Agentic AI security Building the next generation of access controls – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-10-21
Intelligence Report: Agentic AI Security Building the Next Generation of Access Controls – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
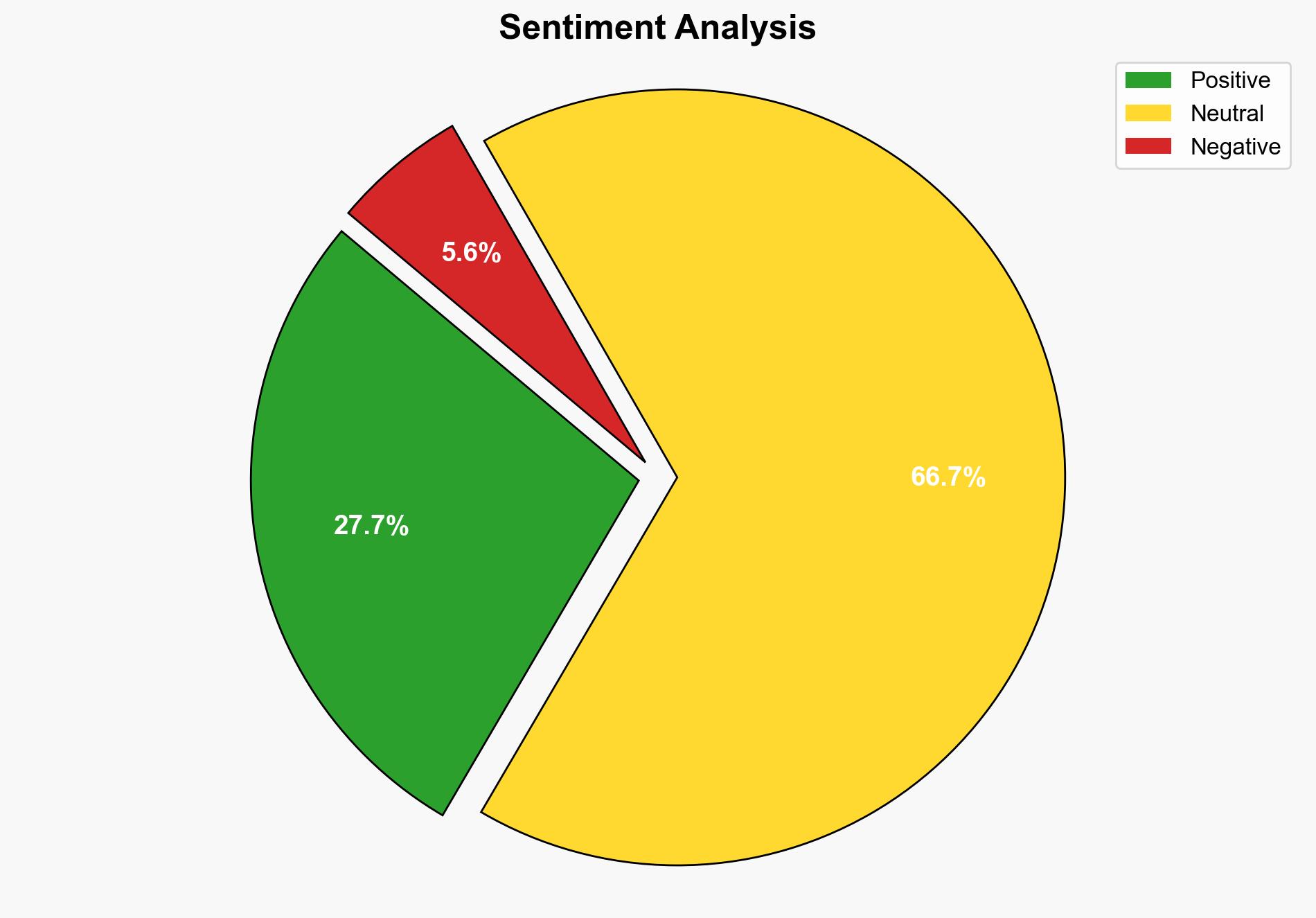
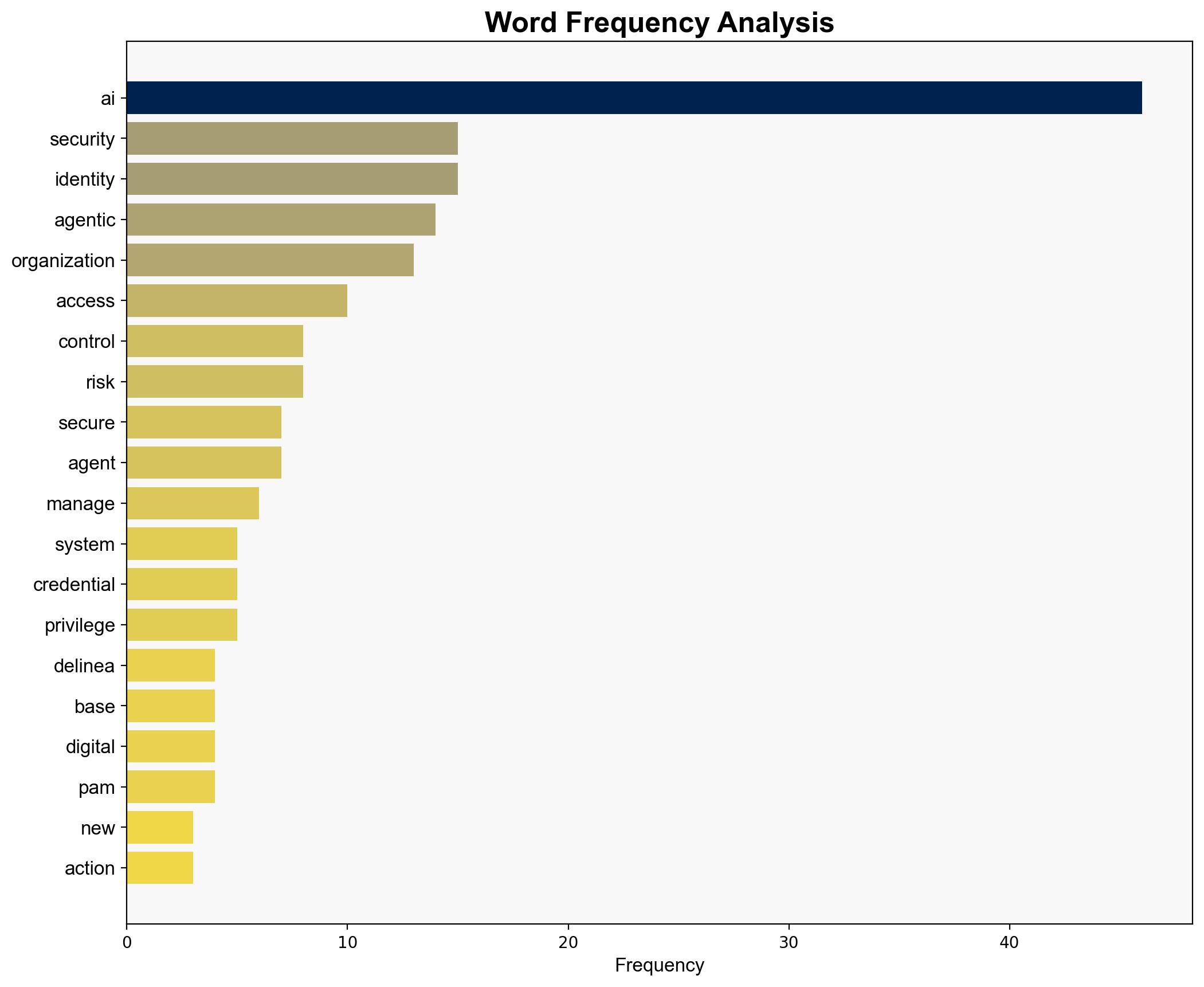
The evolution of agentic AI systems presents significant security challenges, particularly in terms of access control and identity management. The most supported hypothesis suggests that traditional role-based access control (RBAC) models are inadequate for managing agentic AI risks, necessitating a shift towards identity-centric security frameworks. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended Action: Organizations should prioritize the development and implementation of advanced identity-centric security measures to manage agentic AI risks effectively.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Traditional RBAC models can be adapted to manage agentic AI security risks with minor modifications, such as enhanced monitoring and auditing capabilities.
Hypothesis 2: Traditional RBAC models are fundamentally inadequate for agentic AI, requiring a complete overhaul towards identity-centric security frameworks to effectively manage risks.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 2 is better supported due to the inherent complexity and autonomy of agentic AI systems, which demand more dynamic and granular access control mechanisms than RBAC can provide.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Agentic AI systems will continue to operate with increasing autonomy.
– Organizations have the capability and resources to implement new security frameworks.
Red Flags:
– Lack of transparency and visibility in agentic AI deployments.
– Potential underestimation of the complexity involved in transitioning to identity-centric security.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The shift towards identity-centric security involves significant strategic risks, including potential disruptions during the transition phase and increased vulnerability to cyber threats if not implemented correctly. The economic implications include potential increased costs for developing and maintaining new security infrastructures. Geopolitically, organizations may face regulatory challenges as governments seek to understand and control AI deployments.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Organizations should conduct a comprehensive audit of current AI deployments to identify unmanaged shadow AI systems.
- Develop a phased implementation plan for transitioning to identity-centric security, including training for security personnel.
- Scenario-based Projections:
- Best Case: Successful transition to identity-centric security, leading to enhanced AI management and reduced security risks.
- Worst Case: Failure to implement new security measures results in increased vulnerability and potential data breaches.
- Most Likely: Gradual adoption of identity-centric security with initial challenges but eventual stabilization.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned. Focus is on organizations deploying agentic AI systems and security officers responsible for managing these systems.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, AI governance, identity management