AI-Driven Vulnerabilities: Ransomware Exploits Highlight Urgent Need for Enhanced Cybersecurity Measures
Published on: 2026-02-03
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Tipping the Cyber Balance How AI Benchmarks Could Make Software Safer
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
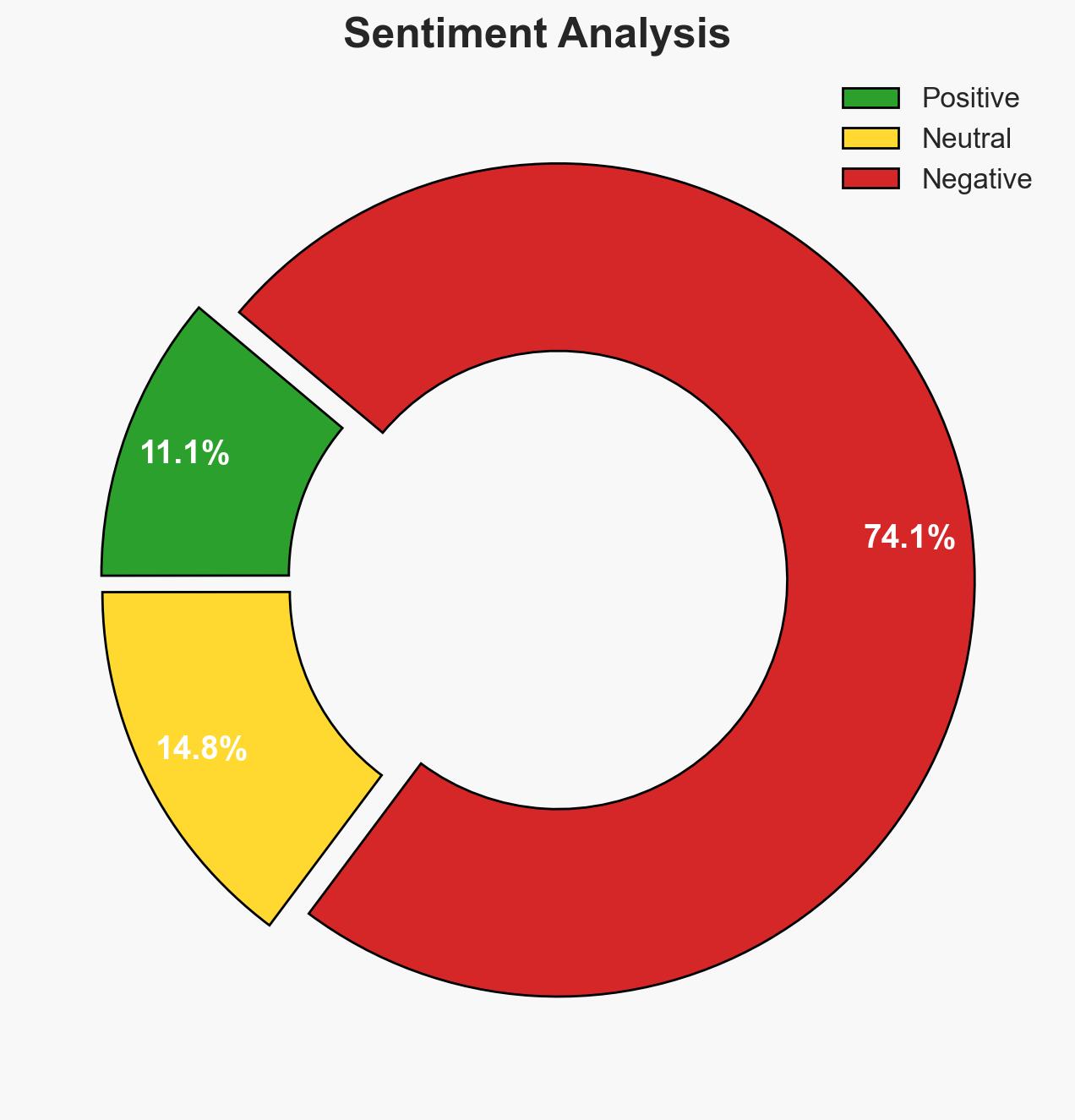
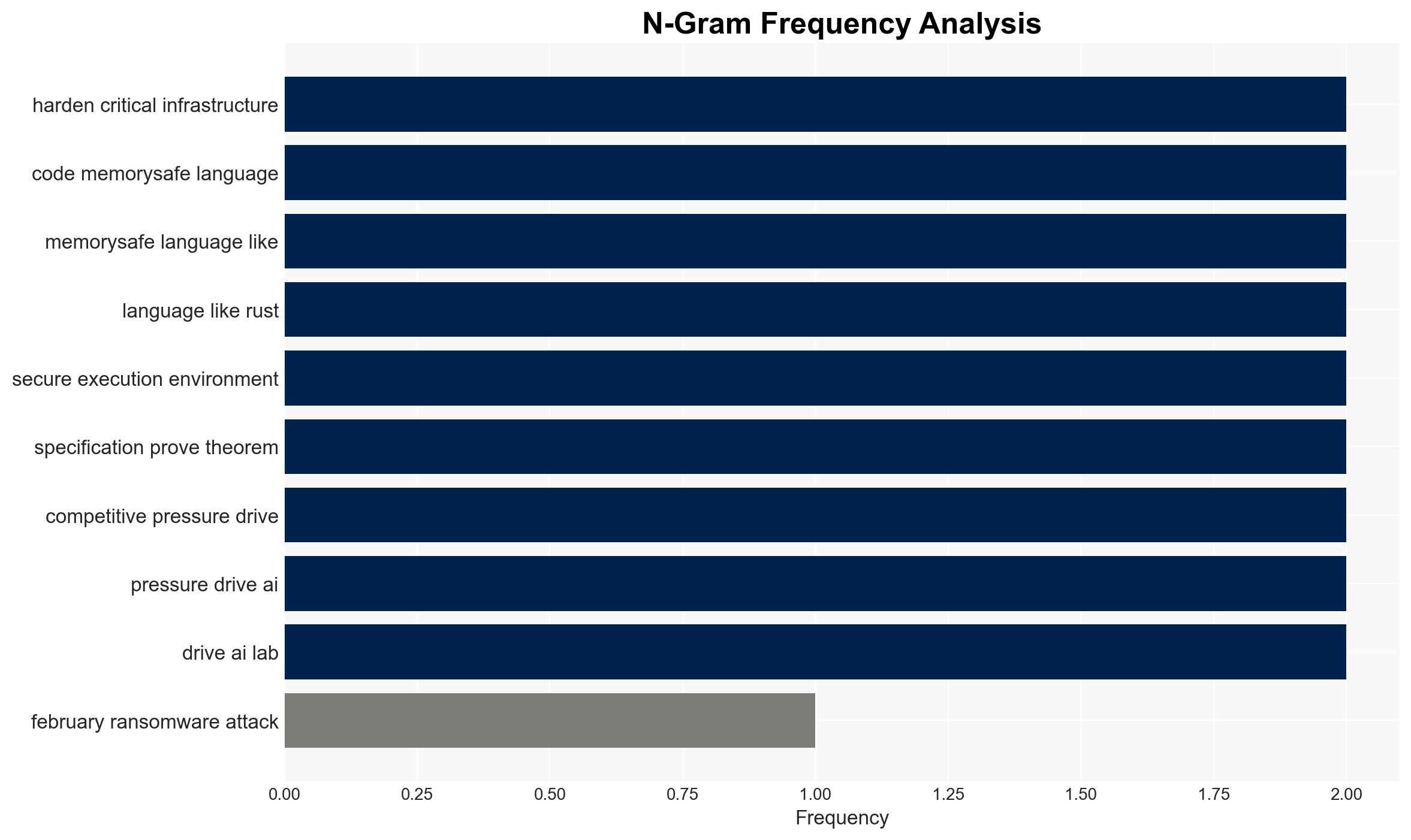
The recent ransomware attack on Change Healthcare highlights vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure due to inadequate cybersecurity measures. Artificial intelligence (AI) could exacerbate these vulnerabilities by enabling rapid exploitation but also offers potential defensive advantages through automated reasoning. The balance of power in cybersecurity could shift towards defenders if AI is leveraged effectively. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI will primarily benefit attackers by accelerating the discovery and exploitation of vulnerabilities. This is supported by the reduced time-to-exploit metrics and the ability of AI to generate exploits quickly. However, the potential for AI to enhance defensive measures is not fully realized, creating uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: AI can be harnessed to strengthen cybersecurity defenses through automated reasoning and formal methods, potentially reversing the current trend. This hypothesis is supported by the potential for AI to systematically harden infrastructure and improve software safety. Contradictory evidence includes the current lack of widespread implementation of such technologies.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the strategic potential of AI in defensive applications, though realization depends on timely and effective implementation. Indicators such as increased adoption of memory-safe languages and formal methods could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI capabilities will continue to advance; defenders will adopt AI-driven tools; attackers will not significantly outpace defenders in AI application.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the current adoption rate of AI-driven defensive measures; effectiveness of AI in real-world defensive scenarios.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential overestimation of AI’s defensive capabilities; reliance on optimistic projections without empirical backing; possible manipulation of AI-generated data by adversaries.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI in cybersecurity could redefine the threat landscape, influencing both defensive and offensive strategies. The interplay between AI advancements and cybersecurity policies will be crucial.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased pressure on governments to regulate AI in cybersecurity; potential for international cooperation or conflict over AI capabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced capabilities for both state and non-state actors to exploit vulnerabilities; potential for AI to aid in counter-terrorism through improved threat detection.
- Cyber / Information Space: Accelerated arms race in cyber capabilities; potential for AI to improve resilience of critical infrastructure.
- Economic / Social: Significant economic impacts from cyberattacks; potential for AI to reduce costs associated with cybersecurity breaches.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of AI developments in cybersecurity; prioritize implementation of multi-factor authentication and basic cybersecurity measures.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in AI-driven defensive technologies; foster public-private partnerships to accelerate adoption of formal methods and memory-safe languages.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: AI significantly reduces vulnerability exploitation; Worst: AI primarily benefits attackers; Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in defenses as AI tools are adopted, contingent on policy and investment.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Change Healthcare
- UnitedHealth Group
- Google’s Mandiant Threat Intelligence
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
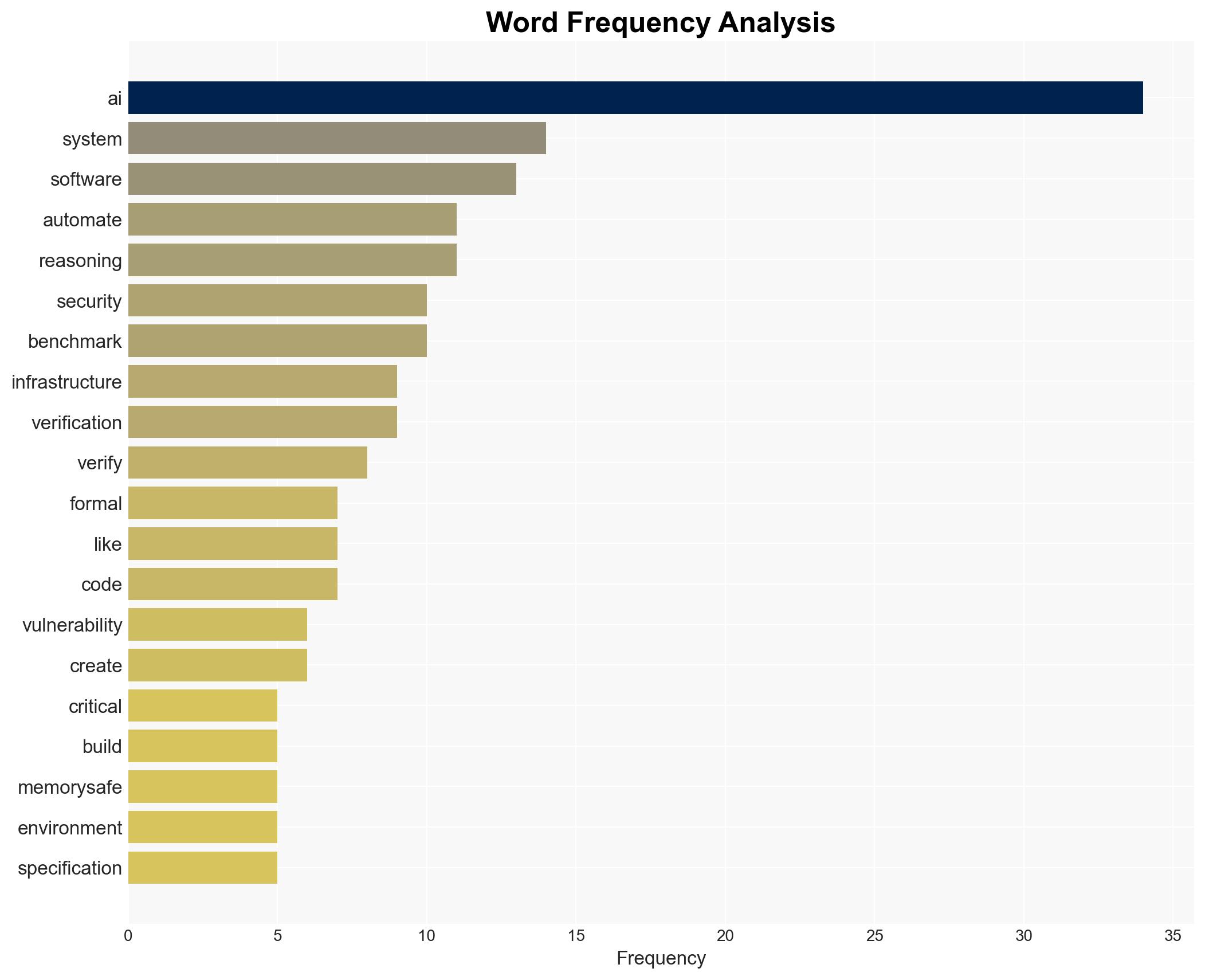
cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, ransomware, critical infrastructure, formal methods, memory-safe languages, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us