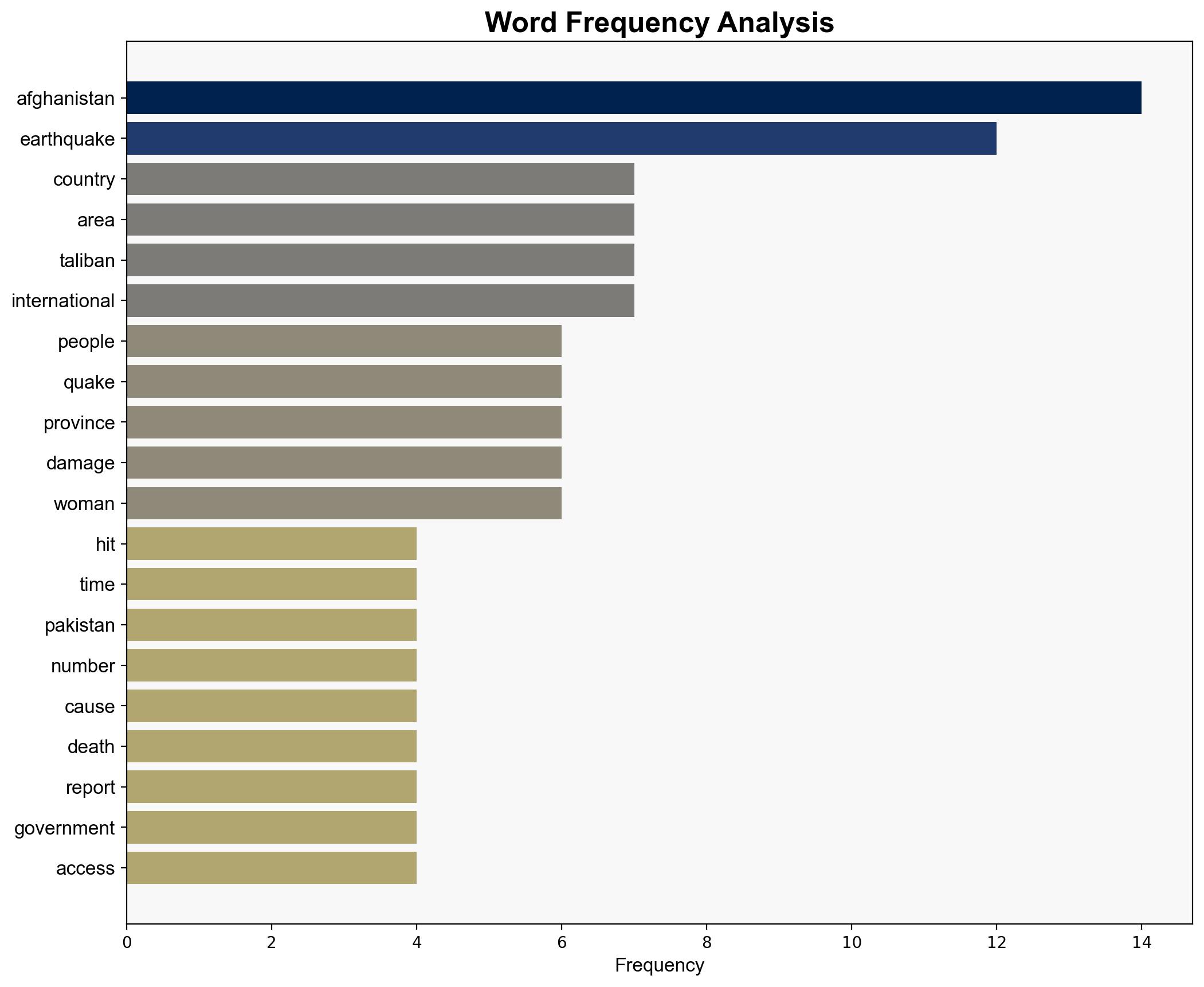
– **Red Flags**: Lack of detailed casualty and damage reports; potential underreporting due to restricted media access.
– **Blind Spots**: Limited information on the Taliban’s cooperation with international agencies.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic**: The earthquake may further strain Afghanistan’s fragile economy, increasing dependency on foreign aid.
– **Geopolitical**: The Taliban’s response to international aid offers could affect diplomatic relations and future aid.
– **Humanitarian**: Delayed aid could lead to increased mortality and morbidity, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Immediate Action**: International organizations should engage with local leaders to facilitate aid delivery.
- **Short-term**: Establish temporary shelters and medical facilities near affected areas.
- **Long-term**: Develop infrastructure resilience programs to mitigate future natural disasters.
- **Scenario Projections**:
- **Best Case**: Effective coordination leads to timely aid delivery, minimizing casualties.
- **Worst Case**: Continued political instability and logistical challenges result in a prolonged humanitarian crisis.
- **Most Likely**: Partial aid delivery with ongoing challenges due to political and logistical barriers.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Salam Al Janabi (UNICEF)
– International organizations like World Vision and USAID
– The Taliban government
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, humanitarian crisis, disaster response, regional instability