AI-Driven Identity Breaches: The New Vulnerability in SaaS Security
Published on: 2025-12-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Inside the AI-powered assault on SaaS why identity is the weakest link
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
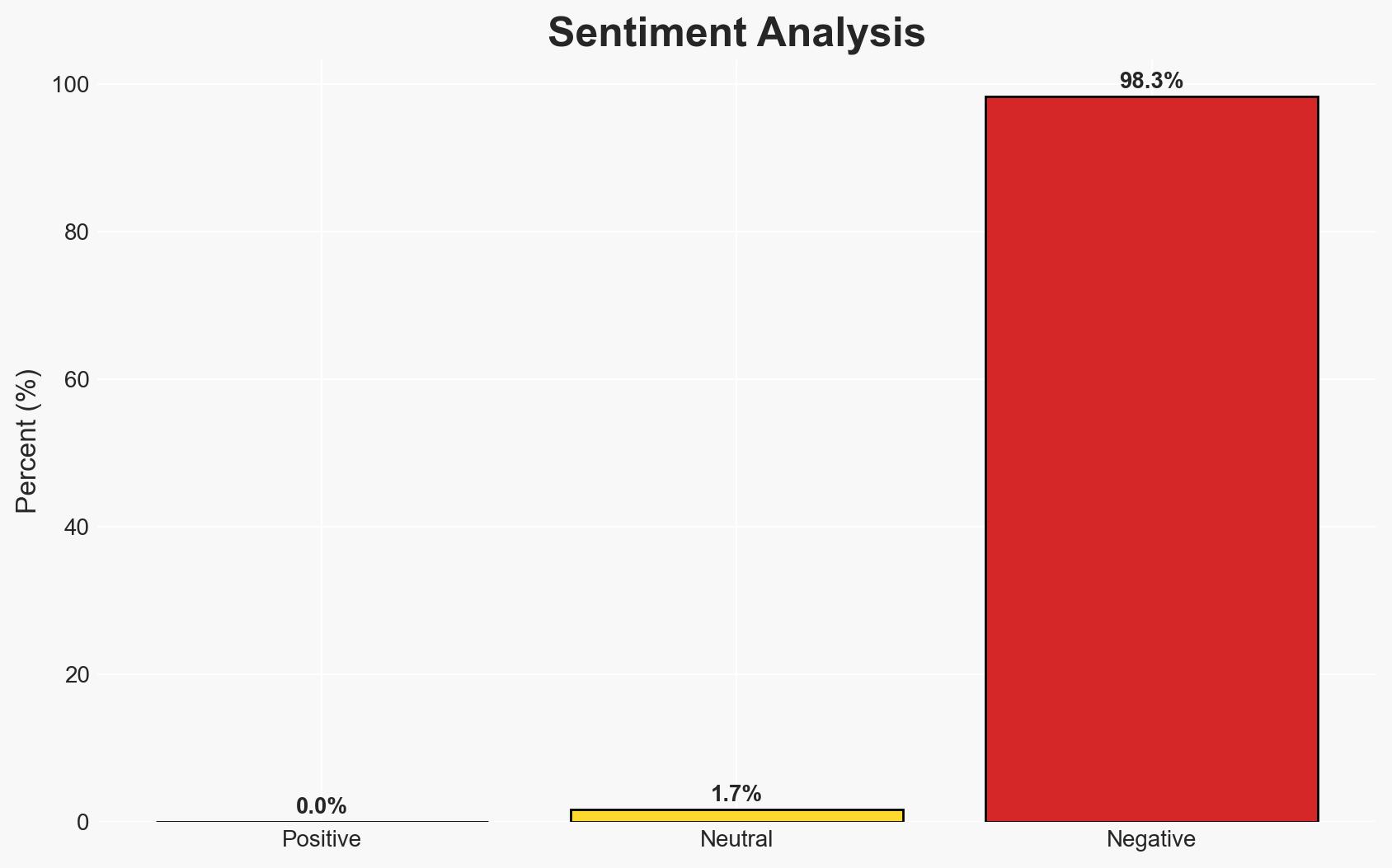
The increasing use of AI by cybercriminals to exploit SaaS platforms through identity breaches represents a significant and evolving cyber threat. The most likely hypothesis is that AI-enhanced identity attacks will continue to rise, affecting enterprises globally by compromising critical data. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the current evidence and trends.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI-powered identity breaches will become the primary method of cyber attacks on SaaS platforms. This is supported by the reported increase in sophisticated phishing campaigns and the high incidence of SaaS-related incidents involving compromised credentials. However, the extent of AI’s role in these attacks remains partially uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Traditional cyber attack methods will remain dominant, with AI playing a supplementary role. This hypothesis is contradicted by the trend towards identity-focused attacks and the documented use of AI in crafting sophisticated phishing lures.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the documented increase in AI-driven attacks and the vulnerabilities associated with identity management in SaaS environments. Indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant breakthrough in traditional cybersecurity measures or a decline in AI’s effectiveness in bypassing security controls.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to advance; SaaS platforms will remain a critical infrastructure for enterprises; identity management will not significantly improve in the near term.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific AI techniques used in identity breaches; comprehensive statistics on the success rate of AI-driven attacks versus traditional methods.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on vendor reports like AppOmni’s; risk of underestimating traditional attack vectors due to focus on AI.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI-powered identity breaches could reshape the cybersecurity landscape, necessitating new defense strategies and policies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international tensions as states may be implicated in sponsoring or failing to prevent such attacks.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment requiring updated countermeasures and intelligence sharing.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased demand for AI-driven cybersecurity solutions and potential for misinformation campaigns exploiting identity breaches.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions from data breaches; loss of consumer trust in SaaS platforms could impact business operations.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of identity-related incidents; conduct security audits focusing on identity management; increase awareness training on phishing and credential protection.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI cybersecurity firms; invest in advanced identity verification technologies; update security protocols to include AI threat mitigation.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid advancements in AI-driven defenses outpace attack capabilities, reducing identity breaches.
- Worst: Widespread identity breaches lead to significant economic and operational disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued increase in AI-powered identity attacks with gradual improvements in defense measures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
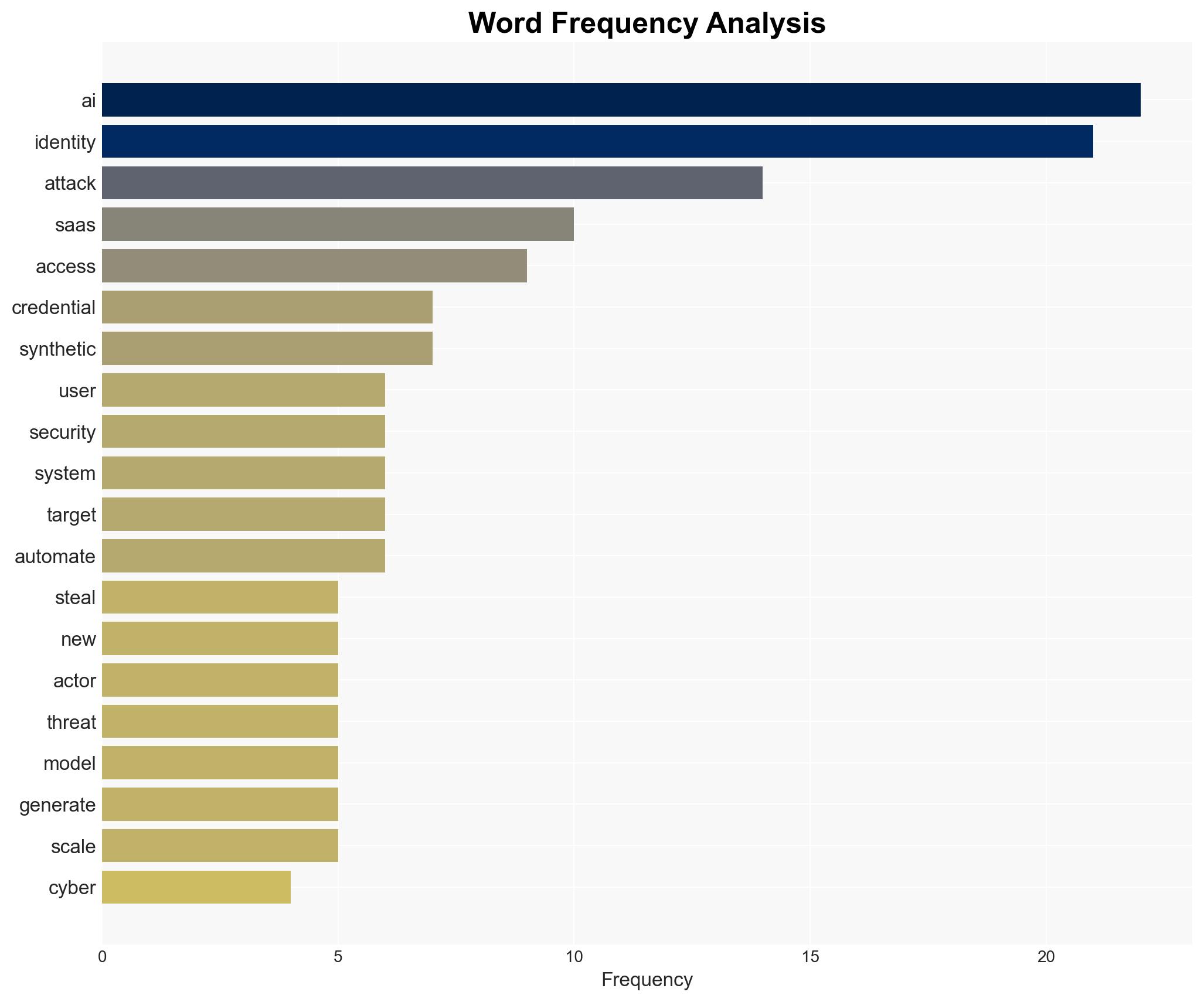
cybersecurity, AI, identity breaches, SaaS, phishing, cyber threats, information security
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us