AI Enhances Phishing Attack Frequency, Leading to One Email Detected Every 19 Seconds in 2025
Published on: 2026-02-04
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: AI Drives Doubling of Phishing Attacks in a Year
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
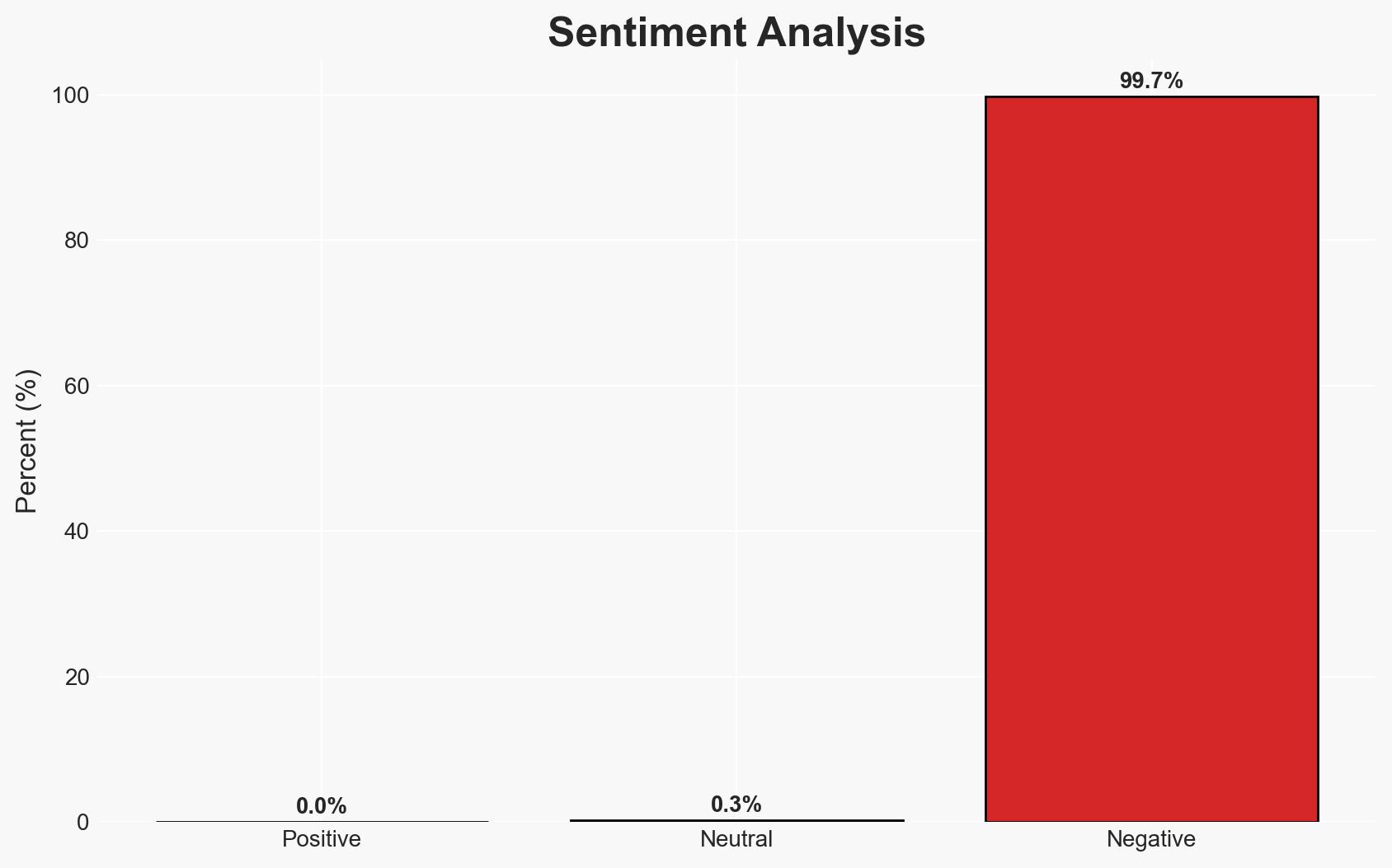
The use of AI has significantly increased the frequency and sophistication of phishing attacks, with security filters detecting one phishing email every 19 seconds in 2025, more than double the previous year. This trend poses a heightened threat to organizations and individuals globally, with moderate confidence in the assessment that AI-driven phishing will continue to evolve and challenge current cybersecurity measures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI is the primary driver of the increased frequency and sophistication of phishing attacks. Evidence includes the reported doubling of phishing email detections and the use of AI to enhance language proficiency and personalization in attacks. Key uncertainties include the extent of AI’s role versus other technological advancements.
- Hypothesis B: Other factors, such as increased internet usage and improved phishing techniques independent of AI, are equally responsible for the rise in phishing attacks. Supporting evidence is limited, but the rapid adoption of digital communication tools could contribute to increased attack surfaces.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific mention of AI capabilities enhancing phishing campaigns. Indicators such as further advancements in AI or changes in attack patterns could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to evolve and be accessible to threat actors; current cybersecurity measures will struggle to keep pace with AI-driven threats; phishing remains a lucrative attack vector.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific AI tools and methods used by threat actors; comparative analysis of phishing trends in regions with varying levels of AI adoption.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in the source’s focus on AI due to its cybersecurity expertise; possibility of threat actors exaggerating AI capabilities to instill fear or confusion.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could lead to increased pressure on cybersecurity infrastructure and a potential arms race in AI capabilities between threat actors and defenders.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased international tension over cyber capabilities and responsibilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment with more sophisticated phishing attacks targeting critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater need for advanced cybersecurity solutions and AI-driven defense mechanisms.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from successful phishing attacks, including financial loss and erosion of trust in digital communications.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of phishing trends, invest in AI-based cybersecurity tools, and increase awareness and training on phishing threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with AI research entities to stay ahead of threat actors, and strengthen international cooperation on cybersecurity standards.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: AI defenses outpace threat actor capabilities; Worst: AI-driven phishing becomes unmanageable; Most-Likely: Continued evolution of both offensive and defensive AI capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, AI, phishing, cybercrime, threat intelligence, business email compromise, remote access tools
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us