Afghanistan Hundreds killed after strong earthquake – DW (English)
Published on: 2025-09-01
Intelligence Report: Afghanistan Hundreds killed after strong earthquake – DW (English)
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
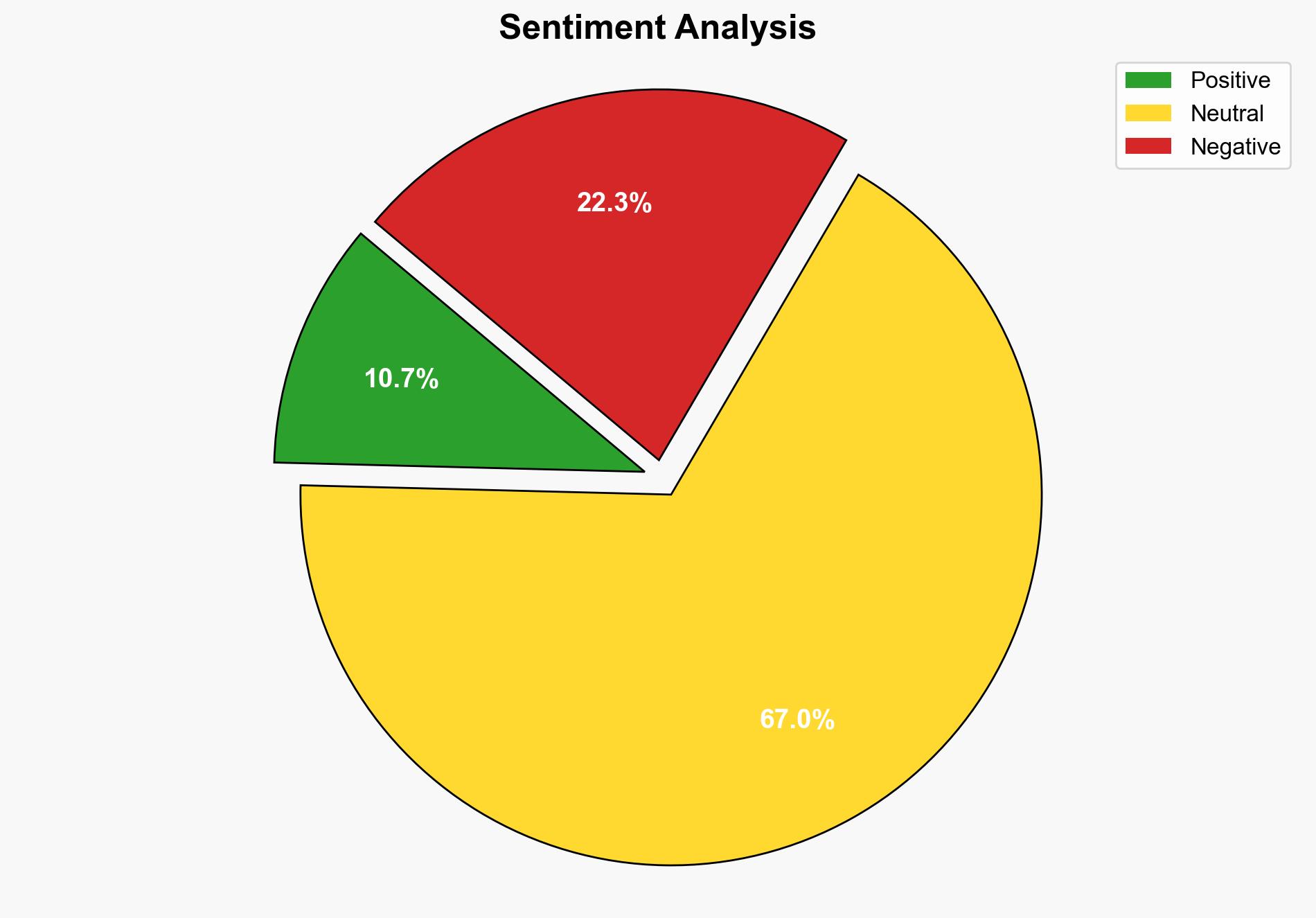
The most supported hypothesis is that the earthquake’s impact is exacerbated by Afghanistan’s current socio-political and economic challenges, particularly budget cuts and limited international aid. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Increase international humanitarian assistance and improve infrastructure resilience to mitigate future disaster impacts.
2. Competing Hypotheses
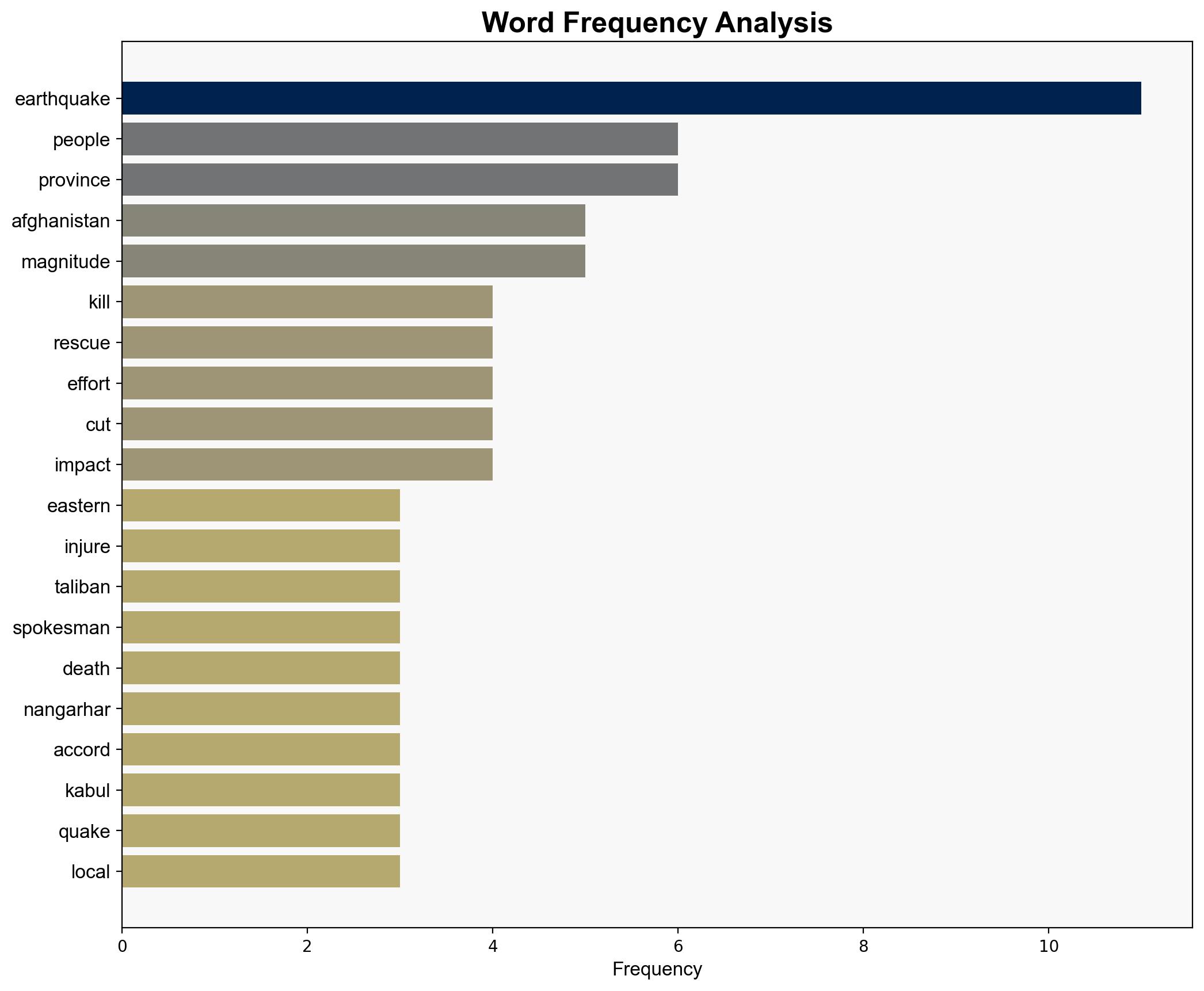
Hypothesis 1: The earthquake’s high casualty rate is primarily due to the natural disaster’s magnitude and timing, compounded by Afghanistan’s geographical vulnerability to seismic activity.
Hypothesis 2: The high casualty rate is significantly influenced by Afghanistan’s socio-political instability, including budget cuts and reduced international aid, which have weakened disaster response capabilities.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 2 is better supported due to evidence of budget cuts and international aid reduction impacting response efforts, as mentioned in the source text.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the reliability of reported casualty figures and the extent of budget cuts affecting response capabilities. A red flag is the potential underreporting of casualties due to inaccessible areas. There is also a risk of cognitive bias in assuming that the earthquake’s impact is solely due to natural causes without considering socio-political factors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The earthquake highlights Afghanistan’s vulnerability to natural disasters amidst socio-political instability. The cascading threat includes potential humanitarian crises and increased regional instability. Economic risks involve further strain on already limited resources, while geopolitical risks include reduced international confidence in Afghanistan’s governance.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Increase international humanitarian aid to support immediate relief efforts and long-term infrastructure development.
- Enhance regional cooperation for disaster preparedness and response.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Increased international aid leads to effective disaster response and improved infrastructure resilience.
- Worst Case: Continued socio-political instability and insufficient aid result in prolonged humanitarian crises.
- Most Likely: Moderate international response alleviates immediate needs but leaves long-term vulnerabilities unaddressed.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
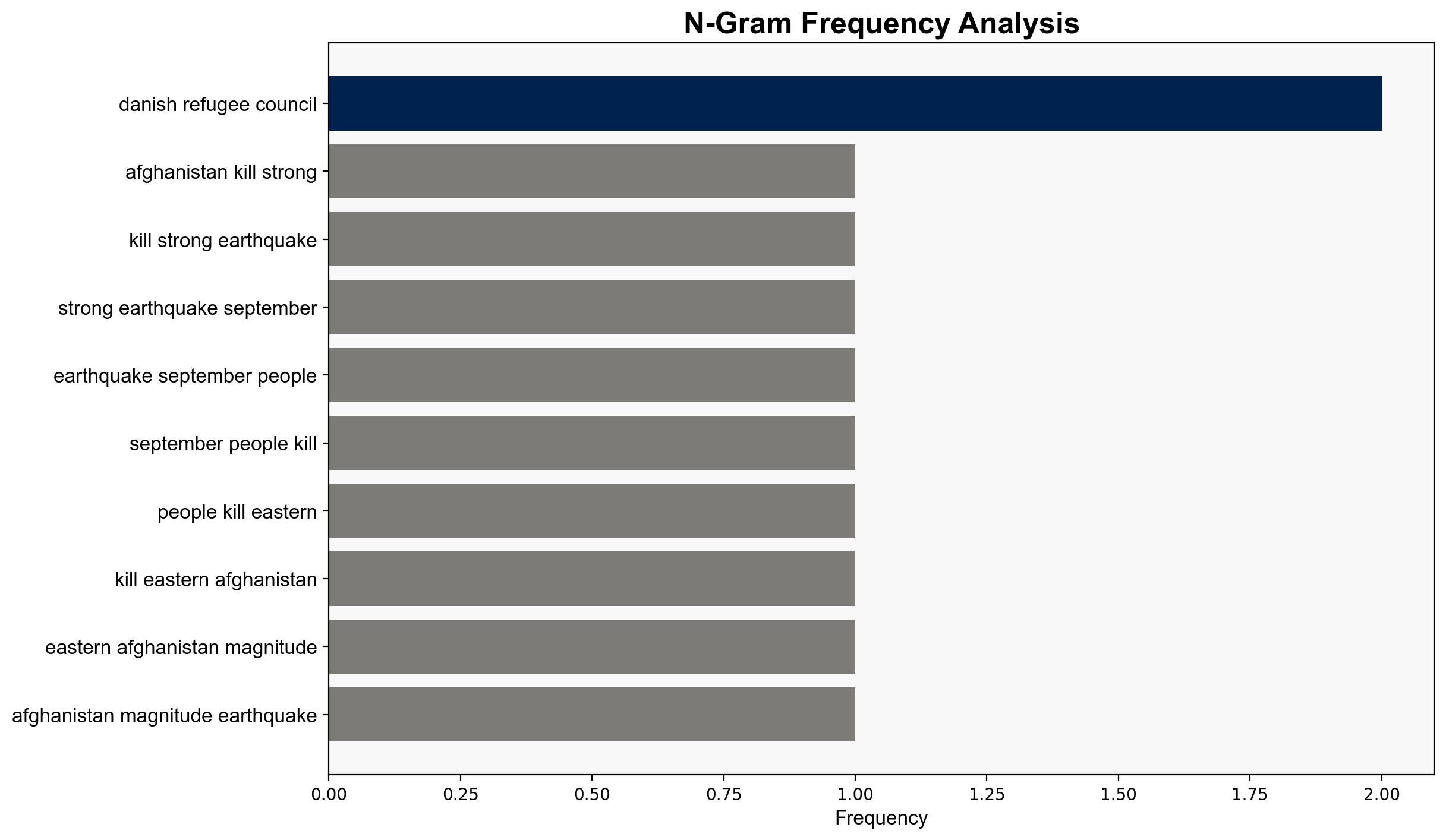
Abdul Mateen Qani, Zabihullah Mujahid, Danish Refugee Council (DRC), US Geological Survey (USGS).
7. Thematic Tags
natural disaster response, humanitarian aid, regional stability, socio-political challenges