AI Chatbots Found Vulnerable to Encryption Flaw, Allowing Hackers to Intercept Private Messages
Published on: 2025-11-26
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Popular AI chatbots have an alarming encryption flaw meaning hackers may have easily intercepted messages
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
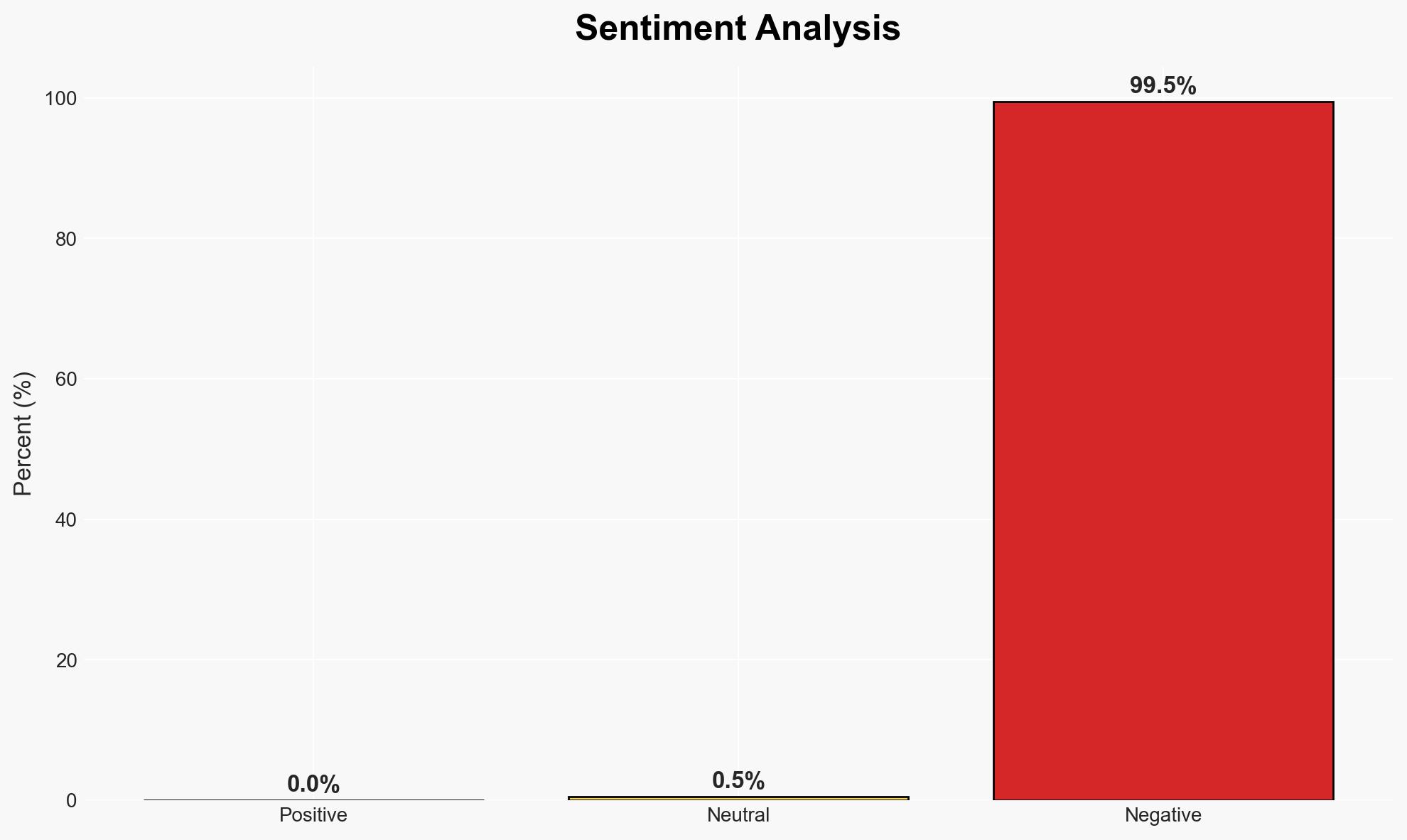
A critical encryption flaw in popular AI chatbots has been identified, potentially allowing hackers to intercept messages. This vulnerability, termed “Whisper Leak,” affects users of large language models (LLMs) such as those developed by OpenAI and Microsoft. The flaw’s exploitation could lead to significant breaches of privacy and data security. Despite the identified risk, LLM providers have not universally implemented fixes. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The encryption flaw is a systemic issue within LLM architecture that requires comprehensive redesign to mitigate. Supporting evidence includes the identification of the flaw by cybersecurity researchers and the lack of immediate fixes by LLM providers. Key uncertainties involve the technical feasibility of a comprehensive redesign.
- Hypothesis B: The encryption flaw can be mitigated through incremental updates and patches without a complete overhaul of the LLM architecture. This is supported by potential mitigation techniques such as random padding and response field adjustments. Contradicting evidence includes the providers’ reluctance to implement these fixes, possibly due to cost or technical limitations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported, as incremental updates are often more feasible and cost-effective than complete redesigns. However, the lack of provider action suggests possible technical or economic barriers. Indicators that could shift this judgment include new technical assessments or changes in provider policies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The flaw is exploitable by adversaries with moderate technical capabilities; LLM providers are aware of the vulnerability; the identified mitigation techniques are technically viable.
- Information Gaps: Specific technical details on the feasibility and cost of implementing proposed fixes; the extent of exploitation by malicious actors.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting due to vested interests of cybersecurity firms; lack of transparency from LLM providers may indicate downplaying of risks.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The identified encryption flaw in AI chatbots could have significant implications across various domains if not addressed. The evolution of this issue could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and loss of consumer trust.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regulatory actions and international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of exploitation by state and non-state actors for intelligence gathering and cyber operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened vulnerability to cyber espionage and data breaches, impacting user privacy and data integrity.
- Economic / Social: Possible economic impact on companies relying on LLMs due to loss of consumer trust and potential legal liabilities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment of current LLM deployments; engage with LLM providers to understand mitigation plans; increase monitoring for potential exploitation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for ongoing vulnerability assessments; invest in research for robust encryption methods for AI communications.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Providers implement effective fixes, restoring trust and security.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to significant data breaches and regulatory backlash.
- Most-Likely: Incremental improvements mitigate some risks, but systemic issues persist, leading to ongoing vulnerabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Microsoft
- OpenAI
- Cybersecurity researchers (e.g., Jonathan Bar, Geoff McDonald)
- Dave Lear, Cybersecurity Analyst
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us