AI for Cybersecurity Building Trust in Your Workflows – Securityaffairs.com
Published on: 2025-08-18
Intelligence Report: AI for Cybersecurity Building Trust in Your Workflows – Securityaffairs.com
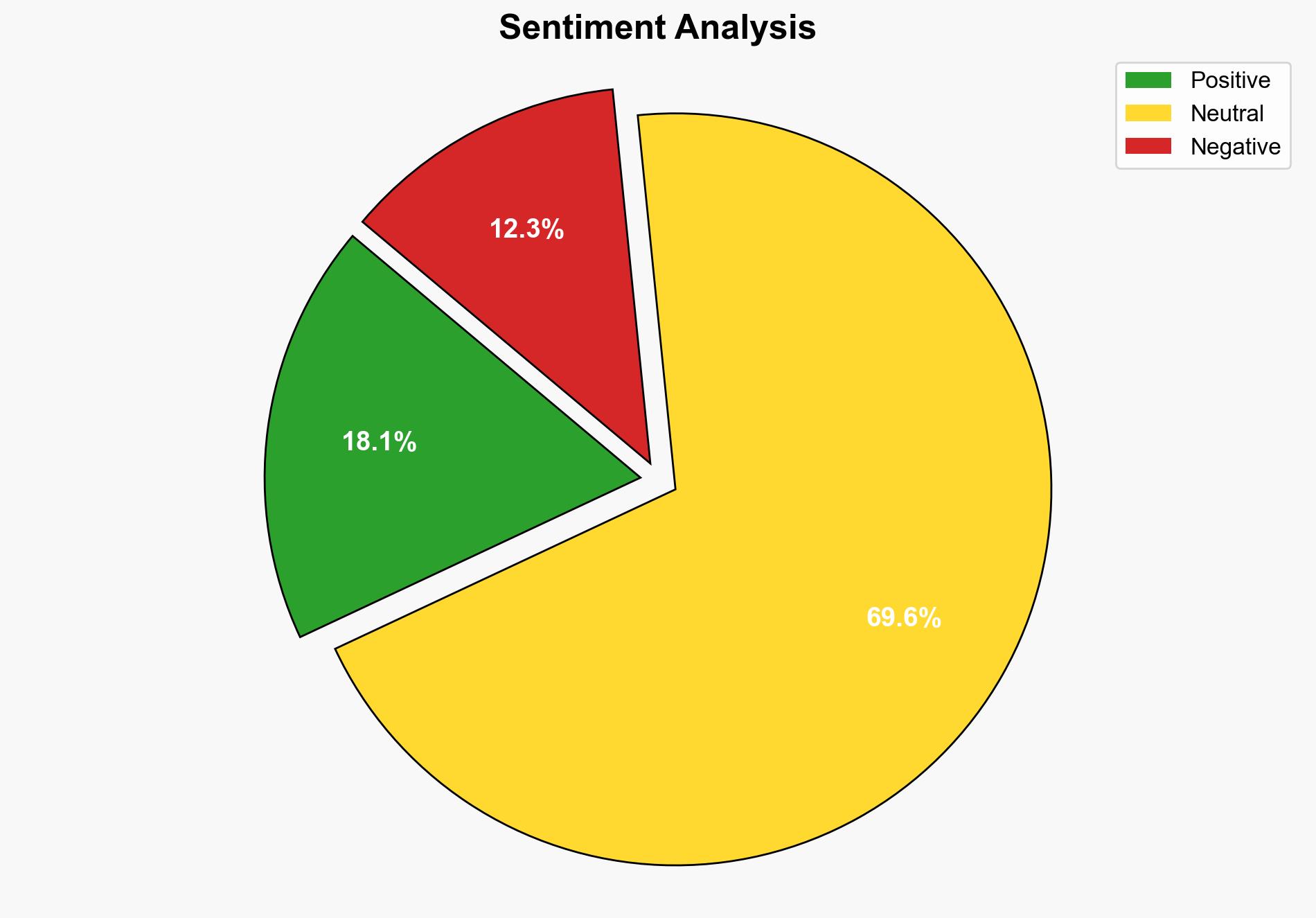
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The integration of AI in cybersecurity workflows offers both significant advantages and potential risks. The hypothesis that AI can enhance cybersecurity by improving detection and response times is better supported by the evidence. However, the risks associated with AI’s autonomous decision-making capabilities require careful management. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended Action: Implement AI with stringent operational guardrails and continuous human oversight to ensure reliability and trust.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: AI in cybersecurity enhances trust and operational efficiency by speeding up detection and response times, thereby reducing vulnerabilities and improving system reliability.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The autonomous nature of AI in cybersecurity introduces new risks, such as misconfigurations and overzealous actions, which could lead to significant operational disruptions and erode trust.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis A is more supported due to AI’s ability to close response gaps and tailor actions to specific organizational needs. However, Hypothesis B cannot be dismissed as the risks of AI’s autonomous actions are real and documented.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: AI systems can accurately interpret and respond to cybersecurity threats without human intervention. Organizations will implement adequate safeguards and oversight.
– **Red Flags**: Over-reliance on AI without sufficient human oversight. Lack of transparency in AI decision-making processes. Potential for AI to act on flawed data or scripts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of AI in cybersecurity could lead to faster threat mitigation, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. However, the potential for AI to act autonomously and make erroneous decisions poses a risk of cascading operational failures. This could have economic and reputational impacts, particularly if critical systems are disrupted.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement AI with robust operational guardrails and continuous human oversight.
- Develop clear protocols for AI decision-making and establish feedback loops for continuous improvement.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best: AI significantly reduces cybersecurity incidents and enhances trust.
- Worst: AI-induced errors lead to major operational disruptions and loss of trust.
- Most Likely: AI improves efficiency but requires ongoing management to mitigate risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Josh Breaker Rolfe, Bora (content writer with a background in journalism and cybersecurity).
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus