AI Adoption Accelerates Cloud Security Vulnerabilities, Report Warns of Rising Risks
Published on: 2025-12-19
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New research reveals AI is fueling an ‘unprecedented surge in cloud security risks’
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The rapid adoption of AI tools and cloud-native AI services is significantly increasing cloud security risks, primarily due to excessive permissions and misconfigurations. Organizations are deploying AI workloads faster than they can secure them, leading to a surge in identity-related security incidents. This development affects businesses globally, with moderate confidence in the assessment due to the reliance on a single source and potential information gaps.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The surge in cloud security risks is primarily driven by the rapid deployment of AI tools without adequate security measures. Supporting evidence includes the reported increase in identity-related incidents and misconfigurations. Key uncertainties involve the extent to which these issues are unique to AI or part of broader cloud security challenges.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in cloud security risks is a result of broader systemic issues in cloud security, with AI adoption being a contributing but not primary factor. This hypothesis is less supported by the report, which emphasizes AI-specific challenges, but it considers the possibility of existing vulnerabilities being exacerbated by AI.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific focus on AI-related issues in the report. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of similar security incidents in non-AI cloud environments.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI tools inherently require broad permissions; organizations lack sufficient security protocols for rapid AI deployment; identity-related issues are primarily due to AI adoption.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on non-AI cloud security incidents; comparative analysis of AI and non-AI cloud environments; insights into organizational security practices.
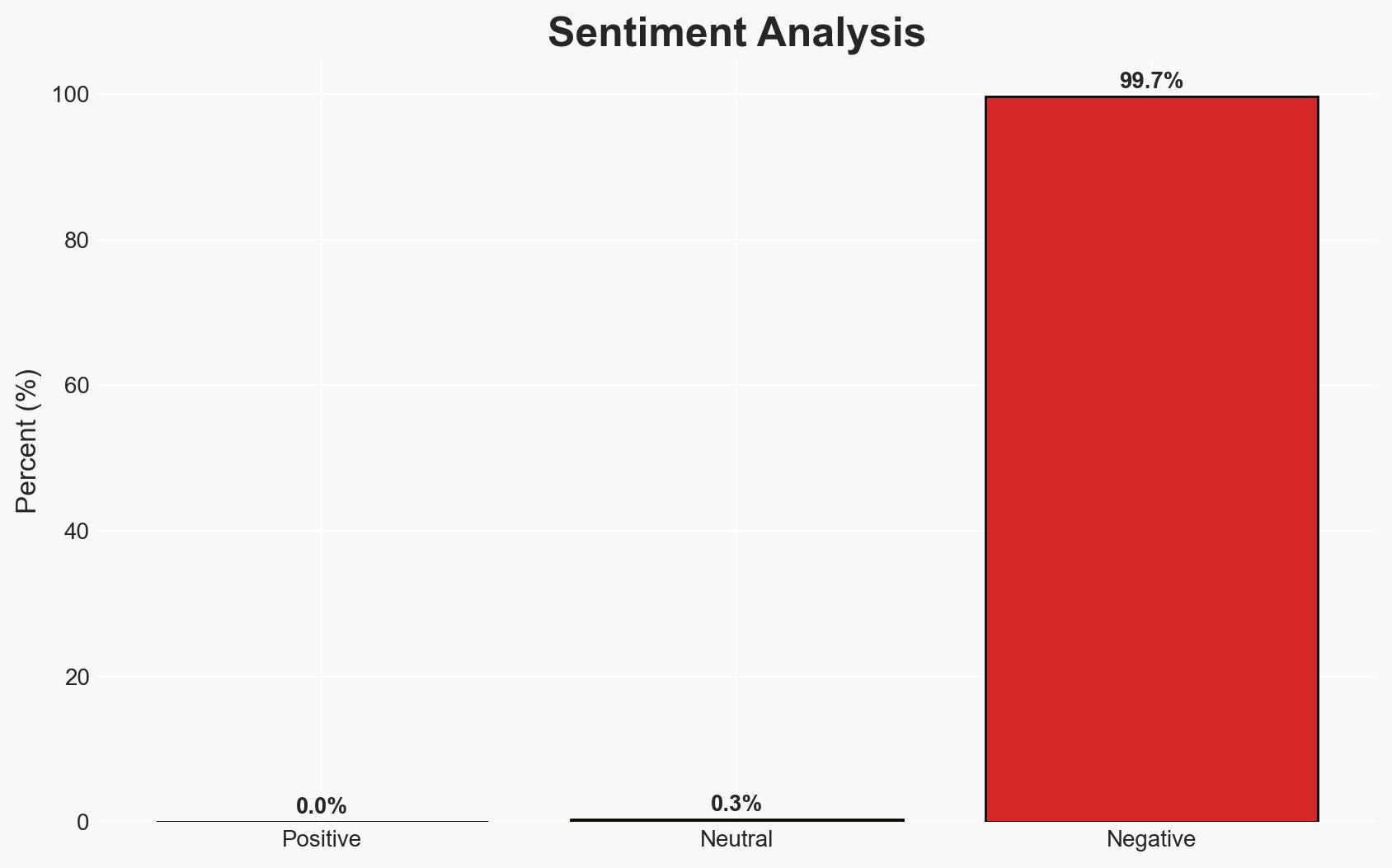
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from Palo Alto Networks as a cybersecurity vendor; reliance on a single report may overlook other perspectives or data sources.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and demand for enhanced cloud security measures. Over time, it may drive innovation in AI security solutions and influence organizational IT strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international collaboration on cybersecurity standards and practices.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of cyber-attacks exploiting AI vulnerabilities, possibly impacting critical infrastructure.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased focus on securing AI systems and managing non-human identities in cloud environments.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from data breaches; increased costs for businesses to enhance security measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct thorough security audits of AI deployments; implement stricter access controls and monitoring for non-human identities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms; invest in AI-specific security training and tools; advocate for industry-wide security standards.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid development of effective AI security solutions mitigates risks.
- Worst: Major breaches occur, leading to significant economic and reputational damage.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security practices reduces incidents over time.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
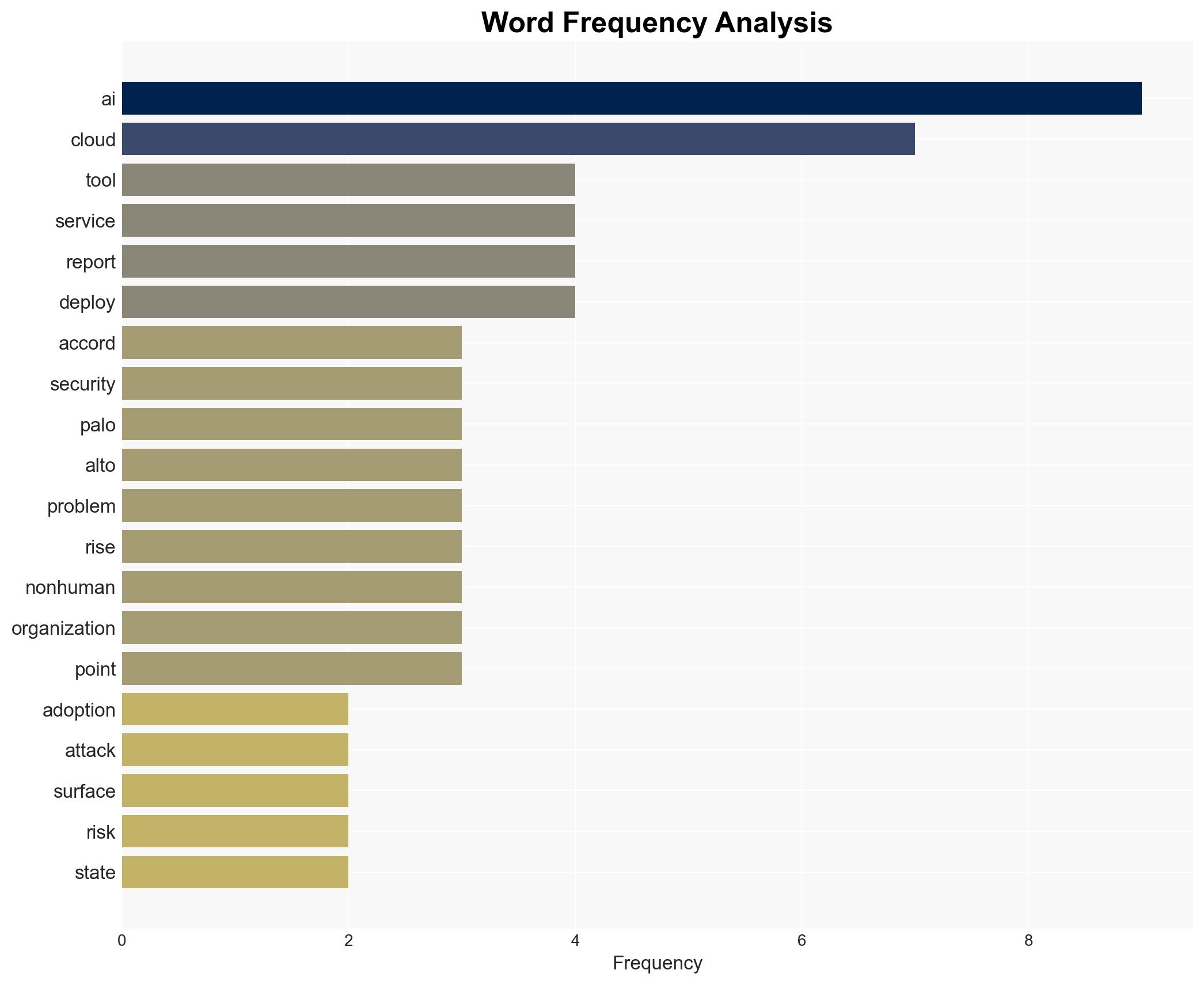
cybersecurity, cloud security, AI adoption, cybersecurity risks, identity management, non-human identities, data breaches, security misconfigurations
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us